A Step-by-Step Example of using an HTML Form to send a "Contact Us" Message via Email without a Backend Server using a Google Script - No PHP, Python, Ruby, Java, Node.js etc.
See a working example here: https://dwyl.github.io/learn-to-send-email-via-google-script-html-no-server/
Warning: Google's API has limits on how many emails it can send in a day. This may vary on your Google account, see the limits here. We recommend implementing this tutorial through Part 3, since the data will always be added to the spreadsheet first, then emailed if possible.
We needed a way of sending an email from a "static" HTML page when you don't (want to) have a server.
- No "Backend" to Deploy/Maintain/Pay for
- Fully Customisabe - every aspect is customisable!
- Email sent via Google Mail which is Whitelisted Everywhere (high deliverability success)
- Collect/Store any form data in a Spreadsheet for easy viewing
(perfect if you need to share it with non-technical people)
Instead of using a server to send your email,
which is easy but requires maintenance,
use Google to send mail on your behalf
and use Google Spreadsheets to keep track of the data!
You could use a "free" service like http://formspree.io/ to process your form submissions if you don't care where you are sending your data and want to manage the data submitted
in your email inbox (messy ... yuck!)
Or... you can invest a few minutes and keep data private/manageable. Take your pick.
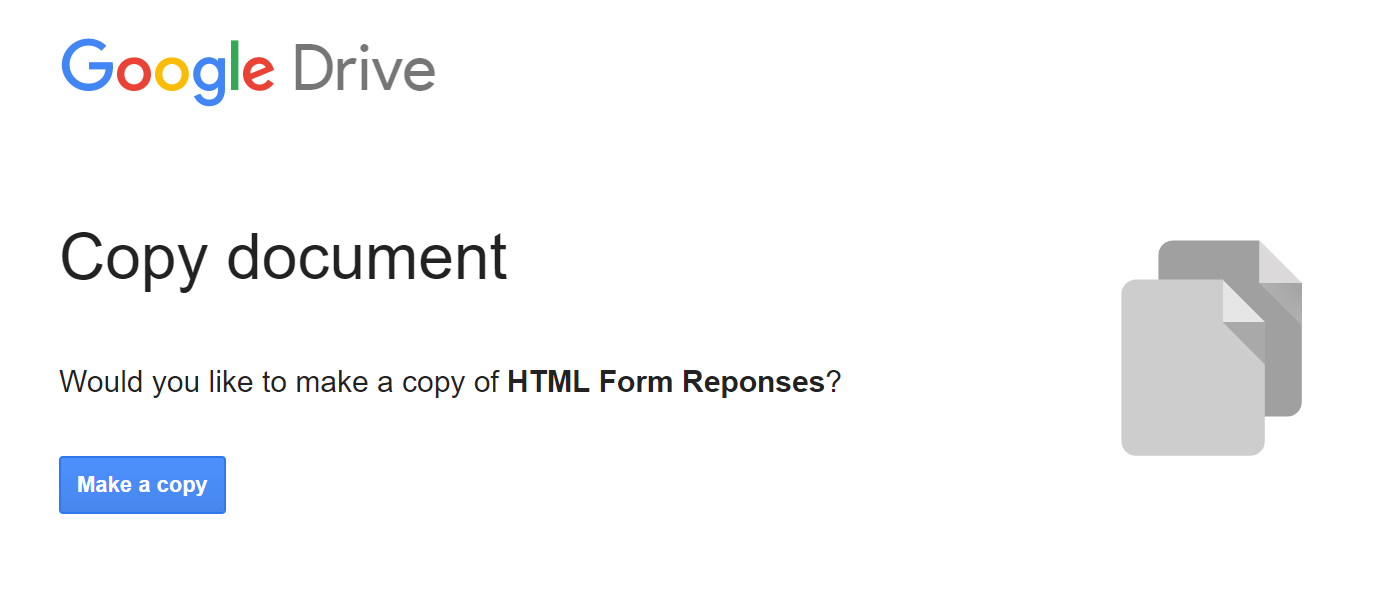
Sample: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1Bn4m6iA_Xch1zzhNvo_6CoQWqOAgwwkOWJKC-phHx2Q/copy
Sign in to your Google account and click on "Make a copy..."
This should give you something like this:
Note: Feel free to change the name of the Copy to anything you want, it will not affect the outcome.
Open the Script editor... by clicking "Tools" > "Script editor..."
Here's a snapshot of the script you need (at this point in the exercise): google-script-just-email.js
Warning: If you do not uncomment and set your email as the value of
TO_ADDRESS, it is possible for someone who has web skills to alter your form
and send emailed data to an arbitrary email address.
This risk may not be very likely. Instead, if you wish, you can leave this
variable commented out if you accept this possible risk but want the added
convenience of setting this email variable inside your HTML form as a
data-email attribute. This allows you to easily change where to send emails
inside your HTML form without going back through steps 2-6. This functionality
does require you to use the provided JS file in Part Two, Step 10.
If you do not want to accept that potential risk, please uncomment the code for
the variable TO_ADDRESS, and set this value equal to the email which should
receive the form's data when submitted.
It's not immediately obvious but you have to click on "Manage Versions..."
Then create your new version:
Select the latest project version to deploy.
Anyone, even anonymous option for the 'Who has access to the app' dropdown or form responses will not be added to the spreadsheet!
Copy the web app URL to your clip board / note pad. Then Click "OK".
Using the template in index.html in this repo,
create your own html file with the basic form. (save the file)
- Each of your form elements must have a
nameattribute equal to that of your column name in the Google sheet - The form
idmust begform, i.e.<form id = "gform">- If you want to alter this later, you will need to create your
own version of
form-submission-handler.jsand amend the expectedid
- If you want to alter this later, you will need to create your
own version of
Remember to change the Form
actionURL to the one you copied in the previous step:
Fill in some sample data in the HTML Form:
Submit the form. You should see a confirmation that it was sent:

Open the inbox for the email address you set in Step 3 (above)
Done. That's it. You just created an HTML form that sends email!
We are going to keep this Super Lean by using PURE CSS
for our Style (fix the "ugly" HTML Form in step 8).
And submit the form using JQuery "AJAX" to keep the person
on your page/site (avoid "ugly" response page)
To prevent the page from changing to the JSON response/result
we need to submit the form using AJAX.
Update your index.html to include the following JavaScript file at the end of your file
(*before the closing </body> tag)
<script data-cfasync="false" type="text/javascript"
src="https://cdn.rawgit.com/dwyl/learn-to-send-email-via-google-script-html-no-server/master/form-submission-handler.js"></script>Warning: If you did not set the TO_ADDRESS variable in Step 3, then
you need to include a data-email="example@email.net" attribute inside the
main form element. See the example form for more details. Otherwise, if you did
set this variable, then you do not need this form attribute.
This will now display a "Thank You" message when the form is submitted:
Keeps the person on the same page. No refresh.
Taylor your message by editing the thankyou_message div:
For this example we are using Pure CSS: http://purecss.io/start/
because its light weight (4.0KB minified and gzipped)
and solves our current "problem": Making it Look Good.
Without spending too much time on this, we can make the form look a lot nicer:
By default, the sent email's body contains the key-value pairs from the form, with the key as an <h4> and the value as a <div>. This is a fairly basic, and foolproof view for the data.
You should get something that looks roughly like:

Bear in mind that this is a work in progress and does potentially open you up to getting more than you bargained for in the email. Because the email content is now looping over all the data sent in the form, if a robot or malicious user decides to
POSTmore than you've asked for, you'll likely get it in your inbox. Use with caution for now. We're investigating improvements.
You can modify this though, via the script editor. The line:
result += "<h4 style='text-transform: capitalize; margin-bottom: 0'>" + key + "</h4><div>" + obj[key] + "</div>";has all you need. You can adjust the markup to suit you. We chose an <h4> because it was the best size for the email, and added the small amount of CSS to it to fix the capitalisation (the keys are all lower case in the JS object) and a bit of default spacing. While inline styles like this are generally bad practice on normal web pages, for email HTML they're about the only reliable way to do CSS!
We went with a <div> for the value part, because it could be anything - single-line, multiline (a <p> for example wouldn't cut it).
While we're here, there's also a replyTo option for the sendEmail() method which is commented out by default:
MailApp.sendEmail({
to: TO_ADDRESS,
subject: "Contact form submitted",
// replyTo: String(mailData.email), // This is optional and reliant on your form actually collecting a field named `email`
htmlBody: formatMailBody(mailData)
});You can uncomment that if you want to add a reply-to field to your email. The example in the script will set the reply-to as the email submitted in the form.
Google's documentation provides more information about MailApp.sendEmail (for example cc/bcc etc.) if you're interested:
https://developers.google.com/apps-script/reference/mail/mail-app
Sending the form data directly to your email inbox is a good first step, but we can do better. Also, as noted above, Google has limits on how many emails you can send in a day, so storing the data into a spreadsheet is safer and less prone to data loss.
This will record the data received from the POST as a row in the spreadsheet.
See: google-apps-script.js for the full code you can copy-paste.
Follow Steps 4, 5 & 6 to save a new version and re-publish the script.
Because we are loading external .js files, our web browser will not allow us to simply open the index.html from a local directory for testing out the form.
Open your terminal and run this command to install the node modules and start the live server:
npm install live-server --save-dev && node_modules/.bin/live-server --port=8000It will take a minute to install,
but once that's done your live-server will start up.
That starts a node.js HTTP server on port 8000 and opens the form you just created in your default browser. If you wish to update the form styles in style.css or the client-side Javascript in form-submission-handler.js, please be sure to edit index.html to load those resources locally rather than via GitHub.
Note: This is a light taste of Node.js for absolute beginners. You do not need node.js to "deploy" this form, you can run it on an any web server that serves HTML/CSS/JavaScript. If you have never used Node.js before, see: http://nodeguide.com/beginner.html but for the purposes of this exercise (submitting a form without a server) you don't need node.js or
live-serverit's just a nice thing to have when you are creating your form because it automatically re-loads the page when you make changes in your text editor!
If you want us to take this tutorial further, please let us know!
For your convenience, we have hosted a working demo of the field on GitHub Pages, check it out to see the code and how it works: https://dwyl.github.io/learn-to-send-email-via-google-script-html-no-server/
In response to Henry Beary's request we made the form handler generic which means you can now add any fields you want to the form.
We also created a form, test.html, which uses all kinds of form input elements
so you can just copy and paste elements as desired into your own form. Just be
sure to update their names and IDs. You can find a working example of this test
form here:
https://dwyl.github.io/learn-to-send-email-via-google-script-html-no-server/test.html
Remember to include the fields inside the form that has the id gform
and ensure that the name of the form element matches the new column heading in your spreadsheet.
e.g:
<fieldset class="pure-group">
<label for="color">Favourite Color: </label>
<input id="color" name="color" placeholder="green" />
</fieldset>This will allow you to capture the person's favourite color:
e.g:

Let us know if you have any questions!
In order to avoid getting spammed and fill up google apps usage quota, we will be implementing a simple SPAM prevention technique that's known as Honeypot where it essentially creates a hidden text field that if filled up is assumed as a spam bot and prevents the form from submit.
<form action="https://script.google.com/macros/s/..." method="post">
<!--input id must be honeypot or else it wont work-->
<label class="sr-only">Keep this field blank</label>
<input id="honeypot" type="text" name="honeypot" value="" />
<!--the rest of your form-->
</form>#honeypot {
display: none; /*makes the field not visible to humans*/
}/* form-submission-handler.js */
/* remove the comment from this if statement */
if (validateHuman(data.honeypot)) { //if form is filled, form will not be submitted
return false;
}- How can I get help using this tutorial?
- Feel free to post an issue describing in detail which steps you have gone through and what isn't working. A working example that reproduces your issue online is most ideal (e.g., host on GitHub Pages or CodePen), and such examples or providing console errors increase your chances of getting a helpful response.
- Can I get edit access to the example spreadsheet?
- No. This is being used to show a working example for anyone to copy, and an editable version could be broken accidentally, or maliciously, by any user.
- Why is the webpage forwarding to a bunch of text when I hit submit?
- You are not properly loading the required Javascript which submits the data via AJAX, or your browser does not support AJAX. Please see Part 2 and check your console logs in case you are finding errors.
- Why is the webpage not successfully submitting the form?
- Check your Javascript console logs. There could be an error while reading in the Javascript we have provided. There could be errors while submitting the form. It is required that your form have an ID of
gform, and also adata-emailattribute if you have not set theTO_ADDRESSvariable inside the Google Script file. Furthermore, the provided Javascript code also expects to see an email form element which it uses to check, a warning message for that element when an improper email is submitted, and then athank-youdiv as well, which is shown after a form is successfully submitted. Please ensure that all of these HTML elements are in your form. See the sample file for code you can copy and paste. When you have all of these elements and a proper form set up, you should not see any error messages in your Javascript console when you hit submit.
- The webpage is saying my data was submitted, but why isn't my data being saved or sent to me?
- When you copied the spreadsheet and published the Google Script, did you set the permissions to "Anyone, even Anonymous"? This is required for the form to work, since anyone on the internet can hit send to give you their data. Be sure that you have deployed the proper version of the script and used "Manage versions..." when making changes.
- How can I upload files?
- Unfortunately, this feature is not currently supported at this time. It may be possible to tap into the Google Drive API via the Google Script, to save files that were uploaded. We would encourage anyone who has a working example to submit a PR or post an issue with how they solved this.
- Is this secure? Can I use it for sensitive data?
- No. While data that is sent over POST may be more protected, the information could easily be intercepted by a third party or middleman, and Google has complete access to the data inside a Google Spreadsheet. Email is also not a very secure communication medium by default. We would recommend you invest in a secure platform and server for storing your data if this is a requirement.
- Google Apps Scripts Basics: https://developers.google.com/apps-script/articles
- Logger (like console.log): https://developers.google.com/apps-script/reference/base/logger
- Simple Mail Merge using Google Spreadsheets: https://developers.google.com/apps-script/articles/mail_merge
- Original Tutorial: AJAX post to google spreadsheet: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10000020/ajax-post-to-google-spreadsheet which points to: