| Version: | 1.1 |
|---|---|
| Copyright: | 2015 REANNZ. All Rights Reserved. |
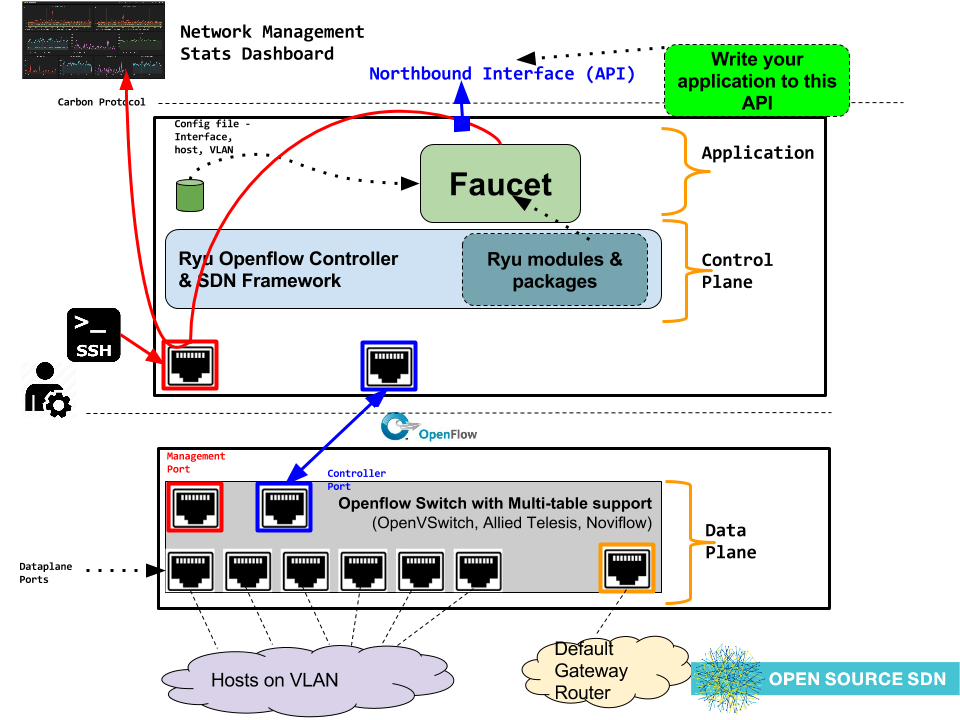
Faucet is an OpenFlow controller for a layer 2 switch based on Waikato University's Valve. It handles MAC learning and supports VLANs and ACLs. It is developed as an application for the Ryu OpenFlow Controller .
It supports:
- OpenFlow v1.3
- Multiple datapaths (using a single process)
- Mixed tagged/untagged ports
- Port statistics
- ACL support: Rules are added in the order specified. The rule language supports anything the Ryu OpenFlow protocol parser supports (q.v. ofctl to_match()).
- Control unicast flooding by port and by VLAN
- BGP advertisement of controller IPs and static routes and Quagga support
- Policy based forwarding to offload processing to external systems (Eg 802.1x via hostapd)
- Support for IPv4 and IPv6 static routes on both tagged and untagged VLANs
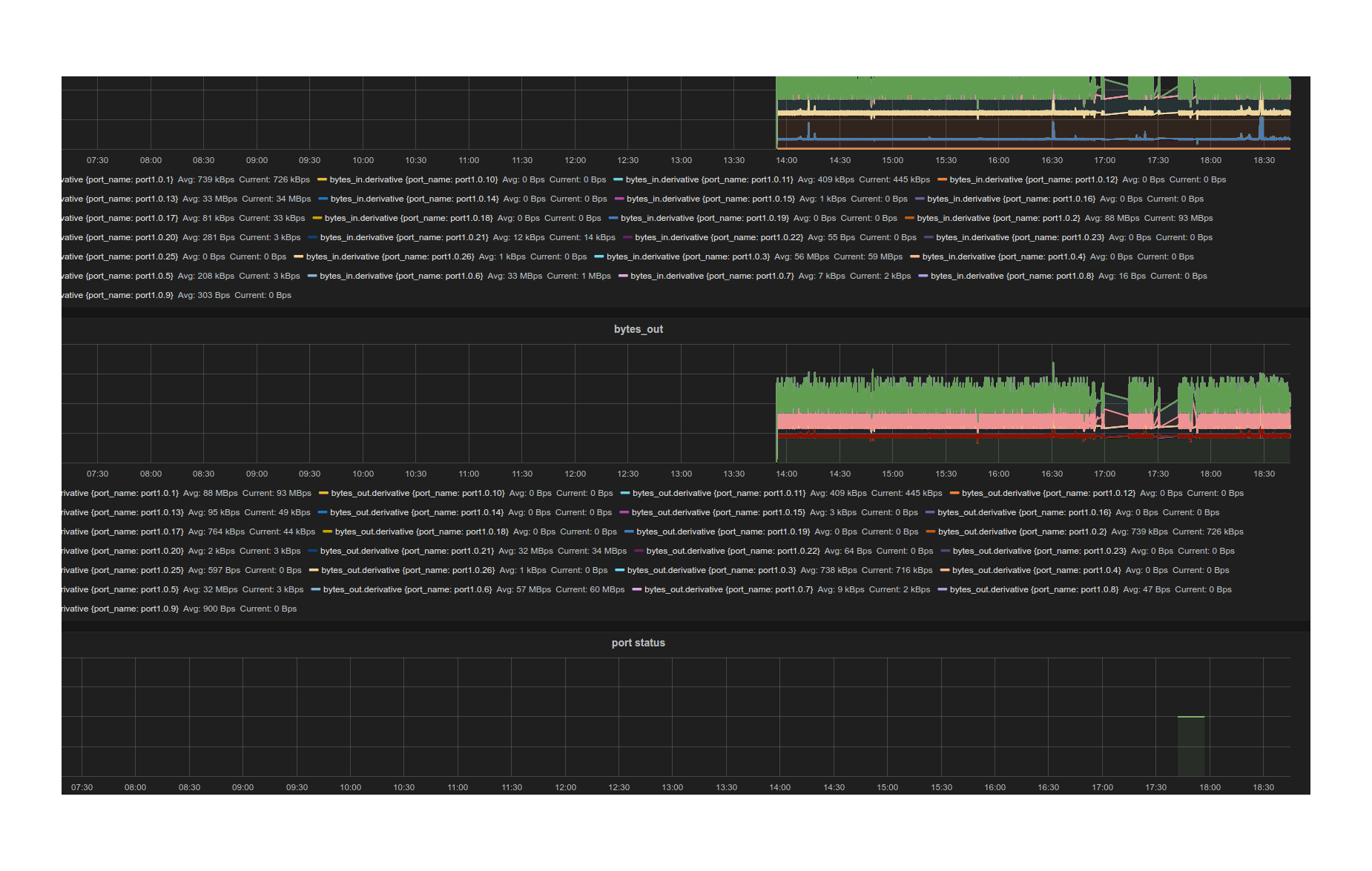
- Integrated support for InfluxDB/Grafana
- Comprehensive Test suite - tests for all features that can be run against mininet (development) and on hardware; Most tests run in parallel to reduce time.
- Code: Python based, easy readability (PEP8 style), documented, Unit tests for all features
- Installation: Python pip (pip install ryu_faucet), pre-built VM available - https://susestudio.com/a/ENQFFD/ryu-faucet, Makefiles to build Docker images
Rules are added in the order specified. The rule language supports anything the Ryu OpenFlow protocol parser supports (q.v. ofctl to_match()). In this example,configure an ACL on port 1, default deny, that passes an IPv4 subnet and ARP. Following config applies an input ACL to port 1.
Supports any ACL rule that https://github.com/osrg/ryu/blob/master/ryu/lib/ofctl_v1_3.py to_match() supports.
---
version: 2
dps:
test-switch-1:
dp_id: 0x000000000001
interfaces:
1:
native_vlan: 2040
acl_in: 1
vlans:
2040:
name: "dev VLAN"
acls:
1:
- rule:
nw_dst: "172.0.0.0/8"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 1
- rule:
dl_type: 0x0806
allow: 1
- rule:
nw_dst: "10.0.0.0/16"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 0
- rule:The default is to flood unknown unicast packets (of course). You might not want unicast flooding on a port for security reasons.
If you add unicast_flood: False to a port, then that port will never get unknown destinations flooded to it. So hosts on that port will have to say something to get learned (or someone will need to ND/ARP for it). Broadcasts and Ethernet multicasts are still flooded to that port (so of course ND and ARP work just fine).
You can also add unicast_flood: False to a VLAN, which will override all the ports. On my untrusted VLAN, the default gateway has permanent_learn enabled, and unicast flooding disabled.
Faucet is configured with a YAML-based configuration file. A sample configuration file is supplied in faucet.yaml.
The datapath ID may be specified as an integer or hex string (beginning with 0x).
A port not explicitly defined in the YAML configuration file will be set down and will drop all packets.
The Faucet configuration file format occasionally changes to add functionality or accommodate changes inside Faucet. If the version field is not specified in faucet.yaml, the current default value is 1.
Version 1 of the Faucet configuration file format does not allow multiple datapaths to be defined. The one datapath configured for this Faucet instance is configured using top level values, a sample of which can be found in faucet.yaml. Previous (1.0 and older) versions of Faucet do not support the version field, so most configuration files in this format should not use it.
This version of the Faucet configuration file format is deprecated and will be removed shortly, so new installations of Faucet should use the version 2 format, documented below.
---
dp_id: 0x000000000001
name: "test-switch-1"
interfaces:
1:
native_vlan: 2040
acl_in: 1
vlans:
2040:
name: "dev VLAN"
acls:
1:
- rule:
nw_dst: "172.0.0.0/8"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 1
- rule:
dl_type: 0x0806
allow: 1
- rule:
nw_dst: "10.0.0.0/16"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 0Version 2 of the Faucet configuration file format adds the version field, and allows multiple datapaths (switches) to be defined in one configuration file using the dps object, with each datapath sharing the vlans and acls objects defined in that file.
---
version: 2
dps:
test-switch-1:
dp_id: 0x000000000001
interfaces:
1:
native_vlan: 2040
acl_in: 1
test_switch_2:
dp_id: 0x000000000002
interfaces:
1:
native_vlan: 2040
acl_in: 1
vlans:
2040:
name: "dev VLAN"
acls:
1:
- rule:
nw_dst: "172.0.0.0/8"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 1
- rule:
dl_type: 0x0806
allow: 1
- rule:
nw_dst: "10.0.0.0/16"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 0Extra DP, VLAN or ACL data can also be separated into different files and included into the main configuration file, as shown below. The include field is used for configuration files which are required to be loaded, and Faucet will log an error if there was a problem while loading a file. Files listed on include-optional will simply be skipped and a warning will be logged instead.
Files are parsed in order, and both absolute and relative (to the configuration file) paths are allowed. DPs, VLANs or ACLs defined in subsequent files overwrite previously defined ones with the same name.
faucet.yaml:
---
version: 2
include:
- /etc/ryu/faucet/dps.yaml
- /etc/ryu/faucet/vlans.yaml
include-optional:
- acls.yamldps.yaml:
---
# Recursive include is allowed, if needed.
# Again, relative paths are relative to this configuration file.
include-optional:
- override.yaml
dps:
test-switch-1:
...
test-switch-2:
...Installation automatically installs dependent Python packages [ryu, pyaml, influxdb client] recursively.
You have run this as root or use sudo
pip install https://pypi.python.org/packages/a3/5a/197046b6fbad2f129e108358d7ba9674ebae638a227e6a1680cd77c7bd13/ryu-faucet-1.1.tar.gz
pip show -f ryu-faucet- To setup InfluxDB v0.11+ - https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v0.10/introduction/getting_started/
- To setup Grafana v3.x - http://docs.grafana.org/installation/
To Uninstall the package
pip uninstall ryu-faucetWe provide official automated builds on Docker Hub so that you can easily run Faucet and it's components in a self-contained environment without installing on the main host system.
Provided are two Docker containers, one for running Faucet and one for running Gauge. The Gauge container needs to be linked to a database container as well as a Grafana container. We also supply a docker-compose.yaml that can be used to start all the components together.
Docker tags are used to differentiate versions of Faucet, latest will always point to master branch on github and stable versions are also tagged e.g v1_0 and v1_1.
- Follow the Docker Installation Guide and install Docker Compose.
- Tweak environment variables, exposed ports, volumes and tags in
docker-compose.yamlto match your environment. - Run
docker-compose upwhich will pull all the correct images and start them.
For more advanced documentation on running Faucet with docker please read README.docker.md.
https://www.google.com/maps/d/u/0/viewer?mid=1MZ0M9ZtZOp2yHWS0S-BQH0d3e4s&hl=en
PACKETS IN +-------------------------+ +-------------------------+
+ | | | |
| | | | CONTROLLER |
| | | | ^ |
| | | | +----+-----+ v
| +-----+----+ +----------+ +---+-+----+ |3:IPv4_FIB| +---+------+ +----------+
| |0:VLAN | |1:ACL | |2:ETH_SRC +->+ +->+5:ETH_DST | |6:FLOOD |
+------>+ | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | +----------+ | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| +->+ +->+ +--------------->+ +->+ |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | +----------+ | | | |
| | | | | | |4:IPv6_FIB| | | | |
| | | | | +->+ +->+ | | |
+----------+ +----------+ +----+-----+ | | +------+---+ +--+-------+
| +----+-----+ | |
v v v v
CONTROLLER CONTROLLER PACKETS OUT
Note: On your system, depending on how Python is installed, you may have to install some additional packages to run faucet.
Run with ryu-manager (uses /etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.yaml as configuration by default):
# export FAUCET_CONFIG=/etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.yaml
# export GAUGE_CONFIG=/etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.yaml
# export FAUCET_LOG=/var/log/faucet/faucet.log
# export FAUCET_EXCEPTION_LOG=/var/log/faucet/faucet_exception.log
# export GAUGE_LOG=/var/log/faucet/gauge_exception.log
# export GAUGE_EXCEPTION_LOG=/var/log/faucet/gauge_exception.log
# export GAUGE_DB_CONFIG=/etc/ryu/faucet/gauge_db.yaml
# $EDITOR /etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.yaml
# ryu-manager --verbose faucet.pyTo find the location of faucet.py, run pip show ryu-faucet to get the Location Path. Then run:
# ryu-manager --verbose <Location_Path>/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/faucet.pyAlternatively, if OF Controller is using a non-default port of 6633, for example 6653, then:
# ryu-manager --verbose --ofp-tcp-listen-port 6653 <Location_Path>/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/faucet.pyOn Mac OS X, for example, one would run this as:
# ryu-manager --verbose /opt/local/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/faucet.pyTo specify a different configuration file set the FAUCET_CONFIG environment variable.
Faucet will log to /var/log/faucet/faucet.log and /var/log/faucet/faucet_exception.log by default, this can be changed with the FAUCET_LOG and FAUCET_EXCEPTION_LOG environment variables.
Gauge will log to /var/log/faucet/gauge.log and /var/log/faucet/gauge_exception.log by default, this can be changed with the GAUGE_LOG and GAUGE_EXCEPTION_LOG environment variables.
If running Faucet in virtualenv and without specifying the environment variables above, the default log and configuration locations will change to reflect the virtual environment's prefix path. For example, the default Faucet log location will be <venv prefix>/var/log/faucet/faucet.log. The Gauge configuration must still be updated in this case by modifying <venv prefix>/etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.yaml to reflect the location of the configuration file used by Faucet (<venv prefix>/etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.conf). When using virtualenv, also create the log directory at its new location, <venv prefix>/var/log/ryu/faucet, rather than the global /var/log/ryu/faucet.
To tell Faucet to reload its configuration file after you've changed it, simply send it a SIGHUP:
pkill -SIGHUP -f "ryu-manager faucet.py"Run the tests to make sure everything works! Mininet test actually spins up virtual hosts and a switch, and a test FAUCET controller, and checks connectivity between all the hosts given a test config. If you send a patch, this mininet test must pass.
git clone https://github.com/onfsdn/faucet
cd faucet/tests
# (As namespace, etc needs to be setup, run the next command as root)
sudo ./faucet_mininet_test.py
./test_config.pyIf you are a hardware vendor wanting to support FAUCET, you need to support all the matches in src/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/valve.py:valve_in_match().
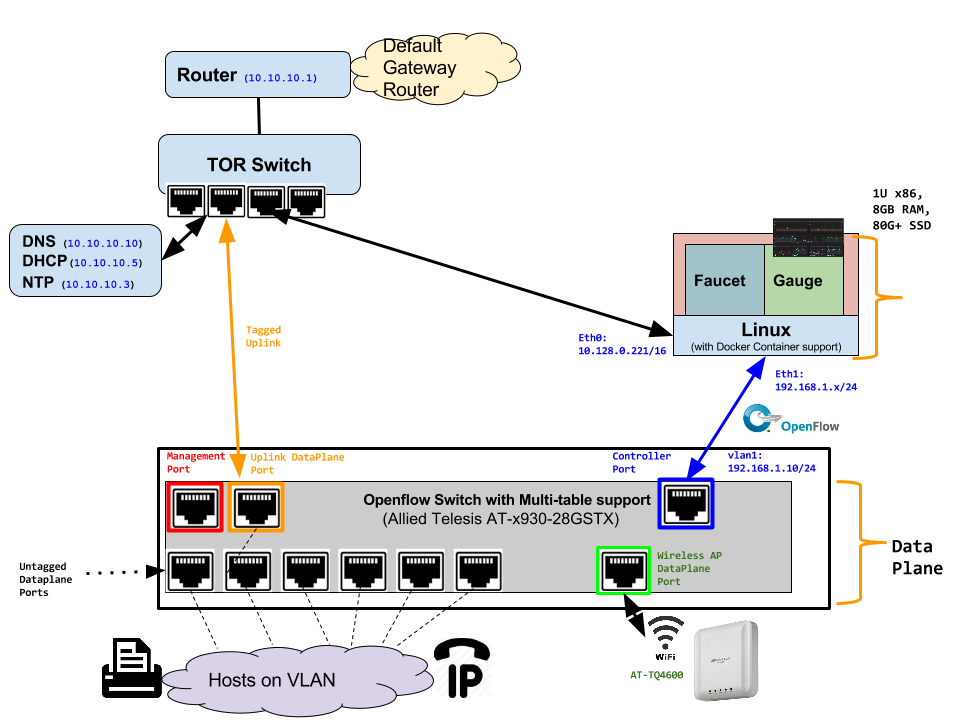
Faucet has been tested against the following switches: (Hint: look at src/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/dp.py to add your switch)
- Open vSwitch v2.1+ - Open Source available at http://www.openvswitch.org
- Lagopus Openflow Switch - Open Source available at https://lagopus.github.io
- Allied Telesis x510 and x930 series - https://www.alliedtelesis.com/products/x930-series
- NoviFlow 1248 - http://noviflow.com/products/noviswitch
- Northbound Networks - Zodiac FX - http://northboundnetworks.com/collections/zodiac-fx
- HP Enterprise Aruba 3810 - http://www.arubanetworks.com/products/networking/switches/3810-series
Faucet's design principle is to be as hardware agnostic as possible and not require TTPs. That means that Faucet excepts the hardware OFA to hide implementation details, including which tables are best for certain matches or whether there is special support for multicast - Faucet excepts the OFA to leverage the right hardware transparently.
Allied Telesis <http://www.alliedtelesis.com/sdn> sells their products via distributors and resellers. To order in USA call ProVantage <http://www.provantage.com/allied-telesis-splx10~7ALL912L.htm>. To find a sales office near you, visit Allied Telesis <http://www.AlliedTelesis.com>
- On Allied Telesis, all vlans must be included in the vlan database config on the switch before they can be used by OpenFlow.
NoviFlow <http://noviflow.com>
NorthBound Networks <http://northboundnetworks.com>
FAUCET supports the Zodiac FX as of v0.60 firmware.
HP Enterprise <http://www.hp.com> and its many distributors and resellers.
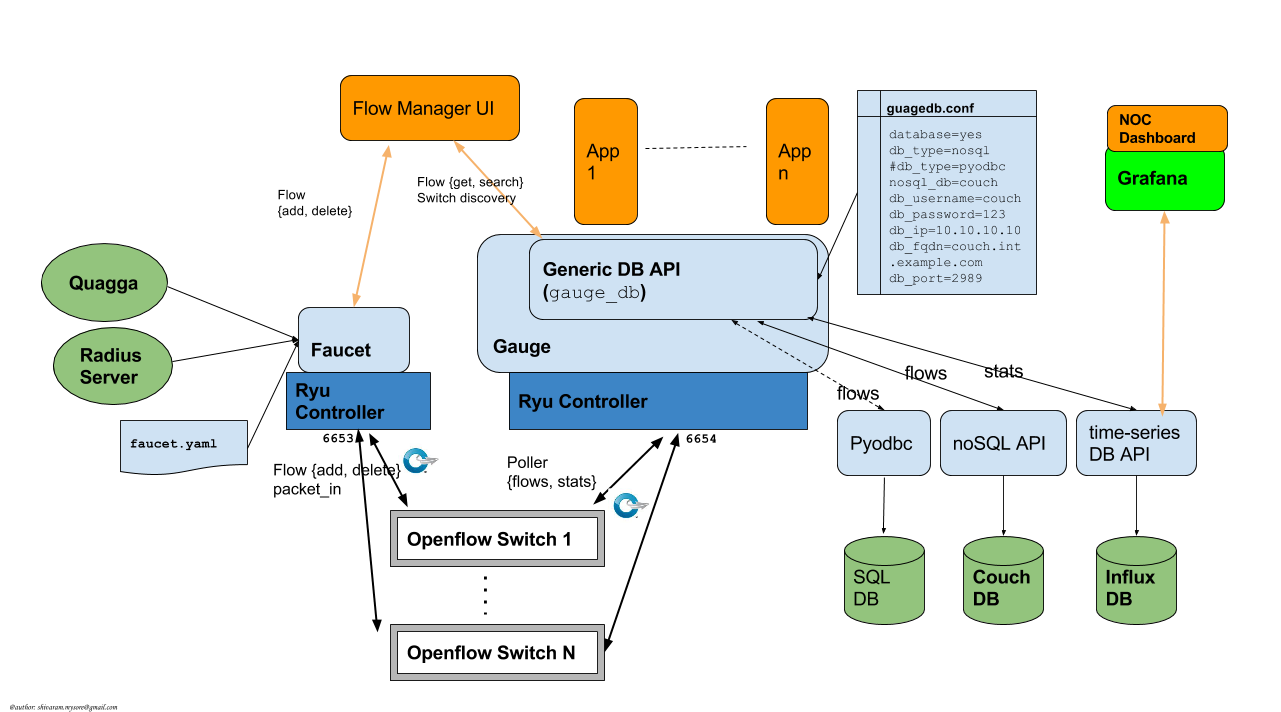
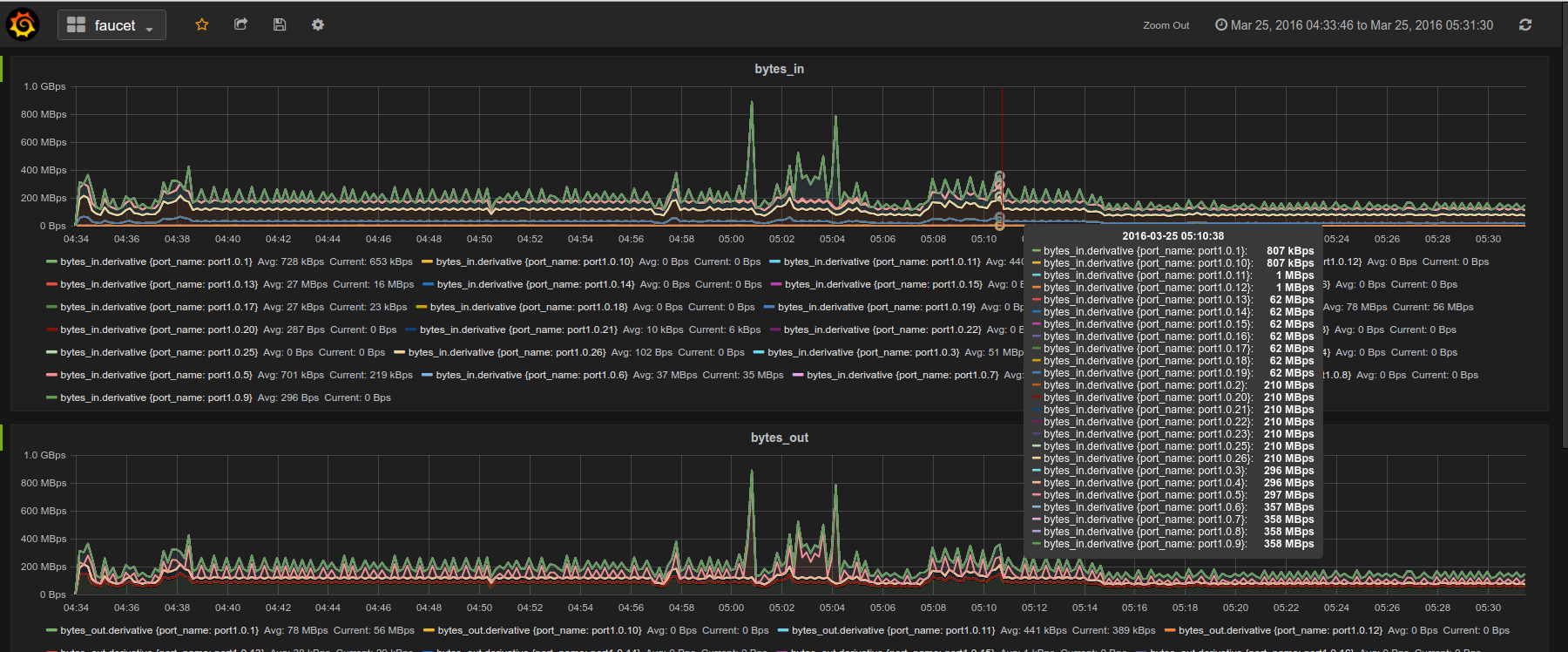
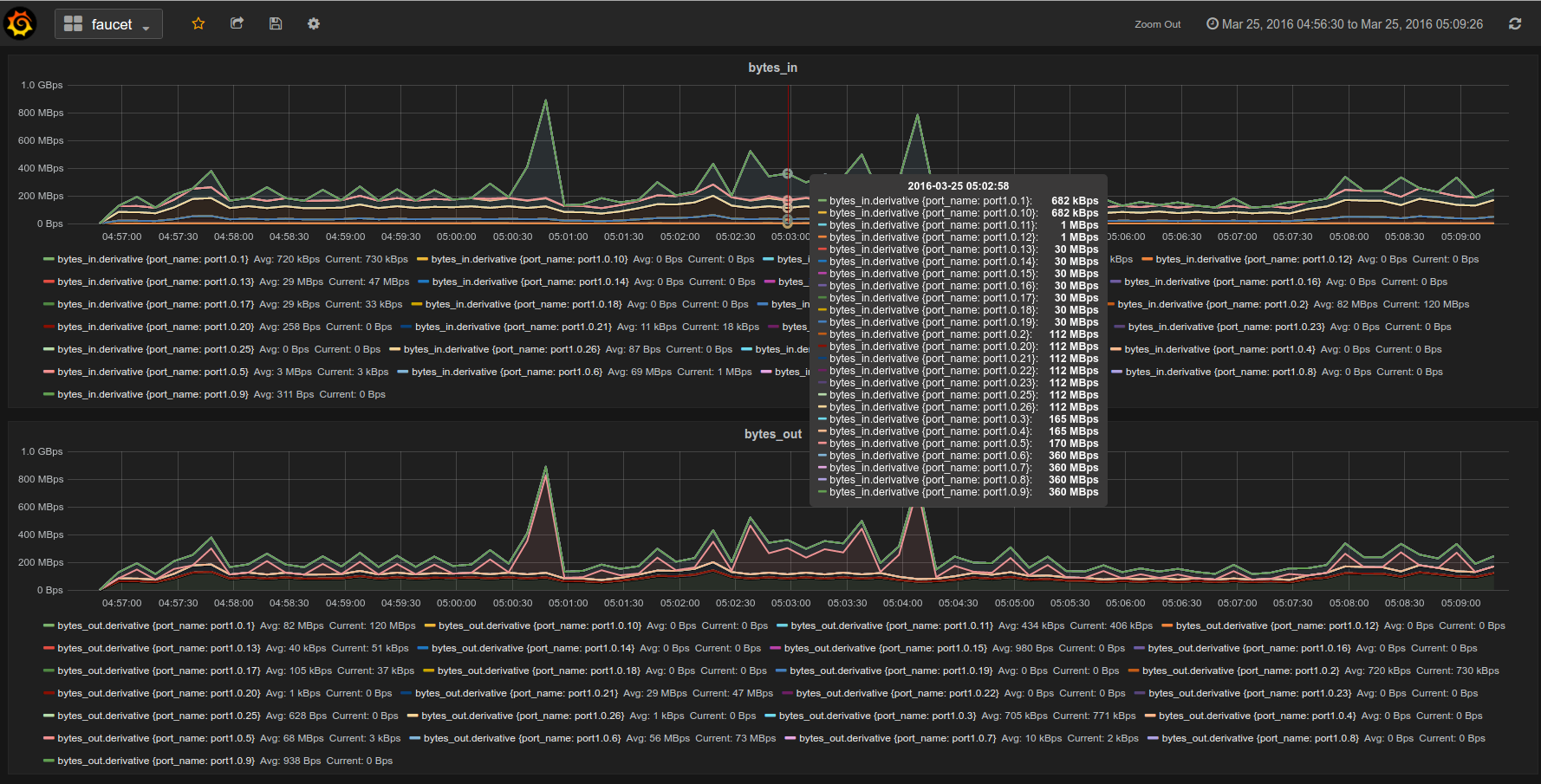
Gauge is the monitoring application. It polls each port for statistics and periodically dumps the flow table for statistics.
Gauge reads the faucet yaml configuration files of the datapaths it monitors. Which datapaths to monitor is provided in a configuration file containing a list of faucet yaml files, one per line.
The list of faucet yaml config is by default read from /etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.yaml. This can be set with the GAUGE_CONFIG environment variable. Exceptions are logged to the same file as faucet's exceptions.
Gauge is run with ryu-manager:
$EDITOR /etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.yaml
ryu-manager gauge.pyIf you have any technical questions, problems or suggestions regarding Faucet please send them to faucet-dev@OpenflowSDN.Org <mailto:faucet-dev@openflowsdn.org>. Mailing list archives are available here <https://groups.google.com/a/openflowsdn.org/forum/#!forum/faucet-dev>.
Documentation is available under the docs <https://github.com/REANNZ/faucet/tree/master/src/docs> directory.
Faucet related blog by Josh Bailey available at http://faucet-sdn.blogspot.co.nz
To create a issue, use GitHub Issues <https://github.com/onfsdn/faucet/issues>