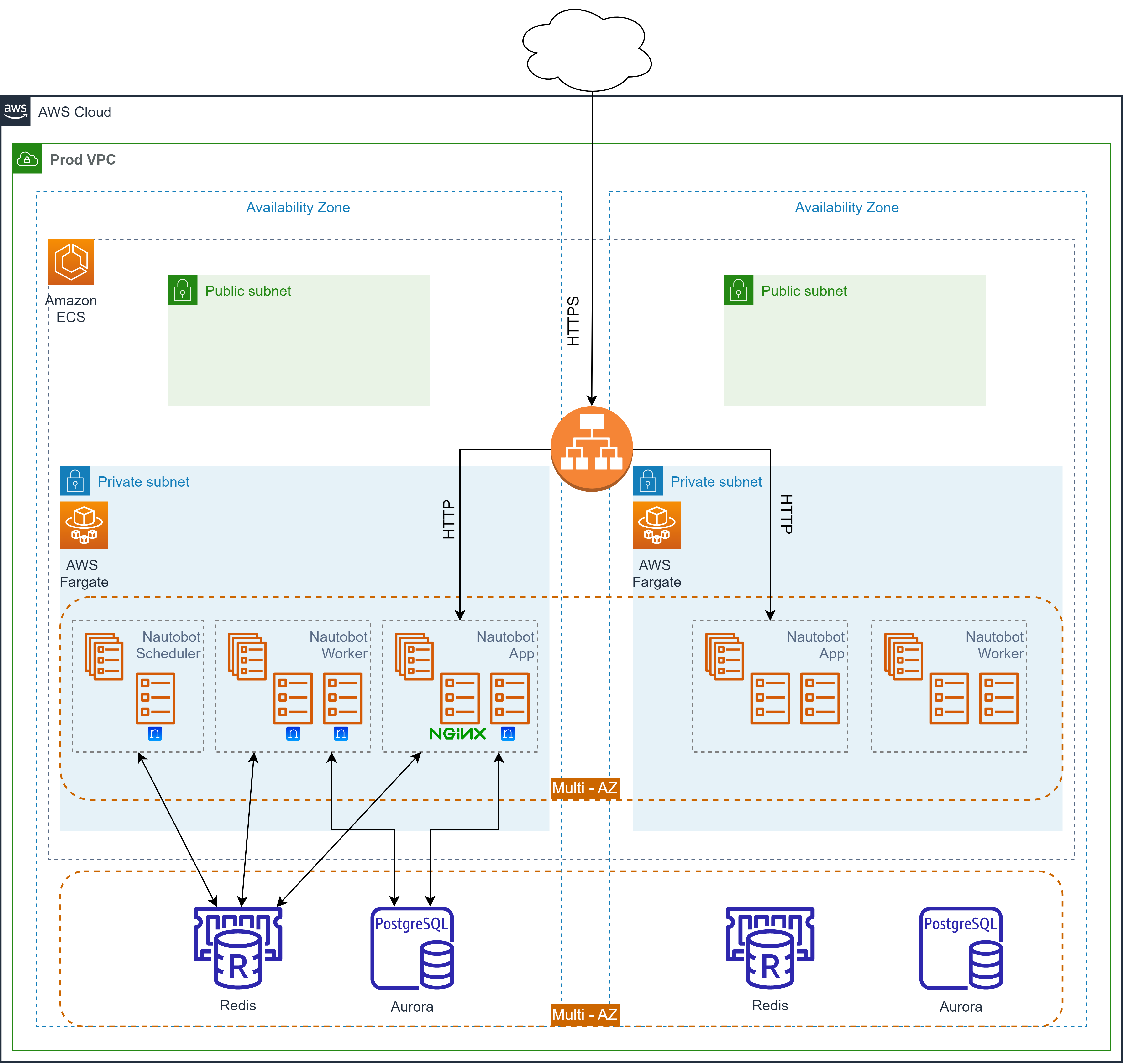
This project contains the AWS CDK code to deploy a multi-environment (dev & prod) Nautobot to AWS ECS/Fargate behind an ALB. The CDK code was influenced by the Nautobot In AWS Fargate blog post by Network to Code which provides a high-level deployment through the AWS Console. This project fills all the gaps and provides a fully automated deployment of Nautobot with CDK.
- Clone the repo
- Edit the
lib/secrets/env-exampleandlib/nautobot-app/.env-examplefiles and rename them to.env - Manipulate the
lib/nautobot-app/nautobot_config.pyfile to your liking. - Run the
deploy.shscript with the--stageoption to deploy todevorprodenvironment. - ~ 20 minutes later and you have a
devandprodNautobot instance running in AWS.
At this time SSL certs are not part of the deployment, but could be a simple change to the ALB and SGs.
If there is a need to access the containers, AWS SSM provides a way to do this. The following commands can be used to access the containers:
ecs-session --list- List the ECS clusters / Containers
Example:
ecs-session nautobotThe cdk.json file tells the CDK Toolkit how to execute your app.
This project is structured to use AWS CDK to build and deploy a Nautobot application using ECS Fargate, with its data stored in RDS PostgreSQL and cached in ElastiCache Redis split into multiple stacks.
The following files and directories represent the core components of the application:
nautobot-app: This directory contains the Dockerfile and other necessary files to build the Docker image for the main Nautobot application.Dockerfile: Describes the Docker image for the Nautobot application.nautobot_config.py: The configuration file for Nautobot.requirements.txt: Lists the Python dependencies for the Nautobot application.README.md: Describes the contents of thenautobot-appdirectory.
nautobot-db-stack.ts: Defines the AWS CDK Stack to set up the Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL database and Amazon ElastiCache for Redis cache.nautobot-docker-image-stack.ts: Defines the AWS CDK Stack to build the Docker image from the local Dockerfile for the main Nautobot container.nautobot-fargate-ecs-stack.ts: Defines the AWS CDK Stack to set up the ECS Fargate service for the Nautobot application.nautobot-secrets-stack.ts: Defines the AWS CDK Stack to manage AWS Secrets Manager secrets for the Nautobot application.nautobot-vpc-stack.ts: Defines the AWS CDK Stack to set up the VPC for the Nautobot application.nginx: This directory contains the Dockerfile and configuration file for the NGINX server.Dockerfile: Describes the Docker image for the NGINX server.nginx.conf: The configuration file for the NGINX server.
nginx-docker-image-stack.ts: Defines the AWS CDK Stack to build the Docker image from the local Dockerfile for the NGINX server.secrets: This directory contains an example environment file.env-example: An example of the environment variables to be used in the application.
There are two .env in this project that are used for the Nautobot Application service. The more sensitive information is under /lib/secrets/env-example. This file is used to create the AWS Secrets Manager secret. The other .env file is under /lib/nautobot-app/.env-example. This file is used to set the environment variables for the Nautobot application. The /lib/secrets/.env-example and lib/nautobot-app/.env-example files are meant to be edited and then renamed or copied .env before running the CDK stack.
Ensure that you have proper AWS credentials set up on your machine via ./aws credentials/profile. Then, run the following commands:
Bootstrap CDK environment to your AWS account
cdk bootstrapThis script allows you to deploy your stack in different environments or stages. It takes one command line argument, --stage, that specifies the deployment stage: either dev or prod.
Depending on the provided stage, the script will pass it to the AWS CDK command cdk deploy as a context variable, which can be used in your CDK stack to customize resource configuration based on the deployment stage.
Replace dev or prod with the stage you want to deploy to.
If you provide an unknown option or do not provide the --stage option, the script will print a help message and stop executing.
Example (deploy to dev stage)
./deploy.sh --stage=dev- Manually delete the
namespacein ECS (Usually this holds it up). Once this is complete, you can run the following command to destroy the stacks:
cdk destroy