In this lab, you are going to reinforce the knowledge of how to create basic authorization and authentication in a web app.
- Fork this repo
- Clone this repo
-
Upon completion, run the following commands:
git add . git commit -m "done" git push origin master -
Create Pull Request so your TAs can check up your work.
In this lab, you literally have to recreate materials your instructors went through in the class. The point is not to blindly copy-paste them, but the opposite of that: to go once again, step by step through the process of registering users and authenticating them in the web app. Try to target all the weak spots, everything you missed to grasp during the lecture time, so you can ask your instructors and assistants to push you through the learning process.
After forking and cloning the project, you will have to install all the dependencies:
$ cd lab-express-basic-auth
$ npm installNow you are ready to start 🚀
We have to create the signup feature - the goal is to enable our users to register in our application. The users have to provide the following information:
- username: must be unique in our application and will identify each user
- password: must be encrypted (you can use the
bcryptjsnpm package).
To complete this first iteration, you have to create the model as well as the corresponding routes and views.
Once the user has signed up, he/she should be able to authenticate themselves. This means the user should be able to log in to the application. Your assignment in this iteration is to create corresponding routes as well as the views to let them log in to the application.
As you know, it is not enough just to allow users to log in. Users should be able to maintain their "presence" in the application (stay logged in when going from a page to a page, after the refresh), and for that, there should be the user(s) in the session. You have learned that you can use the express-session and connect-mongo npm packages to create a session.
At this point, you have implemented the basic authentication in this application. Your next assignment is to create the authentication middleware and protect some routes. Refresher: users can't visit these routes unless they are authenticated (logged in and exist in the session).
Let's create two different routes protected by authentication:
/main- Add a funny picture of a cat and a link back to the home page/private- Add your favoritegifand an<h1>denoting the page as private.
Create the views and the custom authentication middleware function. Once created, use the middleware and protect the routes to prevent access to users who are not being authenticated.
You should handle validation errors when a user signs up:
- The fields can't be empty.
- The username can't be repeated.
You should check if all the fields are correctly filled before authenticating the user.
Let's add validations to our forms. Remember we have two different forms: sign up and log in.
Remember, when a user signs up or logs in, both the username and password fields must be filled in.
Check out the documentation at MDN. See if you can find a constraint that requires the user to fill in a field before submission.
Happy coding! ❤️
I am stuck and don't know how to solve the problem or where to start. What should I do?
If you are stuck in your code and don't know how to solve the problem or where to start, you should take a step back and try to form a clear question about the specific issue you are facing. This will help you narrow down the problem and come up with potential solutions.
For example, is it a concept that you don't understand, or are you receiving an error message that you don't know how to fix? It is usually helpful to try to state the problem as clearly as possible, including any error messages you are receiving. This can help you communicate the issue to others and potentially get help from classmates or online resources.
Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, you will be able to start working toward the solution.
When I try to run the app, I get an error "command not found: nodemon"
Make sure you have
nodemon installed on your machine:
npm install -g nodemonThis will install nodemon globally on your system, making it available to all of your projects.
How to create a Mongoose model?
The mongoose model serves as a blueprint for creating and managing documents within MongoDB collections. The mongoose model is an overlay on top of one MongoDB collection, that we use to query and interact with that database collection.
Here is an example of creating a User model to manage documents in the users collection:
// IMPORT MONGOOSE
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
// CREATE A SCHEMA - defines the shape of the documents
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
firstName: String,
lastName: String
});
// CREATE THE MODEL
const User = mongoose.model('User', schema);
// EXPORT THE MODEL
module.exports = User;In the above example, we created and exported a User model, so that it can be imported and used anywhere in the application for managing the database collection users.
Let's break down the above example and the steps in creating a mongoose model:
- Import mongoose: The first step is to import the
mongooselibrary. - Create a schema: The next step is to create a schema, which defines the shape of the documents that will be stored in the
userscollection. In the above example, the schema has two fieldsfirstNameandlastNamewhich are both strings. - Create the model: The last step is to create the model. This is done using the method
mongoose.model(), which takes two arguments: the name of the model, in this case'User'and the schema it should use. Mongoose automatically pluralizes and converts to lowercase the provided model name and uses it as the name of the collection. In this case, the string'User'is automatically converted into a collection name ->users. - Export the model: After the model is created, it needs to be exported so it can be used in other parts of the application.
I got the error: "[ERR_HTTP_HEADERS_SENT]: Cannot set headers after they are sent to the client". How do I resolve it?
The error [ERR_HTTP_HEADERS_SENT]: Cannot set headers after they are sent to the client occurs when you try to send a response after the response has already been sent. This means that you are calling res.send() or res.render() multiple times in your route, instead of only once at the end of the request.
To fix the issue, check the route that threw the error and verify that you are only calling res.send() or res.render() once in the route in question, after all, database operations and other logic have been completed.
You can start by trying to identify all the res.send() or res.render() calls made in the route code.
This error commonly arises from having nested conditionals or Promises and having multiple calls to res.send() or res.render() in the route logic. To troubleshoot it, it is advisable to check these parts of the route code for any logic errors.
How do I resolve the error "ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE" on my ExpressJS server?
Check that your server route is sending a valid HTTP status code. HTTP status codes are 3-digit numbers that indicate the status of an HTTP request and must be in the range of 100-599. If the server is sending an invalid status code, In particular, if the status code is set by res.status() is invalid, it could cause this error.
What could be causing a redirect to fail in my Express app?
Some possible reasons why a redirect might not work in an ExpressJS app are:
- There might be a typo in the route name or path. Make sure that the route name or path in the res.redirect() function is spelled correctly and matches the name or path of the route you are trying to redirect to.
- Check that you have correctly spelled the res.redirect() function name.
- The route you are trying to redirect to might not be defined. Make sure that you have defined the route you are trying to redirect to.
How do I resolve the error "ValidationError: Path ... is required."?
This error occurs when you try to save a document to the database without a value for a field that is marked as required in the model. To fix this error, make sure that you are providing a value for all required fields when creating or updating a document. You can verify that you are providing the correct values by using the console.log to inspect the data before saving it to the database.
How do I make a field in a Mongoose model, such as 'email', unique?
To make a field in a Mongoose model unique, you should add the unique: true property in the field's schema definition. For example, to make the email field in a Mongoose model unique, you should do the following:
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
email: {
type: String,
unique: true
},
password: String
})This will ensure that no two documents in the database can have the same value for the email field.
I am getting an error: "not defined". How do I fix it?
The "ReferenceError: variable is not defined" error in JavaScript occurs when you try to access a variable or a function that has not been defined yet or is out of scope.
To fix the issue, check that you have defined the variable or function that you are trying to use and double-check the spelling to make sure you are using the correct name.
In case the variable or a function is defined in another file, make sure that the file has been imported or loaded correctly.
My GET form is not working properly. What should I do?
Here are the things you should check in order to fix your GET form:
- Check that the path for your GET route in Express matches the
actionandmethodattributes in the form. For example, if you have a routeGET/search:
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
// form handling logic
});Your form action attribute should have the same path and the method should be the same:
<form action="/search" method="GET">- Check the data you are receiving from the form on the
req.queryby usingconsole.log(). For example, if you have a routeGET/search, you can add aconsole.log()like this:
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
// Print the data coming from the form
console.log(req.query);
});- Check that the
formtag is properly formatted and that it has an opening and a closing tag. Example:
<form action="/search" method="GET">
<!-- Form inputs, labels, button -->
</form>- Check that the submit button is configured properly to submit the form when clicked. Make sure that the button is located inside of the form tag and that it has a
type="submit"attribute. Example:
<form action="/search" method="GET">
<label>Enter search prompt</label>
<input type="text" name="prompt">
<button type="submit"> Search </button>
</form><br>
My links are not working properly. Should I use a relative or an absolute path?
When linking to other pages within your Express app, as a general rule you should use relative paths that start with a forward slash /.
This way you ensure that the links will work correctly both in your development environment and when the app is deployed.
For example, instead of linking to a page with an absolute path like this:
<a href="http://yourdomain.com/contact"> Contact </a>You should use a relative path starting with a forward slash / like this:
<a href="/contact"> Contact </a>If you are embedding values in your Handlebars template, you should still use the relative path that starts with a forward slash / like this:
I got the error "Error: listen EADDRINUSE: Address already in use". How do I fix it?
This error means that the port is taken by another process that is still running on that port. To fix the issue, you need to kill the process using the port and then run the command again. Here's how to do it:
To kill the process running on port 3000, run the following command in the terminal:
sudo kill -9 $(lsof -t -i:3000) Important: Replace the above example port 3000 with the port number of the process you are trying to kill.
To kill the running process on Windows using the Task Manager do the following:
- Open the Task Manager by pressing: Ctrl + Shift + Esc
- Find the Node process you want to terminate.
- Right-click and select End Task
To kill the running process on Windows using the Command Prompt do the following:
- Open the windows Start menu
- Search for CMD in the search bar
- In the search results, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator. This will open the Command Prompt terminal.
- In the Command Prompt terminal, run the following command to find the process ID:
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :3000"If the process happens to be running on another port, simply replace
3000with the number the port number the process is running on.
This will return the process id (PID). You should then run the following command using the process id (PID) you got in the previous step to terminate the process:
taskkill /PID 12345 /fImportant: Replace the above example PID 12345, with the process id (PID) you got in the previous step.
I got the error "Port is already in use". How do I fix it?
This error means that the port is taken by another process that is still running on that port. To fix the issue, you need to kill the process using the port and then run the command again. Here's how to do it:
To kill the process running on port 3000, run the following command in the terminal:
sudo kill -9 $(lsof -t -i:3000) Important: Replace the above example port 3000 with the port number of the process you are trying to kill.
To kill the running process on Windows using the Task Manager do the following:
- Open the Task Manager by pressing: Ctrl + Shift + Esc
- Find the Node process you want to terminate.
- Right-click and select End Task
To kill the running process on Windows using the Command Prompt do the following:
- Open the windows Start menu
- Search for CMD in the search bar
- In the search results, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator. This will open the Command Prompt terminal.
- In the Command Prompt terminal, run the following command to find the process ID:
```bash
netstat -ano|findstr "PID :3000"
```
> If the process happens to be running on another port, simply replace `3000` with the number the port number the process is running on.
This will return the process id (PID). You should then run the following command using the process id (PID) you got in the previous step to terminate the process:
```bash
taskkill /PID 12345 /f
```
**Important:** Replace the above example PID *12345*, with the process id (PID) you got in the previous step.
I got the error: "Error: connect ECONNREFUSED ::1:27017". What should I do?
This error means that the Node.js application is unable to connect to a MongoDB instance running on the local (same) machine. There are a few things you should look at to troubleshoot this:
- Check the database connection string: Check that the connection string is correct. The database connection string should be in the format:
mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/databaseName- Verify that MongoDB is running on your machine: Check that MongoDB is running on your machine. If it is not running, restart the service according to the following instructions:
On Mac:
Check if MongoDB is running on your machine, by running the command:
brew services listYou should see the service mongodb-community listed as started. If not, run the following command to start it:
brew services start mongodb-communityOn Ubuntu:
You can start the mongod process by issuing the following command:
sudo systemctl start mongodIf you receive an error similar to the following when starting mongod:
Failed to start mongod.service: Unit mongod.service not found.
Run the following command first:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadThen run the start command above again.
On Windows:
To open the MongoDB process on Windows, you will need to do these steps:
-
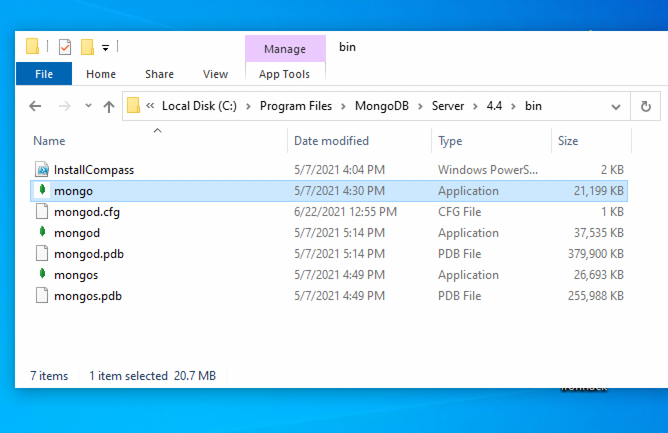
Go to your Program Files in your C: drive - the local disk
-
In Program Files go to the MongoDB folder
-
Inside the MongoDB folder, follow this path
Server/4.4/bin. The version number on your system (4.4) may be slightly different for the newer installations. -
Double-click on the file named mongod.exe.
Why is my database empty even though I am able to connect?
It is normal for the database to be empty if you have not inserted any data into it. If you want to confirm that your connection to the database is working correctly, you can try inserting a simple document into a collection and then querying the collection or checking the database to see if the document was added.
I get the error "MongoDB is not running on the provided host and port" when trying to connect with MongoDB Compass. What should I do?
If you are trying to connect to a MongoDB instance running locally, you should first check that MongoDB is running on your machine. If it is not running, restart the service according to the following instructions:
On Mac:
Check if MongoDB is running on your machine, by running the command:
brew services listYou should see the service mongodb-community listed as started. If not, run the following command to start it:
brew services start mongodb-communityOn Ubuntu:
You can start the mongod process by issuing the following command:
sudo systemctl start mongodIf you receive an error similar to the following when starting mongod:
Failed to start mongod.service: Unit mongod.service not found.
Run the following command first:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadThen run the start command above again.
On Windows:
To open the MongoDB process on Windows, you will need to do these steps:
-
Go to your Program Files in your C: drive - the local disk
-
In Program Files go to the MongoDB folder
-
Inside the MongoDB folder, follow this path
Server/4.4/bin. The version number on your system (4.4) may be slightly different for the newer installations. -
Double-click on the file named mongod.exe.
What is a timestamp in Mongoose schema and how do you use it?
Mongoose schemas have an additional option called timestamps. If you set the option timestamps: true, Mongoose will automatically add two Date properties to your schema:
createdAt: a date that shows when the document was createdupdatedAt: a date that shows the last time the document was updated
Here's an example of how to set the timestamps: true option in a Mongoose schema:
const { Schema, model } = require("mongoose");
const userSchema = new Schema(
{
username: String,
email: String,
password: String,
},
{
// this option adds extra properties: `createdAt` and `updatedAt`
timestamps: true,
}
);
const User = model("User", userSchema);
module.exports = User;For more information, check: Mongoose: Timestamps
I am getting an error: "not defined". How do I fix it?
The "ReferenceError: variable is not defined" error in JavaScript occurs when you try to access a variable or a function that has not been defined yet or is out of scope.
To fix the issue, check that you have defined the variable or function that you are trying to use and double-check the spelling to make sure you are using the correct name.
In case the variable or a function is defined in another file, make sure that the file has been imported or loaded correctly.
I am unable to push changes to the repository. What should I do?
There are a couple of possible reasons why you may be unable to push changes to a Git repository:
- You have not committed your changes: Before you can push your changes to the repository, you need to commit them using the
git commitcommand. Make sure you have committed your changes and try pushing again. To do this, run the following terminal commands from the project folder:
git add .
git commit -m "Your commit message"
git push- You do not have permission to push to the repository: If you have cloned the repository directly from the main Ironhack repository without making a Fork first, you do not have write access to the repository. To check which remote repository you have cloned, run the following terminal command from the project folder:
git remote -vIf the link shown is the same as the main Ironhack repository, you will need to fork the repository to your GitHub account first, and then clone your fork to your local machine to be able to push the changes.
Note: You may want to make a copy of the code you have locally, to avoid losing it in the process.