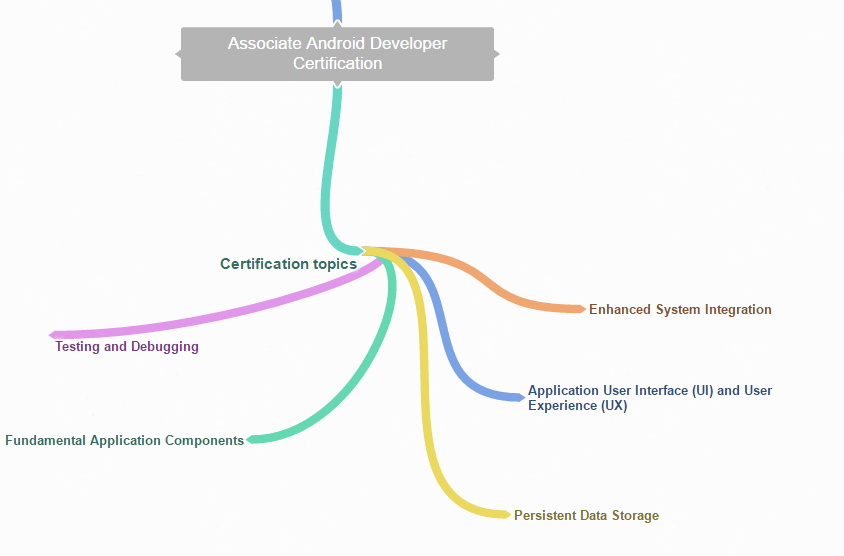
All the info and material about the certification that I've collected so far.
Google has Updated their Courses and every other material below are very necessary to cover, the only new thing is Android Architecture Components.
Scrolldown to the last page to see the Updated Materials
Pull Requests are welcome!
Feel free to make a fork and fill out the checkboxes as you go!
A checkbox in the editor will look like "[ ]". You just need to put an x instead of a space to check it off, like "[x]"!
Thanks to Daita for this contribution.
- Announcement on Google I/O 2016
- Associate Android Developer certification Specs
- Udacity Course Developing Android Apps Covers the Certification Topics
- Associate Android Developer Fast Track
- Android Developer Fundamentals
Writing tests to verify that the application's logic and user interface are performing as expected, and executing those tests using the developer tools. Candidates should be able to analyze application crashes, and find common bugs such as layout errors and memory leaks. This includes working with the debuggers to step through application code and verify expected behavior.
-
Write and execute a local JVM unit test
- [Fragmented Podcast] Episode 78 Ten Testing Strategies with Michael Bailey
- [Fragmented Podcast] Episode 7 Jake Wharton on Testing, SqlBrite, NotRxAndroid, RxJava and Much More
- Getting Started with Testing
- Bulding Effective Unit Tests
- Play List Android Testing Patterns
- Android Testing Codelab
- Android Testing Samples
- Android Testing Blueprint
- Intro to testing part 1, @riggaroo
- Intro to testing part 2, @riggaroo
- Intro to testing part 3, @riggaroo
-
Write and execute a device UI test
- [Fragmented Podcast] Episodeo 78 Ten Testing Strategies with Michael Bailey
- Automating User Interface Tests
- Espresso
- UI Automator
- Advanced Espresso Google I/O 2016
- Advanced Android Espresso (Big Android BBQ 2016)
- Espresso cheat sheet
- Espresso Serie Caster
- [Udacity Course] Advanced Android App Development Lesson: Espresso
-
Given a problem description, replicate the failure
-
Use the system log to output debug information
-
Debug and fix an application crash (uncaught exception)
-
Debug and fix an activity lifecycle issue
-
Debug and fix an issue binding data to views
Implementation of the visual and navigational components of an application's design. This includes constructing layouts–using both XML and Java code–that consist of the standard framework UI elements as well as custom views. Candidates should have a working knowledge of using view styles and theme attributes to apply a consistent look and feel across an entire application. Understanding of how to include features that expand the application's audience through accessibility and localization may also be required.
-
[Fragmented Podcast] Episode 071: UI UX development with GDE Raveesh
-
Mock up the main screens and navigation flow of the application
-
Describe interactions between UI, background task, and data persistence
-
Construct a layout using XML or Java code
-
Create a custom view class and add it to a layout
-
Implement a custom application theme
-
Apply a custom style to a group of common widgets
-
Define a RecyclerView item list
-
Bind local data to a RecyclerView list
-
Implement menu-based or drawer navigation
- [Android Developers Page] Creating a Navigation Drawer
- [Android Developers Blog] Android Design Support Library Navigation View
- [Team Treehouse Blog] How to Add a Navigation Drawer in Android
- [Antonio Leiva Blog] Design Support Library (I): Navigation View
- [Android Development Patterns] Episode 8 Navigation Drawer, DrawerLayout, and NavigationView
- [Udacity Course] Advanced Android App Development Lesson: Fragments
- [Android Developer Page] Fragments
-
Localize the application's UI text into one other language
-
Apply content descriptions to views for accessibility
-
Add accessibility hooks to a custom view
Understanding of Android's top-level application components (Activity, Service, Broadcast Receiver, Content Provider) and the lifecycle associated with each one. Candidates should be able to describe the types of application logic that would be best suited for each component, and whether that component is executing in the foreground or in the background. This includes strategies for determining how and when to execute background work.
- Describe an application's key functional and nonfunctional requirements
- Create an Activity that displays a layout resource
- Schedule a time-sensitive task using alarms
- Schedule a background task using JobScheduler
- Execute a background task inside of a Service
- Implement non-standard task stack navigation (deep links)
- Integrate code from an external support library
Determining appropriate use cases for local persisted data, and designing solutions to implement data storage using files, preferences, and databases. This includes implementing strategies for bundling static data with applications, caching data from remote sources, and managing user-generated private data. Candidates should also be able to describe platform features that allow applications to store data securely and share that data with other applications in a secure manner.
- Define a database schema; include tables, fields, and indices
- Create an application-private database file
- Construct database queries returning single results
- Construct database queries returning multiple results
- Insert new items into a database
- Update or delete existing items in a database
- Expose a database to other applications via Content Provider
- Read and parse raw resources or asset files
- Create persistent preference data from user input
- Toggle application logic based on preference values
Extending applications to integrate with interfaces outside the core application experience through notifications and app widgets. This includes displaying information to the user through these elements and keeping that information up to date. Candidates should also understand how to provide proper navigation from these external interfaces into the application's main task, including appropriate handling of deep links.
- Create an app widget that displays on the device home screen
- Implement a task to update the app widget periodically
- Create and display a notification to the user
Android architecture components are part of Android Jetpack. They are a collection of libraries that help you design robust, testable, and maintainable apps. Start with classes for managing your UI component lifecycle and handling data persistence.
-
Manage your app's lifecycle with ease. New lifecycle-aware components help you manage your activity and fragment lifecycles. Survive configuration changes, avoid memory leaks and easily load data into your UI.
-
Use LiveData to build data objects that notify views when the underlying database changes
-
ViewModel Stores UI-related data that isn't destroyed on app rotations. Note it doesn't replace savedInstanceState
-
Room is an a SQLite object mapping library. Use it to Avoid boilerplate code and easily convert SQLite table data to Java objects. Room provides compile time checks of SQLite statements and can return RxJava, Flowable and LiveData observables. Android Developers Page
-
Insert with @Insert DAO (Database Access Objects)
-
Update or delete existing items in a database Using DAO (Database Access Objects)
-
Android Architecture Components-Paging Libary
- Introduction to Paging Libary
- Architecture Components - Introduction (Google I/O '17)
- Android Jetpack: manage infinite lists with RecyclerView and Paging (Google I/O '18)
- Android Jetpack: what's new in Architecture Components (Google I/O '18)
- Data Persistence with Room-TeamTreehouse
- Udacity has Updated their Course and also added Architecutre Components Course also
Thanks to Pheonix73 to contributing this section.
My Advice is to Keep Learning and Looking for Materials that will help you become an Awesome Android Developerand take the exam!!!
Copyright 2016 Arturo Mejia
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.