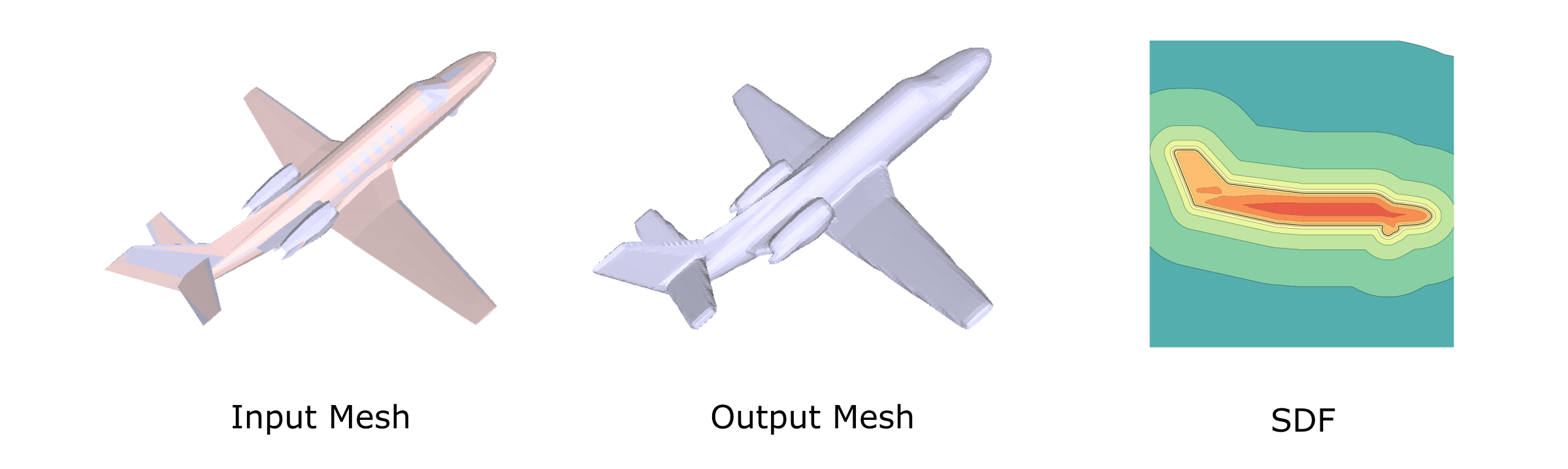
Converts an input mesh to a signed distance field. It can work with arbitrary meshes, even non-watertight meshes from ShapeNet.
mesh2sdf is used in our paper
Dual Octree Graph Networks (SIGGRAPH 2022)
to generate the training data.
mesh2sdf depends on pybind11, and C++
compilers are needed to build the code. Supported compliers are listed
here.
-
Install via the following command:
pip install mesh2sdf
-
Alternatively, install from source via the following commands.
git clone https://github.com/wang-ps/mesh2sdf.git pip install ./mesh2sdf
After installing mesh2sdf, run the following command to process an input mesh
from ShapeNet:
python example/test.py-
Given an input mesh, we first compute the unsigned distance field with the fast sweeping algorithm implemented by Christopher Batty (SDFGen). Note that the unsigned distance field can always be reliably and accurately computed even though the input mesh is non-watertight.
-
Then we extract the level sets with a small value d with the marching cube algorithm. The extracted level sets are represented with triangle meshes and are guaranteed to be manifold.
-
There exist multiple connected components in the extracted meshes, and we only keep the mesh with the largest bounding box.
-
Compute the signed distance field again with the kept triangle mesh as the final output. In this way, the signed distance field (SDF) is computed for a non-watertight input mesh.