This repository contains the official implementation of our paper:
Zhanqiang Guo, Zimeng Tan, Jianjiang Feng, Jie Zhou
Abstract: Vascular structure segmentation plays a crucial role in medical analysis and clinical applications. The practical adoption of fully supervised segmentation models is impeded by the intricacy and time-consuming nature of annotating vessels in the 3D space. This has spurred the exploration of weakly-supervised approaches that reduce reliance on expensive segmentation annotations. Despite this, existing weakly supervised methods employed in organ segmentation, which encompass points, bounding boxes, or graffiti, have exhibited suboptimal performance when handling sparse vascular structure. To alleviate this issue, we employ maximum intensity projection (MIP) to decrease the dimensionality of 3D volume to 2D image for efficient annotation, and the 2D labels are utilized to provide guidance and oversight for training 3D vessel segmentation model. Initially, we generate pseudo-labels for 3D blood vessels using the annotations of 2D projections. Subsequently, taking into account the acquisition method of the 2D labels, we introduce a weakly-supervised network that fuses 2D-3D deep features via MIP to further improve segmentation performance. Furthermore, we integrate confidence learning and uncertainty estimation to refine the generated pseudo-labels, followed by fine-tuning the segmentation network. Our method is validated on five datasets (including cerebral vessel, aorta and coronary artery), demonstrating highly competitive performance in segmenting vessels and the potential to significantly reduce the time and effort required for vessel annotation.
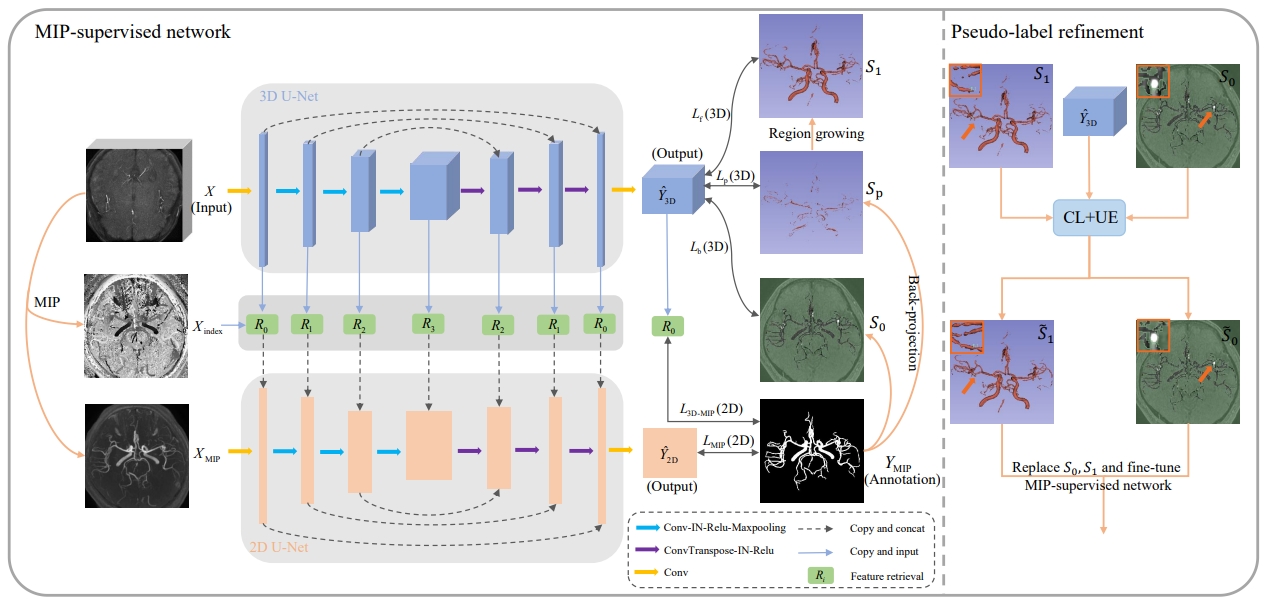
Illustration of The Proposed Weakly-Supervised Vessel Segmentation Framework.
- [Feb 22 2024] 🔔 Code is coming.
- Python = 3.8
- Pytorch = 1.10.0
- CUDA = 11.1
- Install other packages in
requirements.txt
###mra_data The file structure is as follows:
root_path
├── size_img
├── size_label
├── mip_img2
├────── img_0.npy
├────── img_0.png
├────── img_0_label.png
├── data_txt
├────── train.txt
├────── val.txt
└────── test.txt- Pseudo labels Generation.
python data_preprocess/mip_img2.py python data_preprocess/mip_generate_pseudo_label.py
-
Base Training.
python train_mip.py --drop True --one_fold 0 #--one_fold 1,2 python train_mip.py -
Pseudo label Refinement.
python utils/CL_UN.py
-
Network Fine-tune.
python train_mip.py --rec_path 'reconstruction_label2_one_new_cl_un/' --fine-tune True
- Network inference.
python inference.py
We hope you find our work useful. If you would like to acknowledge it in your project, please use the following citation:
@article{guo20243d,
title={3D Vascular Segmentation Supervised by 2D Annotation of Maximum Intensity Projection},
author={Guo, Zhanqiang and Tan, Zimeng and Feng, Jianjiang and Zhou, Jie},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
}
If you have any questions about this code, please do not hesitate to contact me.
Zhanqiang Guo: guozq21@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn