-
forked from wookayin/gpustat (v0.6) (The original repo' s version is higher now, but I have no time to follow up)
-
The code is not quite complex:
gpu_statsin main.py callprint_formatted(sys.stdout, **kwargs)in core.py.
I just modified the two files above. -
My version V.S. original version:
Another GPU trick (not relevant to gpustat, I just put the snippet here)
import os
def find_gpus(num_of_cards_needed=4):
os.system('nvidia-smi -q -d Memory |grep -A4 GPU|grep Free >~/.tmp_free_gpus')
# If there is no ~ in the path, return the path unchanged
with open(os.path.expanduser ('~/.tmp_free_gpus'), 'r') as lines_txt:
frees = lines_txt.readlines()
idx_freeMemory_pair = [ (idx, int(x.split()[2]))
for idx, x in enumerate(frees) ]
idx_freeMemory_pair.sort(reverse=True) # 0号卡经常有人抢,让最后一张卡在下面的sort中优先
idx_freeMemory_pair.sort(key=lambda my_tuple: my_tuple[1], reverse=True)
usingGPUs = [str(idx_memory_pair[0]) for idx_memory_pair in
idx_freeMemory_pair[:num_of_cards_needed] ]
usingGPUs = ','.join(usingGPUs)
print('using GPUs:',end=' ')
for pair in idx_freeMemory_pair[:num_of_cards_needed]:
print(f'{pair[0]}号,此前空闲:{pair[1]/1024:.1f}GB')
return usingGPUs
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = find_gpus(num_of_cards_needed=1) # must before `import torch`\
\
\
Just less than nvidia-smi?
NOTE: This works with NVIDIA Graphics Devices only, no AMD support as of now. Contributions are welcome!
Self-Promotion: A web interface of gpustat is available (in alpha)! Check out gpustat-web.
$ gpustat
Options:
--color: Force colored output (even when stdout is not a tty)--no-color: Suppress colored output-u,--show-user: Display username of the process owner-c,--show-cmd: Display the process name-f,--show-full-cmd: Display full command and cpu stats of running process-p,--show-pid: Display PID of the process-F,--show-fan: Display GPU fan speed-e,--show-codec: Display encoder and/or decoder utilization-P,--show-power: Display GPU power usage and/or limit (drawordraw,limit)-a,--show-all: Display all gpu properties above--watch,-i,--interval: Run in watch mode (equivalent towatch gpustat) if given. Denotes interval between updates. (#41)--json: JSON Output (Experimental, #10)
- To periodically watch, try
gpustat --watchorgpustat -i(#41).- For older versions, one may use
watch --color -n1.0 gpustat --color.
- For older versions, one may use
- Running
nvidia-smi daemon(root privilege required) will make the query much faster and use less CPU (#54). - The GPU ID (index) shown by
gpustat(andnvidia-smi) is PCI BUS ID, while CUDA differently assigns the fastest GPU with the lowest ID by default. Therefore, in order to make CUDA andgpustatuse same GPU index, configure theCUDA_DEVICE_ORDERenvironment variable toPCI_BUS_ID(before settingCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICESfor your CUDA program):export CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER=PCI_BUS_ID.
Install from PyPI:
pip install gpustat
If you don't have root privilege, please try to install on user namespace: pip install --user gpustat.
To install the latest version (master branch) via pip:
pip install git+https://github.com/wookayin/gpustat.git@master
Note that starting from v1.0, gpustat will support only Python 3.4+. For older versions (python 2.7, <3.4), you can continue using gpustat v0.x.
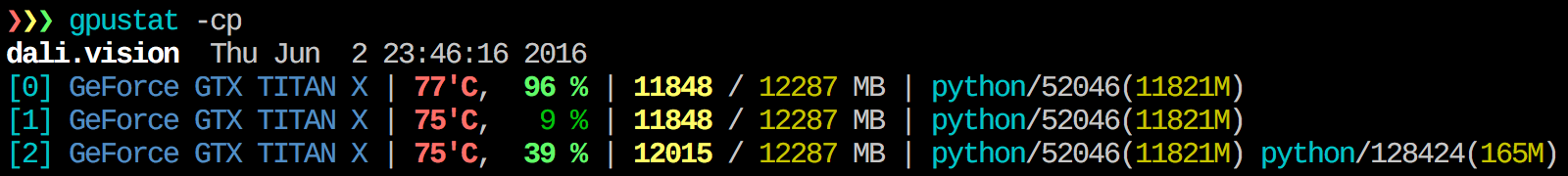
[0] GeForce GTX Titan X | 77'C, 96 % | 11848 / 12287 MB | python/52046(11821M)
[0]: GPUindex (starts from 0) as PCI_BUS_IDGeForce GTX Titan X: GPU name77'C: Temperature96 %: Utilization11848 / 12287 MB: GPU Memory Usagepython/...: Running processes on GPU (and their memory usage)
See CHANGELOG.md