An intelligent web browsing agent controlled by natural language.
Language is the most natural interface through which humans give and receive instructions. Instead of writing bespoke automation or scraping code which is brittle to changes, creating and adding agents should be as simple as writing plain English.
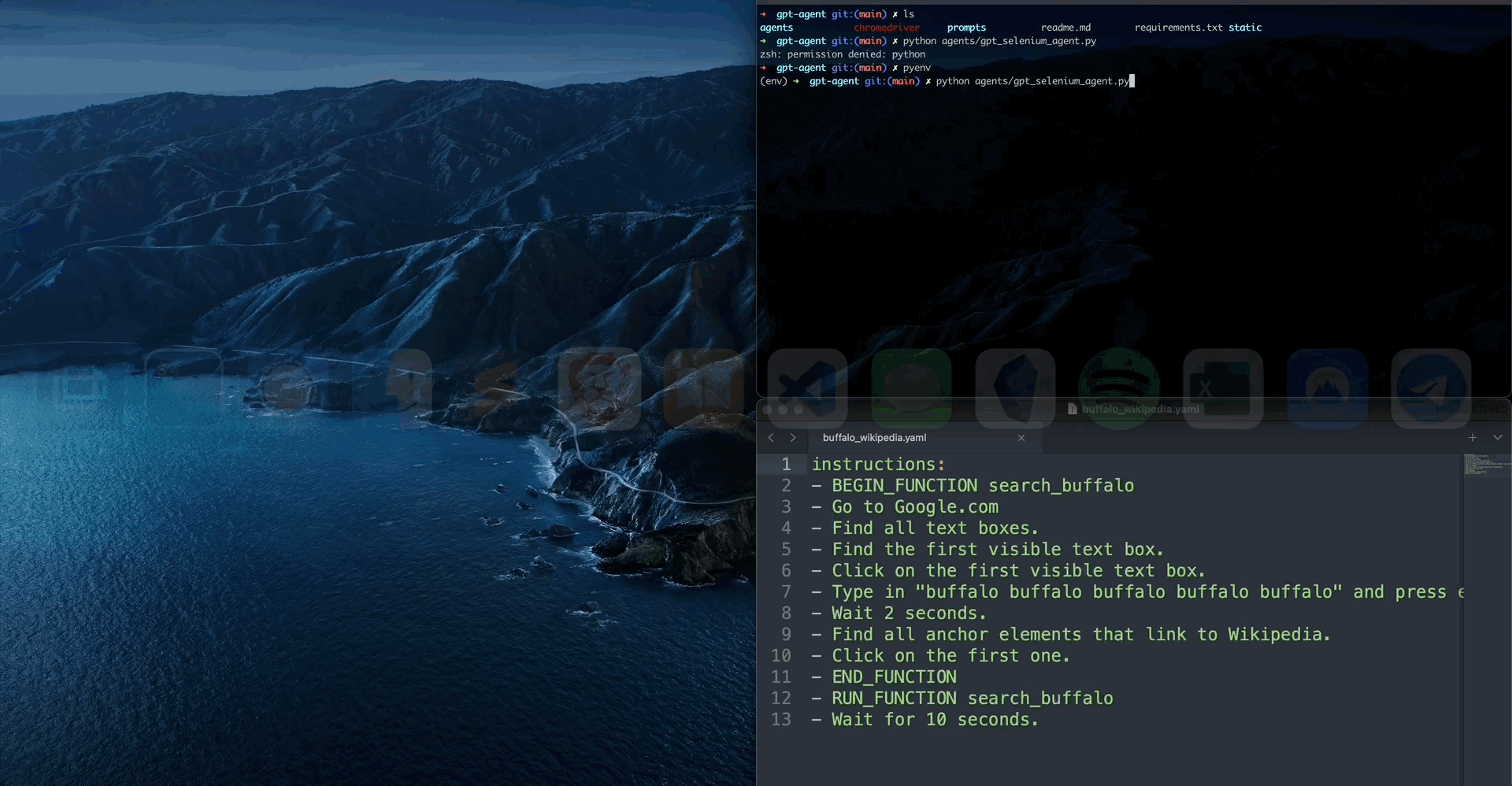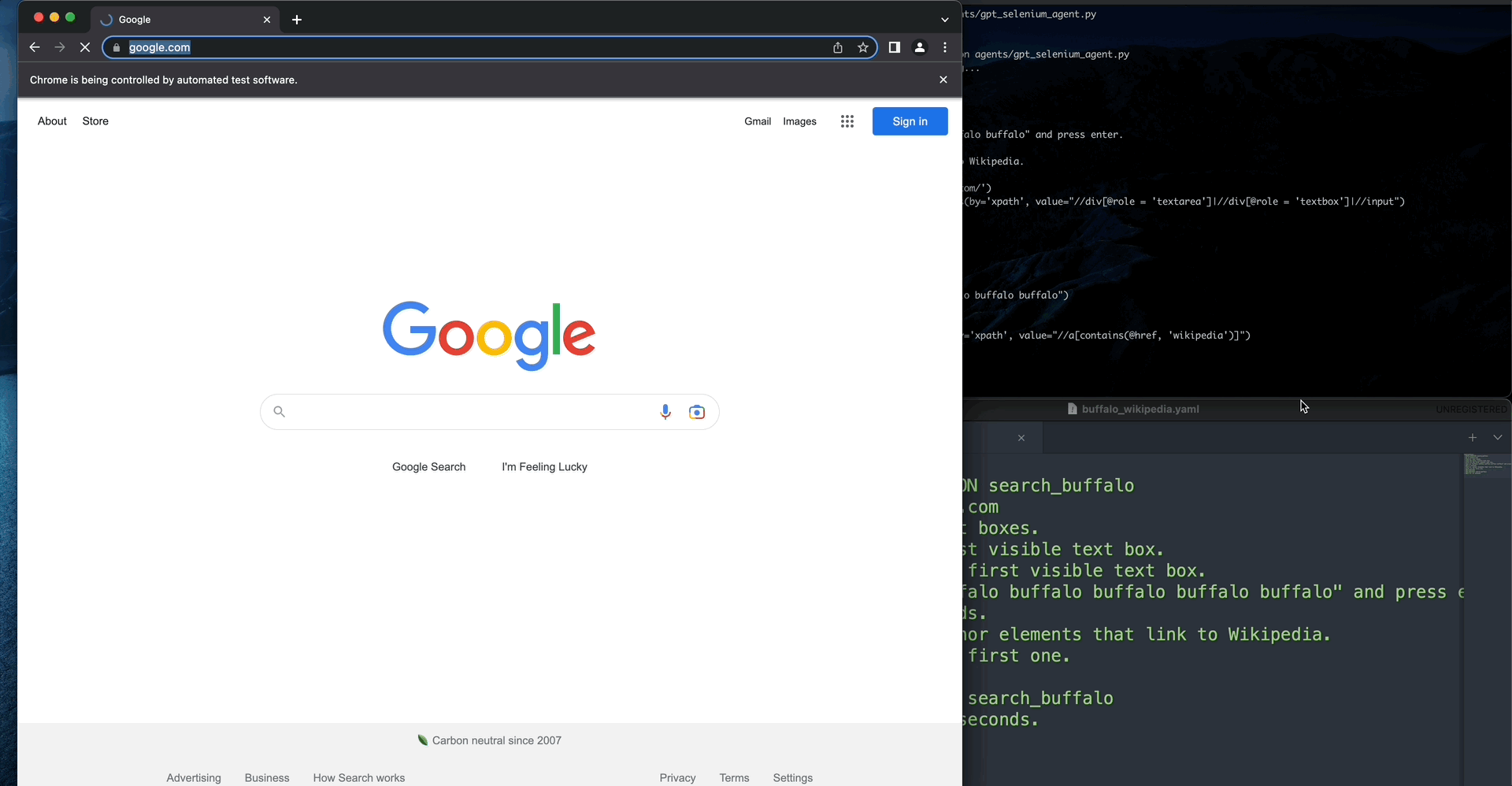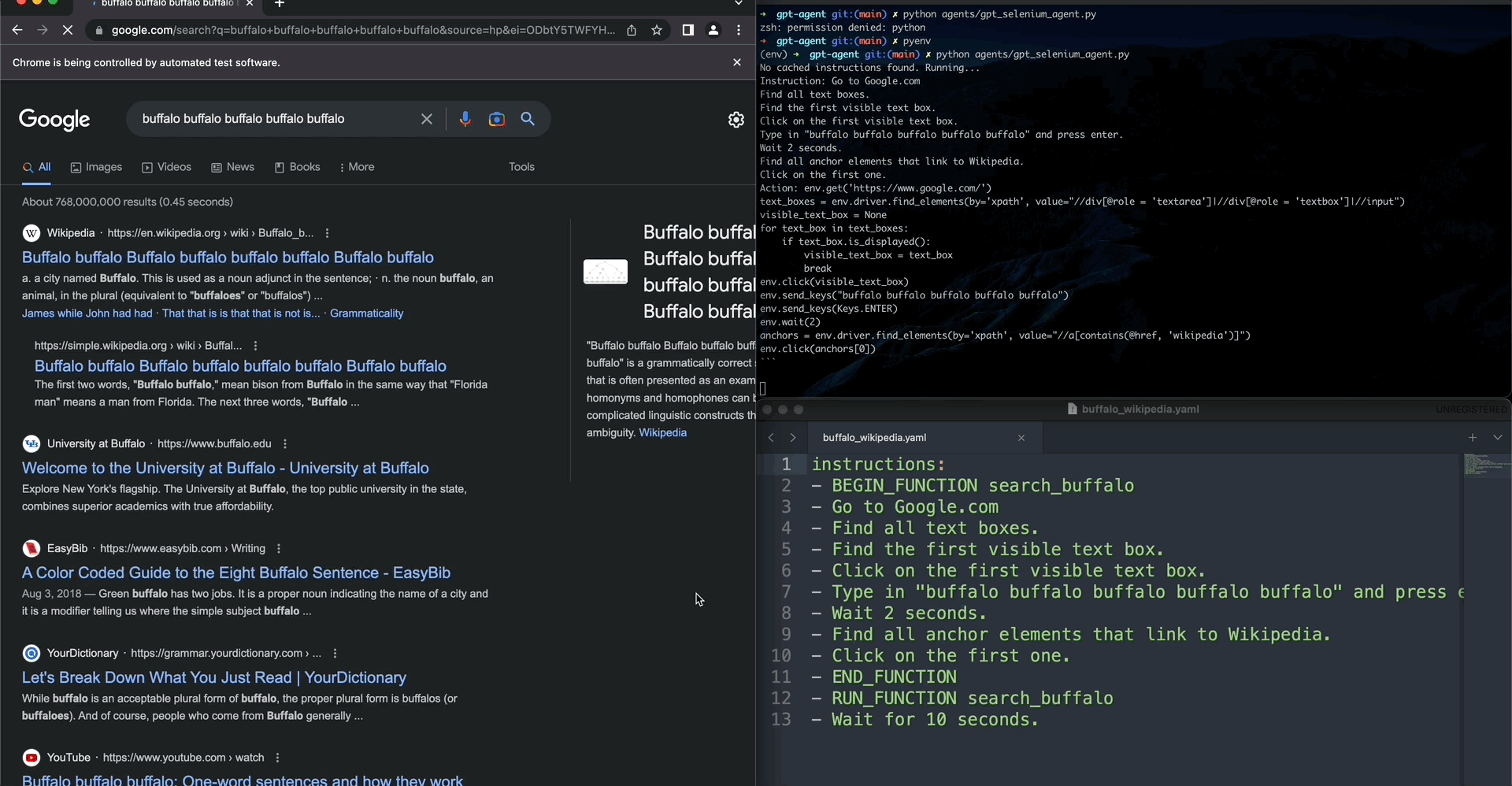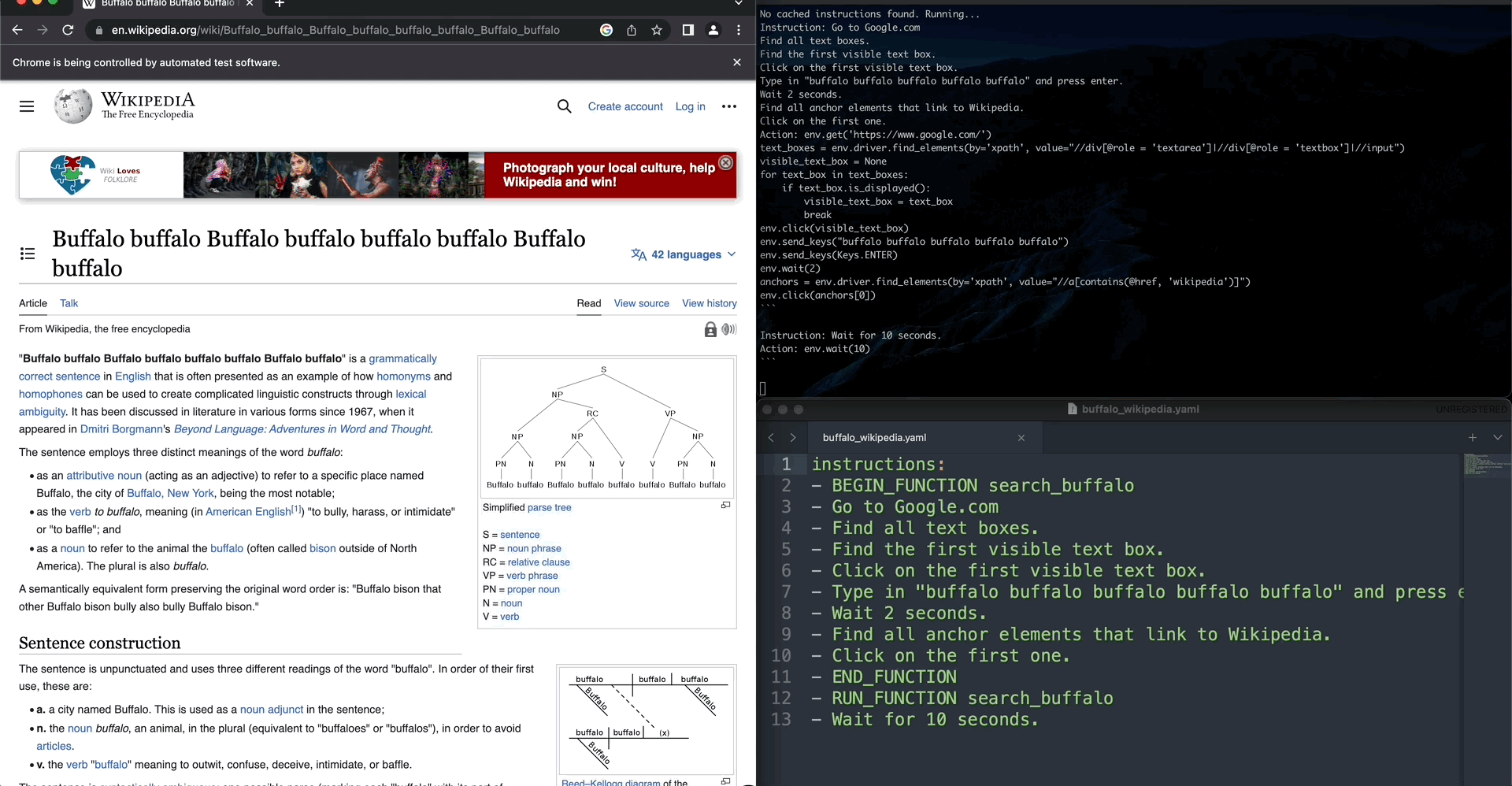
pip install browserpilot- Download Chromedriver (latest stable release) from here and place it in the same folder as this file. Unzip. In Finder, right click the unpacked chromedriver and click "Open". This will remove the restrictive default permissions and allow Python to access it.
- Create an environment variable in your favorite manner setting OPENAI_API_KEY to your API key.
The form factor is fairly simple (see below).
from browserpilot.agents.gpt_selenium_agent import GPTSeleniumAgent
instructions = """Go to Google.com
Find all textareas.
Find the first visible textarea.
Click on the first visible textarea.
Type in "buffalo buffalo buffalo buffalo buffalo" and press enter.
Wait 2 seconds.
Find all anchor elements that link to Wikipedia.
Click on the first one.
Wait for 10 seconds."""
agent = GPTSeleniumAgent(instructions, "/path/to/chromedriver")
agent.run()The harder (but funner) part is writing the natural language prompts.
It helps if you are familiar with how Selenium works and programming in general. This is because this project uses GPT-3 to translate natural language into code, so you should be as precise as you can. In this way, it is more like writing code with Copilot than it is talking to a friend; for instance, it helps to refer to things as inputs or textareas (vs. "text box" "search box") or "button which says 'Log in'" rather than "the login button". Sometimes, it will also not pick up on specific words that are important, so it helps to break them out into separate lines. Instead of "find all the visible textareas", you do "find all the textareas" and then "find the first visible textarea".
You can look at some examples in prompts/examples to get started.
Create "functions" by enclosing instructions in BEGIN_FUNCTION func_name and END_FUNCTION, and then call them by starting a line with RUN_FUNCTION or INJECT_FUNCTION. Below is an example:
BEGIN_FUNCTION search_buffalo
Go to Google.com
Find all textareas.
Find the first visible textarea.
Click on the first visible textarea.
Type in "buffalo buffalo buffalo buffalo buffalo" and press enter.
Wait 2 seconds.
Get all anchors on the page that contain the word "buffalo".
Click on the first link.
END_FUNCTION
RUN_FUNCTION search_buffalo
Wait for 10 seconds.
You may also choose to create a yaml or json file with a list of instructions. In general, it needs to have an instructions field, and optionally a compiled field which has the processed code.
See buffalo wikipedia example.
You may pass a instruction_output_file to the constructor of GPTSeleniumAgent which will output a yaml file with the compiled instructions from GPT-3, to avoid having to pay API costs.
There are two ways I envision folks contributing.
- Adding to the Prompt Library: Read "Writing Prompts" above and simply make a pull request to add something to
prompts/! At some point, I will figure out a protocol for folder naming conventions and the evaluation of submitted code (for security, accuracy, etc). This would be a particularly attractive option for those who aren't as familiar with coding. - Contributing code: I am happy to take suggestions! The main way to add to the repository is to extend the capabilities of the agent, or to create new agents entirely. The best way to do this is to familiarize yourself with "Architecture and Prompt Patterns" above, and to (a) expand the list of capabilities in the base prompt in
InstructionCompilerand (b) write the corresponding method inGPTSeleniumAgent.
This repo was inspired by the work of Yihui He, Adept.ai, and Nat Friedman. In particular, the basic abstractions and prompts used were built off of Yihui's hackathon code. The idea to preprocess HTML and use GPT-3 to intelligently pick elements out is from Nat.
- The prompts used can be found in instruction compiler. The base prompt describes in plain English a set of actions that the browsing agent can take, some general conventions on how to write code, and some constraints on its behavior. These actions correspond one-for-one with methods in
GPTSeleniumAgent. Those actions, to-date, include:env.driver, the Selenium webdriver.env.find_elements(by='id', value=None)finds and returns list of elements.env.find_element(by='id', value=None)is similar toenv.find_elements()except it only returns the first element.env.find_nearest(e, xpath)can be used to locate an element near another one.env.send_keys(element, text)sendstextto element.env.get(url)goes to url.env.click(element)clicks the element.env.wait(seconds)waits forsecondsseconds.env.scroll(direction, iframe=None)scrolls the page. Will switch toiframeif given.directioncan be "up", "down", "left", or "right".env.get_llm_response(text)asks AI about a stringtext.env.retrieve_information(prompt)returns a string, information from a page given a prompt. Use prompt="Summarize:" for summaries. Invoked with commands like "retrieve", "find in the page", or similar.env.ask_llm_to_find_element(description)asks AI to find an element that matches the description.env.query_memory(prompt)asks AI with a prompt to query its memory (an embeddings index) of the web pages it has browsed. Invoked with "Query memory".env.save(text, filename)saves the stringtextto a filefilename.env.get_text_from_page()returns the free text from the page.
- The rest of the code is basically middleware which exposes a Selenium object to GPT-3. For each action mentioned in the base prompt, there is a corresponding method in GPTSeleniumAgent.
- An
InstructionCompileris used to parse user input into semantically cogent blocks of actions.
- An
- The agent has a
Memorywhich enables it to synthesize what it sees.
0.2.51
- Thanks to @rapatel0, you can now run BrowserPilot with Selenium Grid, remotely.
-0.2.42 - 0.2.44
- Small changes in
examples.pyand dependencies. - Refactor for the big Llama Index upgrade.
0.2.38 - 0.2.41
- Change
enable_memorytomemory_fileto enable more control over what the memory is called. Allow users to load memory as well. - Make
get_text_from_pagesimpler.
0.2.26 - 0.2.37
- Bit the bullet and switched the default model to gpt-3.5-turbo. Will be much cheaper!
- Also fixed retries. I wasn't actually getting the retry action!
- Fiddle with the prompt a bit for GPT-3.5.
- Concerningly, gpt-3.5-turbo keep trying to import modules. I manually remove lines that try to import modules.
- Compatibility with new Llama Index updates.
0.2.14 - 0.2.25
- Add options to avoid website detection of bots.
- Add more OpenAI API error handling.
- Improve stack trace prompt and a few other prompts.
- Add "displayed in viewport" capability.
- Make
from browserpilot.agents import <agent>possible. - Make
find_elementandfind_elementssearch only for displayed elements. - Save memory once finished running.
- Add scroll option to top and bottom.
0.2.10 - 0.2.13
- Add more error handling for OpenAI exceptions.
- Change all the embedding querying to use ChatGPT.
- Get rid of the nltk dependency! Good riddance.
- Expand the max token window for asking the LLM a question on a web page.
- Fix an issue with the Memory module which tried to access OpenAI API key before it's initialized. Change the prompt slightly.
- ❗️ Enable ChatGPT use with GPT Index, so that we can use GPT3.5-turbo to query embeddings.
0.2.7 - 0.2.9
- Vacillating on the default model. ChatGPT does not work well for writing code, as it takes too many freedoms with what it returns.
- Also, I tried condensing the prompt a bit, which is growing a bit long.
0.2.4 - 0.2.6
- Give the agent a memory (still very experimental and not very good). Add capability to screenshot elements.
- Bug fixes around versioning and prompt injection.
0.2.3
- Move
chrome_optionsto somewhere more sensible. Just keep the yaml clean, you know?
0.2.2
- ChatGPT support.
0.2.1
- Dict support for loading instructions.
0.2.0
- 🎬 a
StudioCLI which helps iteratively test prompts! - JSON loading.
- Basic iframe support.
<0.2.0
- GPTSeleniumAgent should be able to load prompts and cached successful runs in the form of yaml files. InstructionCompiler should be able to save instructions to yaml.
- 💭 Add a summarization capability to the agent.
- Demo/test something where it has to ask the LLM to synthesize something it reads online.
- 🚨 Figured out how to feed the content of the HTML page into the GPT-3 context window and have it reliably pick out specific elements from it, that would be great!
This package runs code output from the OpenAI API in Python using exec. This is not considered a safe convention. Accordingly, you should be extra careful when using this package. The standard disclaimer follows.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.