HumaRobotics Dynamixel Library
HumaRobotics Dynamixel Library is a Python 2.7 library for programming Robotis Dynamixel motors directly from python or through the ROS bindings provided separately in https://github.com/HumaRobotics/dynamixel_hr_ros . It also comes with a GUI that allows to quickly identify/configure/manipulate your motors.
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 1
Dynamixel models supported
- At the moment it can handle the following models:
- AX12*
- AX18*
- MX12*
- MX28*
- MX64*
- RX64*
- CM730
Adding other models is very easy, have a look in :mod:`dxl.dxlmotors` and simply add the corresponding model class that will contain the definitions of registers and conversion functions.
Dynamixel Lab
Dynamixel Lab is a tk-based GUI for manipulating and programming Dynamixel motors that makes use of the Dynamixel Library.
- It provides the following features:
- Fast scanning of serial port on multiple baud rates using Ping broadcast (can be deactivated)
- Automatic identification of all elements on the chain
- Easy validation and reconfiguration of dynamixel chain using JSON formatted files
- Access to all motors registers
- Visualization and manipulation of motor IDs, baudrates, documentation
- Pose recording and replay, saved as JSON files for easy modification
- Motor window for quick manipulation of motor positions and speed
- In-GUI Python coding for easy programming of chains of motors
- Direct activation of ROS bindings, with optional conversion to SI units
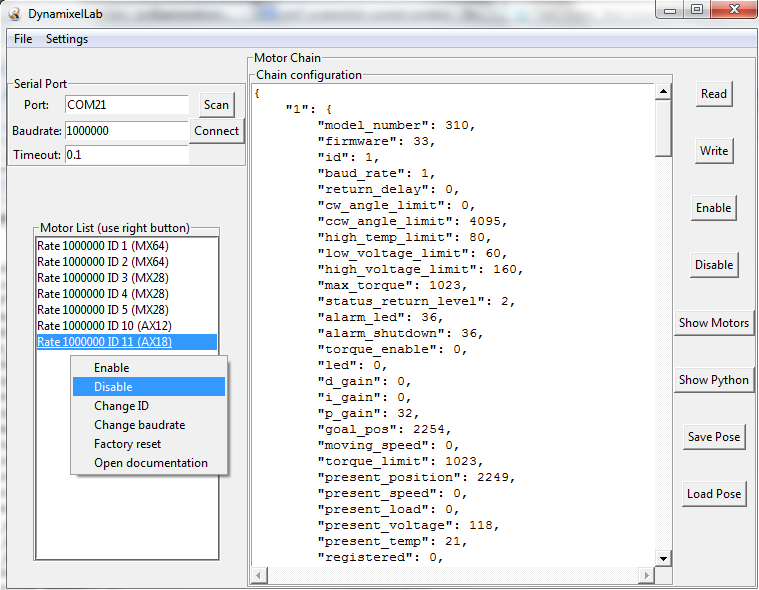
Main window of the Dynamixel Lab GUI
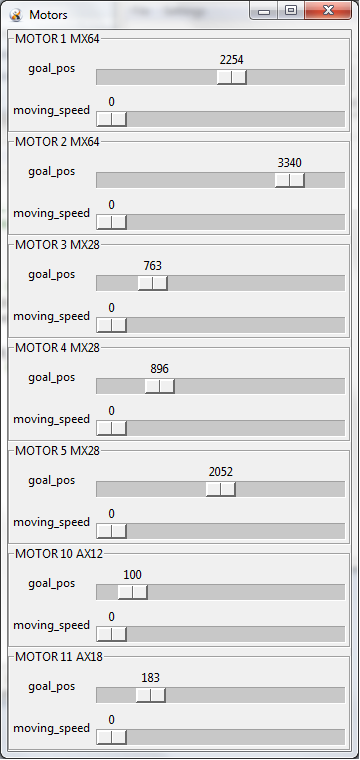
Motor window of the Dynamixel Lab GUI
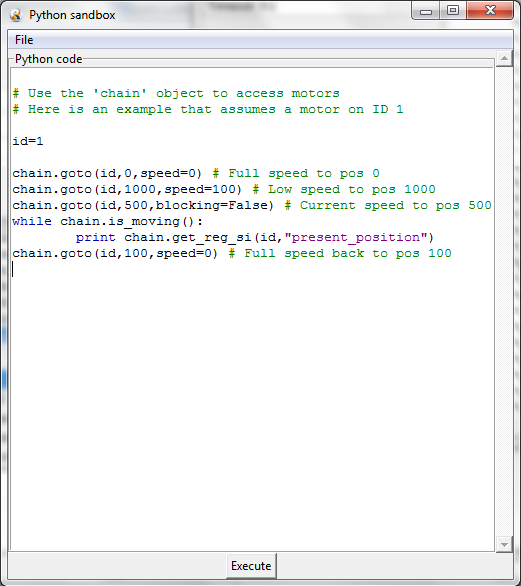
Python window of the Dynamixel Lab GUI
Download
You can obtain the latest sources using our Git repository: git clone git@github.com/HumaRobotics:dynamixel_hr
You can also download the latest release as a compressed archive from: http://www.humarobotics.com/downloads/dynamixel_hr.zip
Installation
Windows
- Setup drivers for USB2Dynamixel:
- Install FTDI driver for USB2Dynamixel from http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/CDM/CDM20830_Setup.exe :
- You may want to check documentation at http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm
- Follow instructions from http://support.robotis.com/en/software/dynamixel_sdk/usb2dynamixel/usb2dxl_windows.htm
- Set USB: Port 21, max baudrate, delay 1
- Setup python and pyserial:
- Install Python 2.7 from http://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.6/python-2.7.6.msi
- Install pyserial from https://pypi.python.org/packages/any/p/pyserial/pyserial-2.7.win32.exe
If required you can install the library by running the following command from the dynamixel_hr folder:
python setup.py install
Ubuntu
Install python and pyserial:
sudo apt-get install python2.7 python-serial
Access to the serial device (/tty/USB0 by default) needs special rights, so you'll need either to sudo or add your user to the dialout group:
sudo usermod -a -G dialout username
If required you can install the library by running the following command from the dynamixel_hr folder:
sudo python setup.py install
Dynamixel Lab Usage
You can start the Dynamixel Lab by running:
python ToolDynamixelLab.py
Library
The provided Dynamixel Library is composed of several modules. However, from a user perspective only the dxl.dxlchain which provides Python access to the Dynamixel motors is directly used. Here is a typical code example:
from dxl.dxlchain import DxlChain
# Open the serial device
chain=DxlChain("/dev/ttyUSB0",rate=3000000)
# Load all the motors and obtain the list of IDs
motors=chain.get_motor_list() # Discover all motors on the chain and return their IDs
print motors
# Move a bit
chain.goto(1,500,speed=200) # Motor ID 1 is sent to position 500 with high speed
chain.goto(1,100) # Motor ID 1 is sent to position 100 with last speed value
# Move and print current position of all motors while moving
chain.goto(1,1000,speed=20,blocking=False) # Motor ID 1 is sent to position 1000
while chain.is_moving():
print chain.get_position()
# Disable the motors
chain.disable()