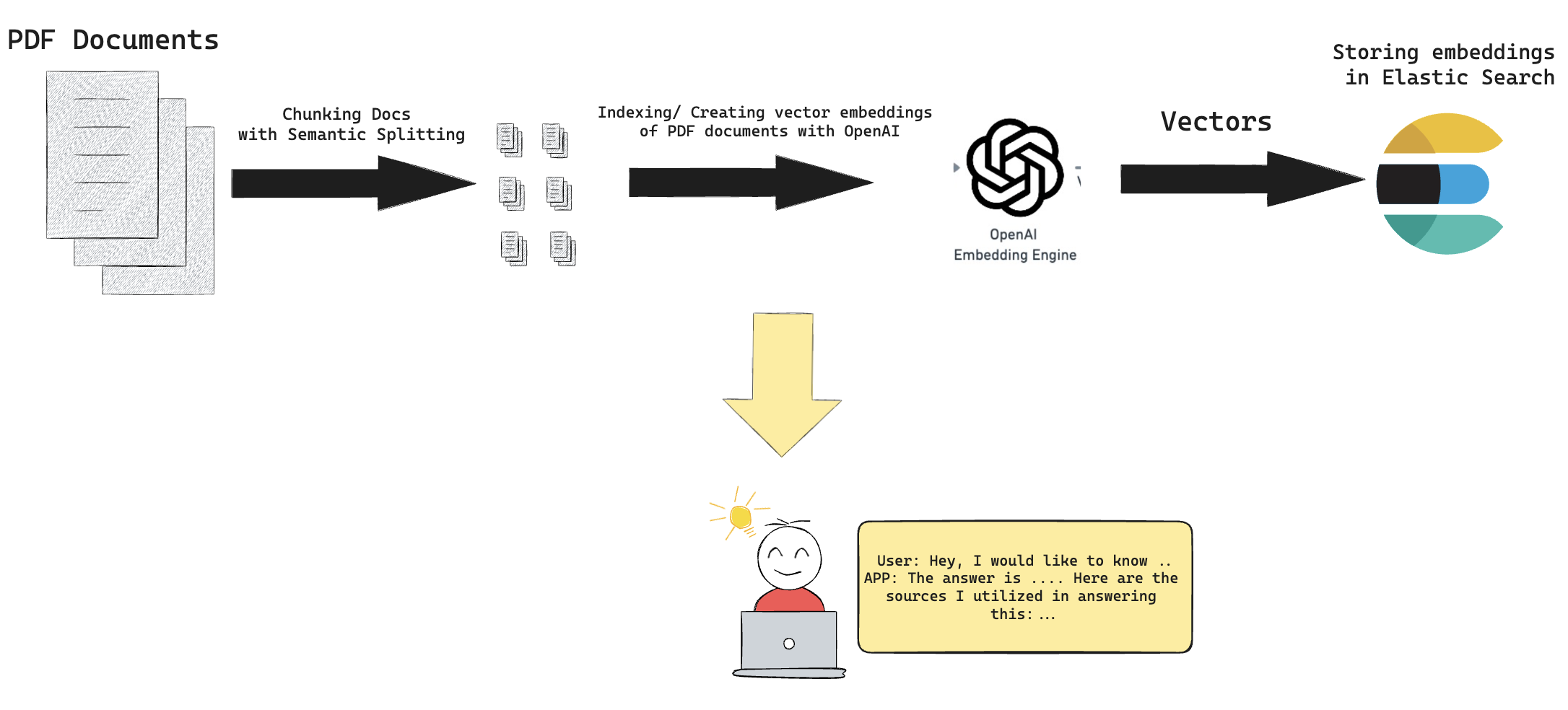
Given a pdf folder consisting of various pdf files, this app deploys elastich search along with LLamaindex and can be used as Question Answering to your documents. Together with FastAPI, one can give query and get response and sources as output. Also can be used by companies as their QA app for their long policy documents to automate customer queiries regarding parental leave and so forth. I would like to hear your comments and feedbacks!
For custom use, you can add your own documents to /pdfs folder. Currently there are two articles added by default
This section details the steps required to set up and run the service locally for development, testing, and deployment using Docker. Follow these instructions to get your environment ready.
To run the application using Docker, follow these steps and make sure you are in the project directory:
-
Set Your OPENAI_API_KEY:
- You have to set your OPENAI_API_KEY before running Docker as an environment variable. You can do this by running the following command in the terminal on macOS and Linux (You can use "set" instead of "export" on Windows):
export OPENAI_API_KEY='your-api-key'
- You have to set your OPENAI_API_KEY before running Docker as an environment variable. You can do this by running the following command in the terminal on macOS and Linux (You can use "set" instead of "export" on Windows):
-
Build the Docker Application:
- Use Docker Compose to build the application. This will read the
docker-compose.ymlfile and set up the necessary Docker containers:docker-compose build
- Use Docker Compose to build the application. This will read the
-
Start the Application:
- Once the build is complete, start the application by running:
docker-compose up - This command starts all the services defined in your Docker Compose configuration. The application will be running on
http://localhost:8000and you can send queries to the API to try onhttp://localhost:8000/docs#/default/perform_query_query__post.
- Once the build is complete, start the application by running:
-
Create a Virtual Environment:
- It's recommended to use a virtual environment to isolate package dependencies. To create a virtual environment, run:
python3 -m venv venv - Activate the virtual environment:
- On Windows:
.\venv\Scripts\activate - On macOS and Linux:
source venv/bin/activate
- On Windows:
- It's recommended to use a virtual environment to isolate package dependencies. To create a virtual environment, run:
-
Install Required Packages:
- Install all the necessary packages using pip. This includes libraries specified in your
requirements.txt:pip install -r requirements.txt
- Install all the necessary packages using pip. This includes libraries specified in your
-
Install Test Dependencies:
- Ensure that your testing environment is also ready by installing the required packages for testing:
pip install pytest
- Ensure that your testing environment is also ready by installing the required packages for testing:
To execute tests, first ensure that the Docker containers are up and running. Also make sure you properly followed the steps "Local Development Setup" above to create venv and install requirement files. You can perform the following:
-
Start Docker Containers:
- If not already running, start your Docker containers:
docker-compose up
- If not already running, start your Docker containers:
-
Run Tests:
- Execute the tests using
pytestby running the following command in the terminal while you are in the project directory and the Docker containers are running:pytest
- Execute the tests using
These steps will help you set up the development environment, run the application, and execute tests efficiently. Adjust the commands according to your specific configurations if necessary.
This section provides an overview of the main directories and files in this repository, explaining how they contribute to the project.
- app.py: The entry point of the program. Contains the main functionalities executed when the project is run via FAST api.
- IndexManager.py: Contains the IndexManager class with attributes and methods handling index loading, index initialization, creation, query engine creation and formatting output
- ingest.py: Implements the data ingestion part from pdfs into llamaindex nodes
- index.py: Takes the generated nodes and setup a Elasticsearch vector store and assemble a query engine of llamaindex.
- querying.py: Takes a query and generates a response.
- evaluate.py: Generates synthetic data out of document nodes for model evaluation via RelevancyEvaluator.
- e2e_test.py: contains methods for end-to-end test cases covering different possible scenarious while taking user queries etc.
- config.py: contains the configuration variables for the model.
- Description: Includes a single pdf file that explains the experiments and the final solution method.
- Description: Includes data files (which are shared pdf files) used in the project.
- Description: Includes py notebooks that come with 2-3 different solutions for the QA task. The file semanticChunker.ipynb is the final solution method. The details were explained in experiments.pdf
- Description: Contains index checker and loader files that implement the main pipeline with hardcoded variables.
- Description: It only includes raw results of RelevancyEvaluator of the final method/solution (semanticChunker)
- Description: Provides an overview of the project, installation instructions, and usage examples.
- Description: Specifies intentionally untracked files to ignore.