The Data and Analytics Transportation app demonstrates a data analytics workflow that uses a combination of Bluemix and open source applications to create a visualization of information. The data is retrieved from a transportation system in Madrid, filtered and then saved in Object Storage. The information is then analyzed, and the results are presented in a Node-RED Freeboard.
After registering for Bluemix and DevOps Services, you can deploy the Data and Analytics Transportation app (DAT) into your personal DevOps space.
Sign up for Bluemix at https://console.ng.bluemix.net and DevOps Services at https://hub.jazz.net. When you sign up, you'll create an IBM ID, create an alias, and register with Bluemix.
This solution requires a free public IP. In order to determine if a public IP is available, you will need to find the number of used and your max quota of IP addresses allowed for your space. To find this information, follow these steps:
- Log into your Dashboard at https://console.ng.bluemix.net.
- Select DASHBOARD.
- Select the space you where you would like DAT to deploy.
- In the Containers tile you will see information about your IP addresses.
- Check that the Public IPs Requested field has at least one available IP address.
If you have an IP address available, you are ready to Deploy to Bluemix. If all of your public IP addresses have been used, you will need to release one prior to deploying. In order to release a public IP, install the CF IC plugin, which can be found at the website below.
https://www.ng.bluemix.net/docs/containers/container_cli_ov.html#container_cli_cfic_install
Once installed:
- Log into your Bluemix account and space.
cf login
- Initialize your IBM Containers CLI.
cf ic login
- List your current external IP addresses.
cf ic ip list
- Release an IP address.
cf ic ip release < public IP >
Click the Deploy to Bluemix button below to deploy the source code to DevOps Services. This creates the needed Cloud Foundry and Container applications as well as instances of Object-Storage, Cloudant, and Spark. These instances are then bound to your application. Note: The service plan for Spark may have additional monthly charges.
After the pipeline has been configured, you can monitor the deployment by following these steps:
- Select your newly created project in DevOps Services.
- Go to MY PROJECTS.
- Select BUILD & DEPLOY.
- You can monitor the stages by selecting View logs and history.
Download data schemas from the IDS project and upload them to your container. The schemas define what information Secor pulls from Kafka and allow Spark to read the stored data.
-
Go to your project in DevOps Services, and download secor/DataServices.metaKeys and secor/DataServices.schema to your local machine.
-
From your application's dashboard select DAT-objectstorage.
-
From the Actions drop down menu, select Add Container and name it secorSchema.
-
Create another container and name it DataServices.
-
Select your secorSchema container, and from the Actions drop down menu, select Add File.
- Select the DataServices.metaKeys file you downloaded to your local machine.
- Select the DataServices.schema file you downloaded to your local machine.
To complete Spark configuration, add your Object Storage and IPython notebook to the service.
- In DevOps Services, select your project and download dat_notebook.ipynb to your local machine.
- Inside the Spark service, click Open at the top right.
- Select your newly created DAT-spark instance.
- Click NOTEBOOKS and at the top select Object Storage and select Add Object StorageE.
- Select Bluemix at the top.
- Select DAT-objectstorage from the options. Select the container DataServices and press SELECT.
- Click My Notebooks at the top and select New Notebook.
- Select From File at the top. Name the notebook and give it a description.
- Click on Choose File and select the dat_notebook.ipynb downloaded to your local machine.
- Select Create Notebook.
Add the external IP address of your container to Node-RED.
- Obtain the public IP of your DAT-container on the container's tile at your Bluemix Dashboard.
- Return to your cf application's dashboard and click the route at the top of the page to launch the Node-RED website.
- Click Go to your Node-RED flow editor. Once there, you will see the customized flow.
- Connect the initial Every 5 minutes node to the Get traffic status from Madrid node.
- Double click on the Send to Kafka node at the far right to edit the Kafka producer node. Click the pencil icon to edit the DAT Kafka Zookeeper Server.
- In the Edit kafka-credentials config node window, modify the Zookeeper Server Address field to the public IP address of your DAT container.
- Press Update.
- Click OK to close the window.
- Click Deploy at the upper right to deploy the updated flow to Node-RED.
- Go to the project in your Bluemix Dashboard, and choose Apache Spark.
- Click OPEN and select your Apache Spark instance.
- Click on the notebook you created.
- Update the variable "containerIP" to your own container's public IP address.
- Click Play at the top.
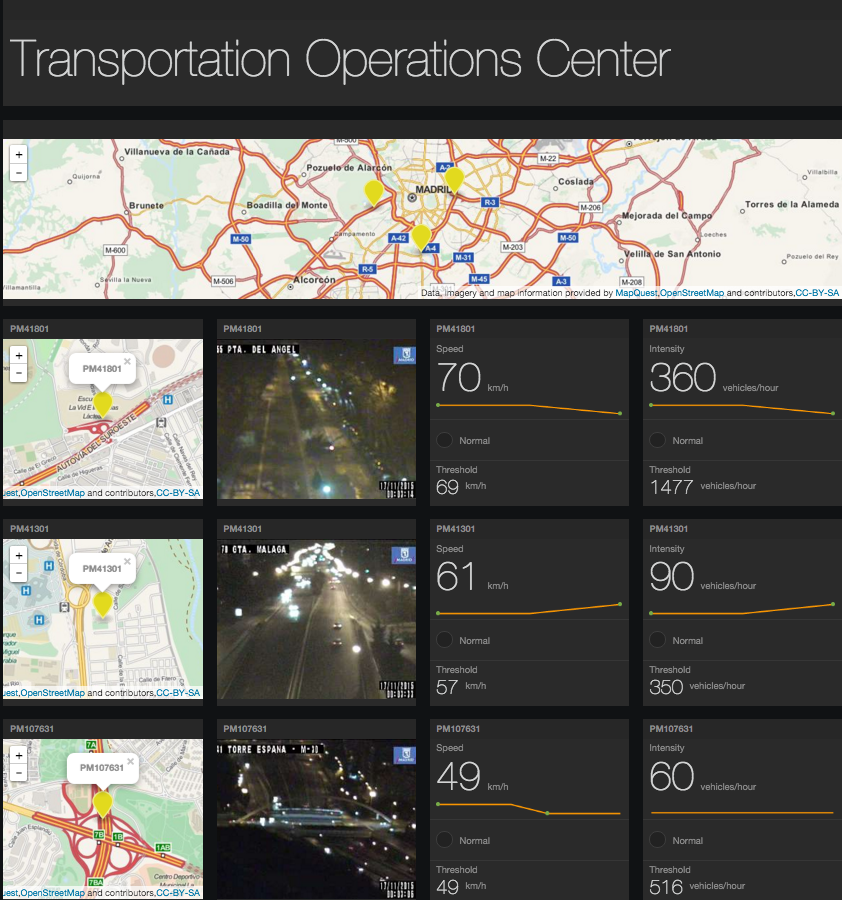
Once the data is processed, you will be able to see a visual representation of real-time traffic information displayed in a Node-RED Freeboard. The information on the Freeboard is collected from three separate areas of Madrid and the three data points are simultaneously displayed. You are able to see the live feed from traffic cameras, as well as, the speed and intensity of traffic and their analyzed thresholds.
- Return to your Cloud Foundry's application dashboard and select the route for your application to access Node-RED.
- Click Go to your Freeboard dashboard to load your newly configured Freeboard.
The Data and Analytics Transportation sample app combines several different Bluemix and open source applications.
Apache Kafka: a message hub that provides a commit log of updates.
Secor: a reliable logging service that takes information from Kafka and converts it into parquet files. Those files are then placed into Object Storage within Bluemix.
Apache Spark: a data processing engine.
IPython: an interactive computational environment where you can combine coding, text, math, and media.
Node-RED: a tool for wiring together the Internet of Things.
Node-RED Freeboard: a data visualization dashboard.
Object Storage: uses unique ID's and containers to store information in a scalable way.