API client for AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui
Supports txt2img, img2img, extra-single-image, extra-batch-images API calls.
API support have to be enabled from webui. Add --api when running webui. It's explained here.
You can use --api-auth user1:pass1,user2:pass2 option to enable authentication for api access. (Since it's basic http authentication the password is transmitted in cleartext)
API calls are (almost) direct translation from http://127.0.0.1:7860/docs as of 2022/11/21.
pip install webuiapi
webuiapi_demo.ipynb contains example code with original images. Images are compressed as jpeg in this document.
import webuiapi
# create API client
api = webuiapi.WebUIApi()
# create API client with custom host, port
#api = webuiapi.WebUIApi(host='127.0.0.1', port=7860)
# create API client with custom host, port and https
#api = webuiapi.WebUIApi(host='webui.example.com', port=443, use_https=True)
# create API client with default sampler, steps.
#api = webuiapi.WebUIApi(sampler='Euler a', steps=20)
# optionally set username, password when --api-auth is set on webui.
api.set_auth('username', 'password')
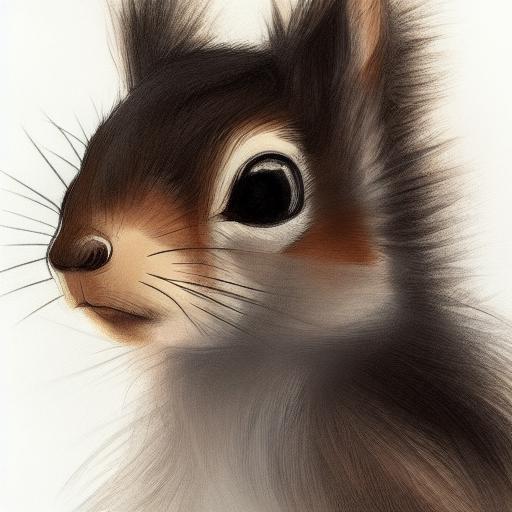
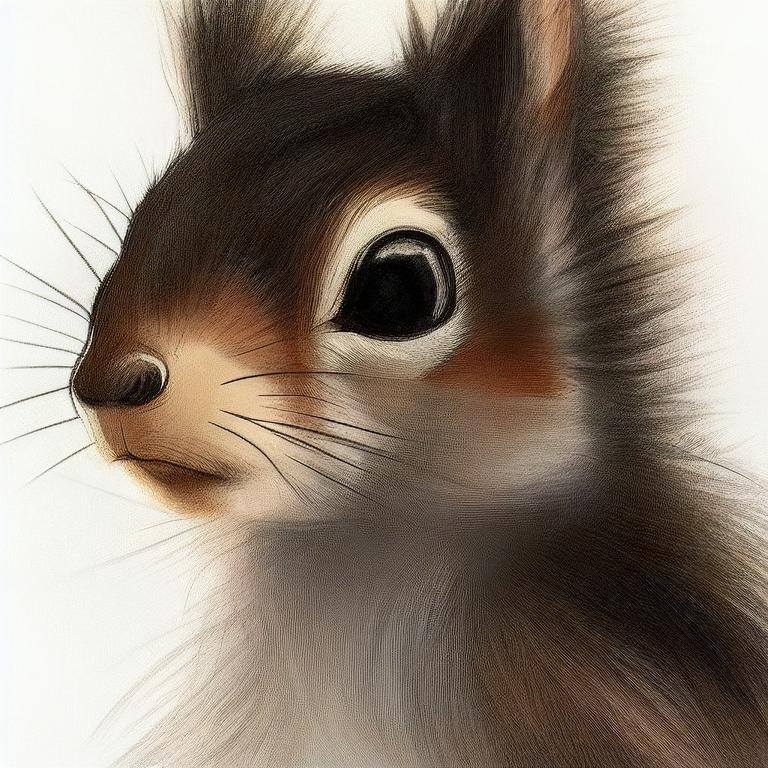
result1 = api.txt2img(prompt="cute squirrel",
negative_prompt="ugly, out of frame",
seed=1003,
styles=["anime"],
cfg_scale=7,
# sampler_index='DDIM',
# steps=30,
# enable_hr=True,
# hr_scale=2,
# hr_upscaler=webuiapi.HiResUpscaler.Latent,
# hr_second_pass_steps=20,
# hr_resize_x=1536,
# hr_resize_y=1024,
# denoising_strength=0.4,
)
# images contains the returned images (PIL images)
result1.images
# image is shorthand for images[0]
result1.image
# info contains text info about the api call
result1.info
# info contains paramteres of the api call
result1.parameters
result1.image
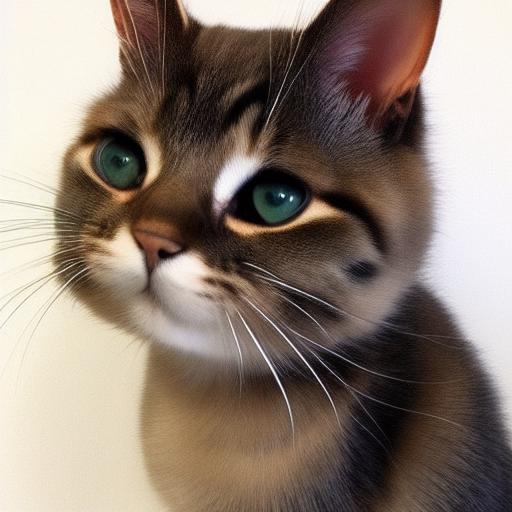
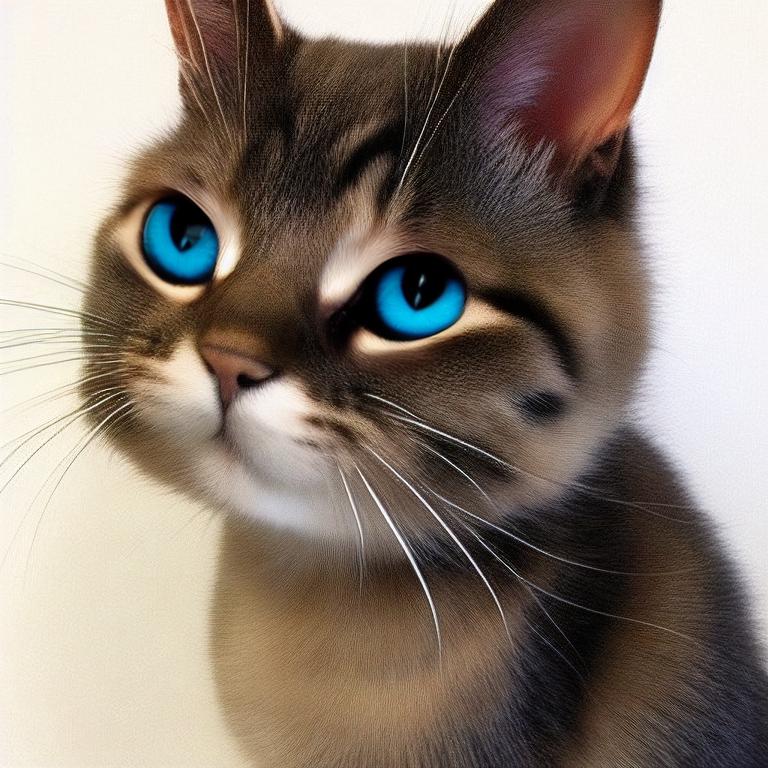
result2 = api.img2img(images=[result1.image], prompt="cute cat", seed=5555, cfg_scale=6.5, denoising_strength=0.6)
result2.image
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
mask = Image.new('RGB', result2.image.size, color = 'black')
# mask = result2.image.copy()
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(mask)
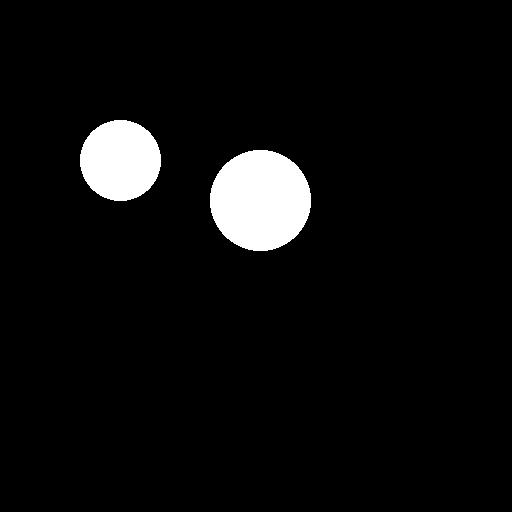
draw.ellipse((210,150,310,250), fill='white')
draw.ellipse((80,120,160,120+80), fill='white')
mask
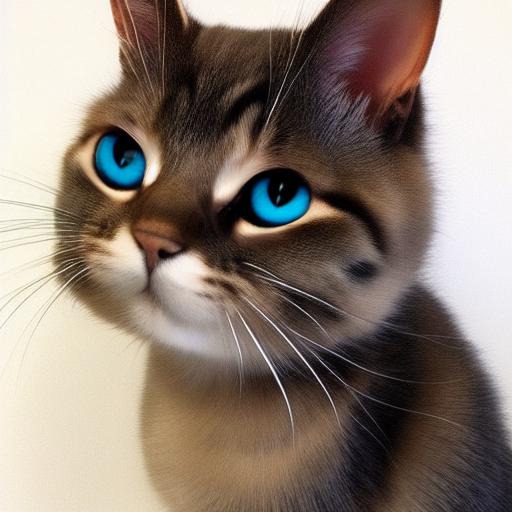
inpainting_result = api.img2img(images=[result2.image],
mask_image=mask,
inpainting_fill=1,
prompt="cute cat",
seed=104,
cfg_scale=5.0,
denoising_strength=0.7)
inpainting_result.image
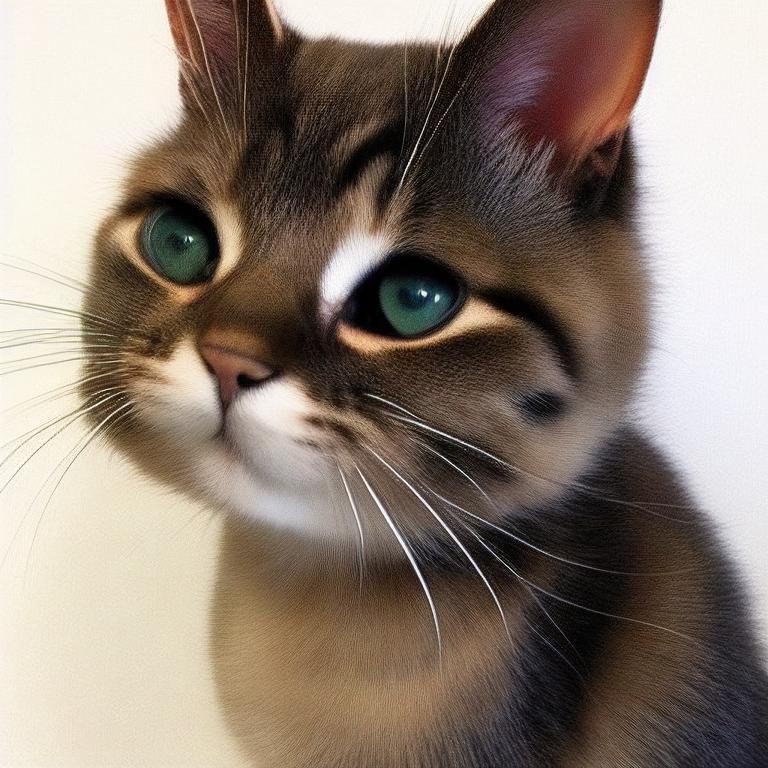
result3 = api.extra_single_image(image=result2.image,
upscaler_1=webuiapi.Upscaler.ESRGAN_4x,
upscaling_resize=1.5)
print(result3.image.size)
result3.image
(768, 768)
result4 = api.extra_batch_images(images=[result1.image, inpainting_result.image],
upscaler_1=webuiapi.Upscaler.ESRGAN_4x,
upscaling_resize=1.5)
result4.images[0]
result4.images[1]
Scripts from AUTOMATIC1111's Web UI are supported, but there aren't official models that define a script's interface.
To find out the list of arguments that are accepted by a particular script look up the associated python file from
AUTOMATIC1111's repo scripts/[script_name].py. Search for its run(p, **args) function and the arguments that come
after 'p' is the list of accepted arguments
(scripts/xyz_grid.py file from AUTOMATIC1111's repo)
def run(self, p, x_type, x_values, y_type, y_values, z_type, z_values, draw_legend, include_lone_images, include_sub_grids, no_fixed_seeds, margin_size):
...
List of accepted arguments:
- x_type: Index of the axis for X axis. Indexes start from [0: Nothing]
- x_values: String of comma-separated values for the X axis
- y_type: Index of the axis type for Y axis. As the X axis, indexes start from [0: Nothing]
- y_values: String of comma-separated values for the Y axis
- z_type: Index of the axis type for Z axis. As the X axis, indexes start from [0: Nothing]
- z_values: String of comma-separated values for the Z axis
- draw_legend: "True" or "False". IMPORTANT: It needs to be a string and not a Boolean value
- include_lone_images: "True" or "False". IMPORTANT: It needs to be a string and not a Boolean value
- include_sub_grids: "True" or "False". IMPORTANT: It needs to be a string and not a Boolean value
- no_fixed_seeds: "True" or "False". IMPORTANT: It needs to be a string and not a Boolean value
- margin_size: int value
# Available Axis options (Different for txt2img and img2img!)
XYZPlotAvailableTxt2ImgScripts = [
"Nothing",
"Seed",
"Var. seed",
"Var. strength",
"Steps",
"Hires steps",
"CFG Scale",
"Prompt S/R",
"Prompt order",
"Sampler",
"Checkpoint name",
"Sigma Churn",
"Sigma min",
"Sigma max",
"Sigma noise",
"Eta",
"Clip skip",
"Denoising",
"Hires upscaler",
"VAE",
"Styles",
]
XYZPlotAvailableImg2ImgScripts = [
"Nothing",
"Seed",
"Var. seed",
"Var. strength",
"Steps",
"CFG Scale",
"Image CFG Scale",
"Prompt S/R",
"Prompt order",
"Sampler",
"Checkpoint name",
"Sigma Churn",
"Sigma min",
"Sigma max",
"Sigma noise",
"Eta",
"Clip skip",
"Denoising",
"Cond. Image Mask Weight",
"VAE",
"Styles",
]
# Example call
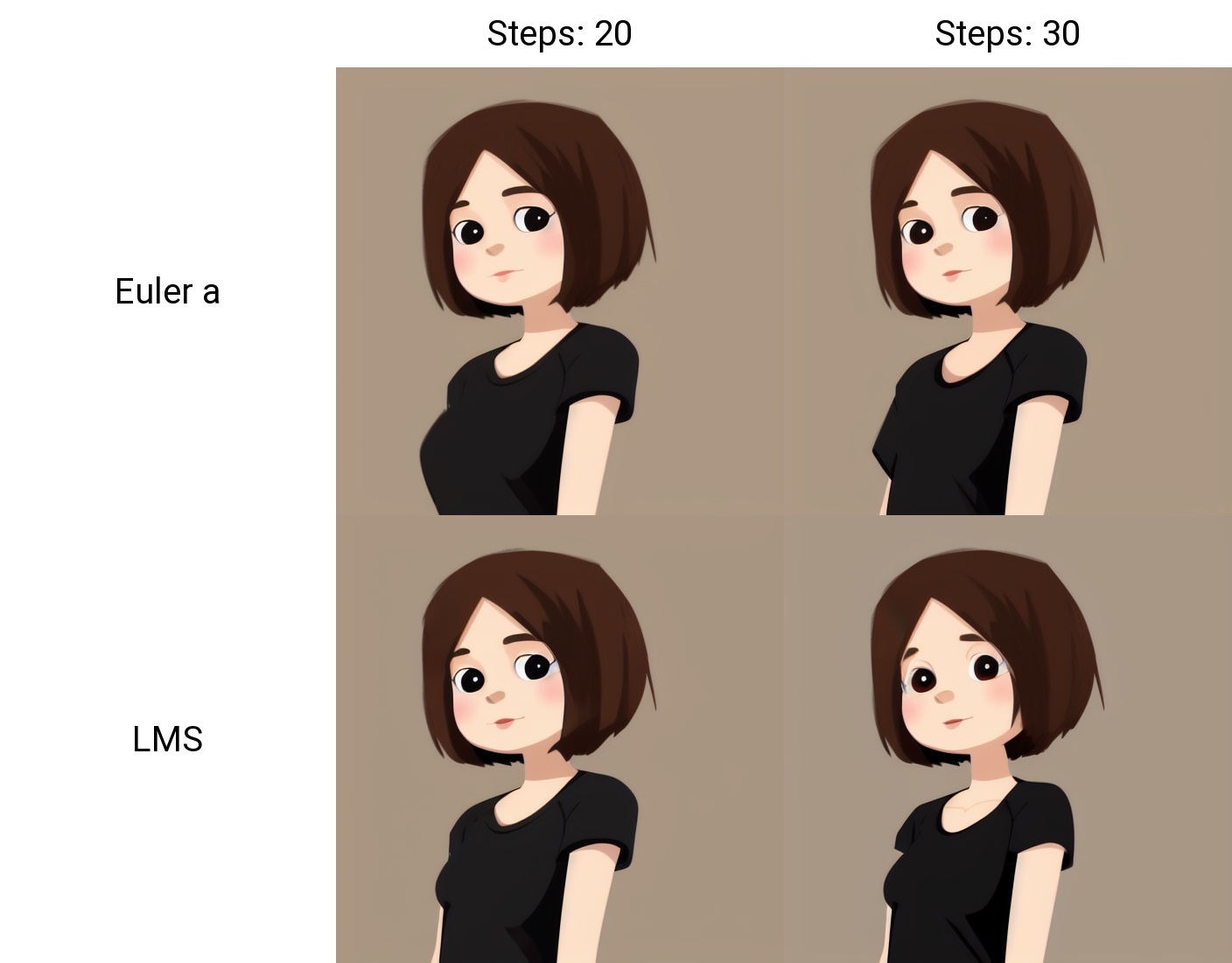
XAxisType = "Steps"
XAxisValues = "20,30"
YAxisType = "Sampler"
YAxisValues = "Euler a, LMS"
ZAxisType = "Nothing"
ZAxisValues = ""
drawLegend = "True"
includeLoneImages = "False"
includeSubGrids = "False"
noFixedSeeds = "False"
marginSize = 0
# x_type, x_values, y_type, y_values, z_type, z_values, draw_legend, include_lone_images, include_sub_grids, no_fixed_seeds, margin_size
result = api.txt2img(
prompt="cute girl with short brown hair in black t-shirt in animation style",
seed=1003,
script_name="X/Y/Z Plot",
script_args=[
XYZPlotAvailableTxt2ImgScripts.index(XAxisType),
XAxisValues,
XYZPlotAvailableTxt2ImgScripts.index(YAxisType),
YAxisValues,
XYZPlotAvailableTxt2ImgScripts.index(ZAxisType),
ZAxisValues,
drawLegend,
includeLoneImages,
includeSubGrids,
noFixedSeeds,
marginSize, ]
)
result.image
# return map of current options
options = api.get_options()
# change sd model
options = {}
options['sd_model_checkpoint'] = 'model.ckpt [7460a6fa]'
api.set_options(options)
# when calling set_options, do not pass all options returned by get_options().
# it makes webui unusable (2022/11/21).
# get available sd models
api.get_sd_models()
# misc get apis
api.get_samplers()
api.get_cmd_flags()
api.get_hypernetworks()
api.get_face_restorers()
api.get_realesrgan_models()
api.get_prompt_styles()
api.get_artist_categories()
api.get_artists()
api.get_progress()
# save current model name
old_model = api.util_get_current_model()
# get list of available models
models = api.util_get_model_names()
# set model (use exact name)
api.util_set_model(models[0])
# set model (find closest match)
api.util_set_model('robodiffusion')
# wait for job complete
api.util_wait_for_ready()
r = api.txt2img(prompt='photo of a cute girl with green hair <lora:Moxin_10:0.6> shuimobysim __juice__',
seed=1000,
save_images=True,
alwayson_scripts={"Simple wildcards":[]} # wildcards extension doesn't accept more parameters.
)
r.image
# https://github.com/mix1009/model-keyword
mki = webuiapi.ModelKeywordInterface(api)
mki.get_keywords()
ModelKeywordResult(keywords=['nousr robot'], model='robo-diffusion-v1.ckpt', oldhash='41fef4bd', match_source='model-keyword.txt')
# Instruct-Pix2Pix extension is now deprecated and is now part of webui.
# You can use normal img2img with image_cfg_scale when instruct-pix2pix model is loaded.
r = api.img2img(prompt='sunset', images=[pil_img], cfg_scale=7.5, image_cfg_scale=1.5)
r.image
# https://github.com/Mikubill/sd-webui-controlnet
cn = webuiapi.ControlNetInterface(api)
cn.model_list()
['control_canny-fp16 [e3fe7712]', 'control_depth-fp16 [400750f6]', 'control_hed-fp16 [13fee50b]', 'control_mlsd-fp16 [e3705cfa]', 'control_normal-fp16 [63f96f7c]', 'control_openpose-fp16 [9ca67cc5]', 'control_scribble-fp16 [c508311e]', 'control_seg-fp16 [b9c1cc12]']
Use of ControlNetInterface txt2img/img2img is deprecated. Please use the txt2img and img2img api with controlnet_units parameter.
# normal txt2img
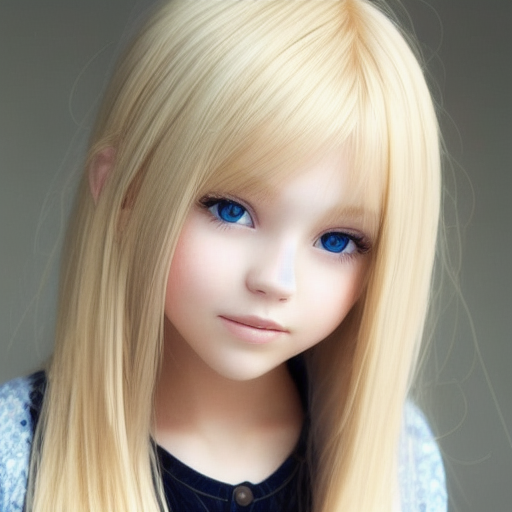
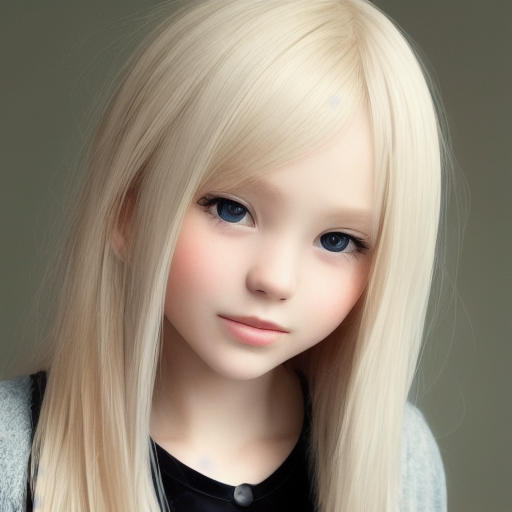
r = api.txt2img(prompt="photo of a beautiful girl with blonde hair", height=512, seed=100)
img = r.image
img
# txt2img with ControlNet
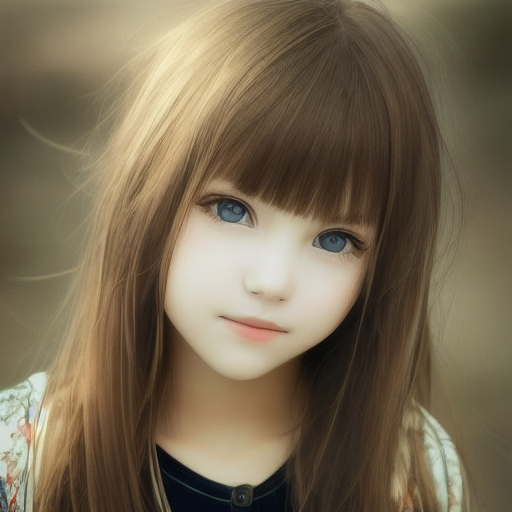
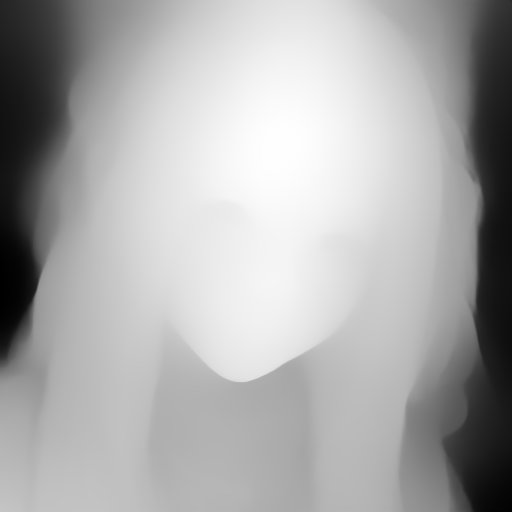
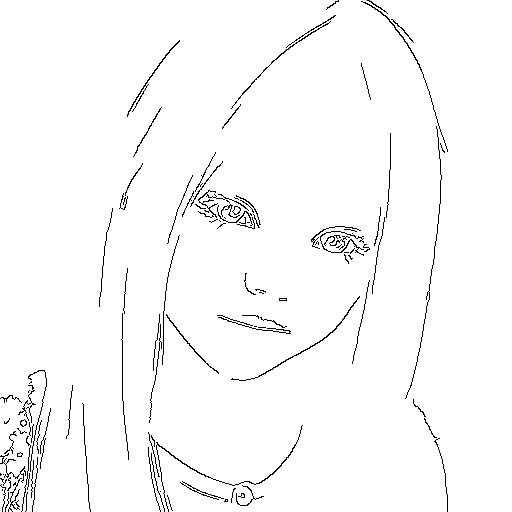
unit1 = webuiapi.ControlNetUnit(input_image=img, module='canny', model='control_canny-fp16 [e3fe7712]')
r = api.txt2img(prompt="photo of a beautiful girl", controlnet_units=[unit1])
r.image
# img2img with multiple ControlNets
unit1 = webuiapi.ControlNetUnit(input_image=img, module='canny', model='control_canny-fp16 [e3fe7712]')
unit2 = webuiapi.ControlNetUnit(input_image=img, module='depth', model='control_depth-fp16 [400750f6]', weight=0.5)
r2 = api.img2img(prompt="girl",
images=[img],
width=512,
height=512,
controlnet_units=[unit1, unit2],
sampler_name="Euler a",
cfg_scale=7,
)
r2.image
r2.images[1]
r2.images[2]