# 创建虚拟环境
conda create -n MLpro python=3.8
# 启动虚拟环境
conda actiavte MLpro
# 安装 aeon 和必要的库
conda install scikit-learn
conda install scikit-learn-intelex
conda install numpy
pip install aeon拉取代码
# 进入工作目录(没有需自己创建), 进入虚拟环境
cd workspace/ML/
conda activate MLpro
# 按照 readme 的意思.先拉取源码或fork我的这个分支
git clone https://github.com/baraline/convst.git
# 或者
git clone https://github.com/hawk2333/convst.git
cd convst
# pip 安装一下依赖包.(这个包的版本应该不是最新的,但是也是依赖项)
pip install convst
pip install toml
# 安装源码的软件包
python setup.py install
# 如果有 N卡的话,再执行这个命令
conda install -c numba irr_rt
#如果找不到irr——rt, 运行
conda install numba搭建好环境之后,用一个小型数据集 Gunpoint 来测试一下 RDST_Ridge 模型的性能
from convst.classifiers import R_DST_Ridge
from convst.utils.dataset_utils import load_UCR_UEA_dataset_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, _ = load_UCR_UEA_dataset_split('GunPoint')
# First run may be slow due to numba compilations on the first call.
# Run a small dataset like GunPoint if this is the first time you call RDST on your system.
# You can change n_shapelets to 1 to make this process faster. The n_jobs parameter can
# also be changed to increase speed once numba compilation are done.
rdst = R_DST_Ridge(n_shapelets=10_000, n_jobs=1).fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Accuracy Score for RDST : {}".format(rdst.score(X_test, y_test)))本fork内的源码已经调通,按照步骤一步步即可浮现论文结果,该分支里也有我们已经跑出的结果。
直接跑通代码:
cd ./PaperScripts
# 跑基准测试
python benchmark_new.py
# 更建议运行benchmark.ipynb文件,更直观
# 测试模型在UCR数据集上的性能
python test_models.py如果test_models.py运行时间过长,可以选择只测试单个或部分数据集
方法:在文件test_models.py里,把
dataset_names = return_all_univariate_dataset_names()改为
dataset_names = np.asarray(["ACSF1", ])
# "ACSF1"为UCR中第一个数据集名称对于基准测试, 我们已经跑完的结果路径是:convst/PaperScripts/benchmark.csv 和 convst/PaperScripts/n_samples_benchmarks.csv
。这两个结果中为了在本地(16Gb内存)跑通,只测试了RDST的四种模型
对于UCR数据集上的测试,已经跑出的结果是:convst/PaperScripts/New_CV_30_results_default.csv。
我们在一台8核48G内存的服务器上跑了近58小时,跑完了大约1/3.因为没钱组服务器了所以没继续跑。
详细情况看后面提交的探索研究报告和学习笔记以及ppt。谢谢老师!
Starting from v0.3.0, this package will not be updated, bugfixes will still be included if issues are raised. You can already find RDST in the Aeon package at https://github.com/aeon-toolkit/ . Further improvements are planned for further speeding up RDST, these improvement will only be implemented in aeon.
ALL FUNCTIONALITIES OF THIS PACKAGE OUTSIDE OF THE INTEPRETER ARE NOW PORTED INTO AEON FROM V0.6.0, PLEASE REFER TO THE AEON IMPLEMENTATION WHEN DOING EXPERIMENTS.
AN EXAMPLE NOTEBOOK ON HOW TO CORRECTLY INTERPRET SHAPELETS FROM RDST IS PLANNED (see aeon-toolkit/aeon#973)
If these functionnalities are what you need, I highly recommend that you use aeon as I spent more time on the aeon implementation and tests compared to convst.
Welcome to the convst repository. It contains the implementation of the Random Dilated Shapelet Transform (RDST) along with other works in the same area.
This work was supported by the following organisations:
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Compatibility |  |
| CI/CD |   |
| Code Quality |  |
| Downloads |
The recommended way to install the latest stable version is to use pip with pip install convst. To install the package from sources, you can download the latest version on GitHub and run python setup.py install. This should install the package and automatically look for the dependencies using pip.
We recommend doing this in a new virtual environment using anaconda to avoid any conflict with an existing installation. If you wish to install dependencies individually, you can see dependencies in the setup.py file.
An optional dependency that can help speed up numba, which is used in our implementation, is the Intel vector math library (SVML). When using conda it can be installed by running conda install -c numba icc_rt. I didn't test the behavior with AMD processors, but I suspect it won't work.
We give here a minimal example to run the RDST algorithm on any dataset of the UCR archive using the aeon API to get datasets:
from convst.classifiers import R_DST_Ridge
from convst.utils.dataset_utils import load_UCR_UEA_dataset_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, _ = load_UCR_UEA_dataset_split('GunPoint')
# First run may be slow due to numba compilations on the first call.
# Run a small dataset like GunPoint if this is the first time you call RDST on your system.
# You can change n_shapelets to 1 to make this process faster. The n_jobs parameter can
# also be changed to increase speed once numba compilation are done.
rdst = R_DST_Ridge(n_shapelets=10_000, n_jobs=1).fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Accuracy Score for RDST : {}".format(rdst.score(X_test, y_test)))If you want a more powerful model, you can use R_DST_Ensemble as follows (note that additional Numba compilation might be needed here):
from convst.classifiers import R_DST_Ensemble
rdst_e = R_DST_Ensemble(
n_shapelets_per_estimator=10_000,
n_jobs=1
).fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Accuracy Score for RDST : {}".format(rdst_e.score(X_test, y_test)))You can obtain faster result by using more jobs and even faster, at the expense of some accuracy, with the prime_dilation option:
rdst_e = R_DST_Ensemble(
n_shapelets_per_estimator=10_000,
prime_dilations=True,
n_jobs=-1
).fit(X_train, y_train)
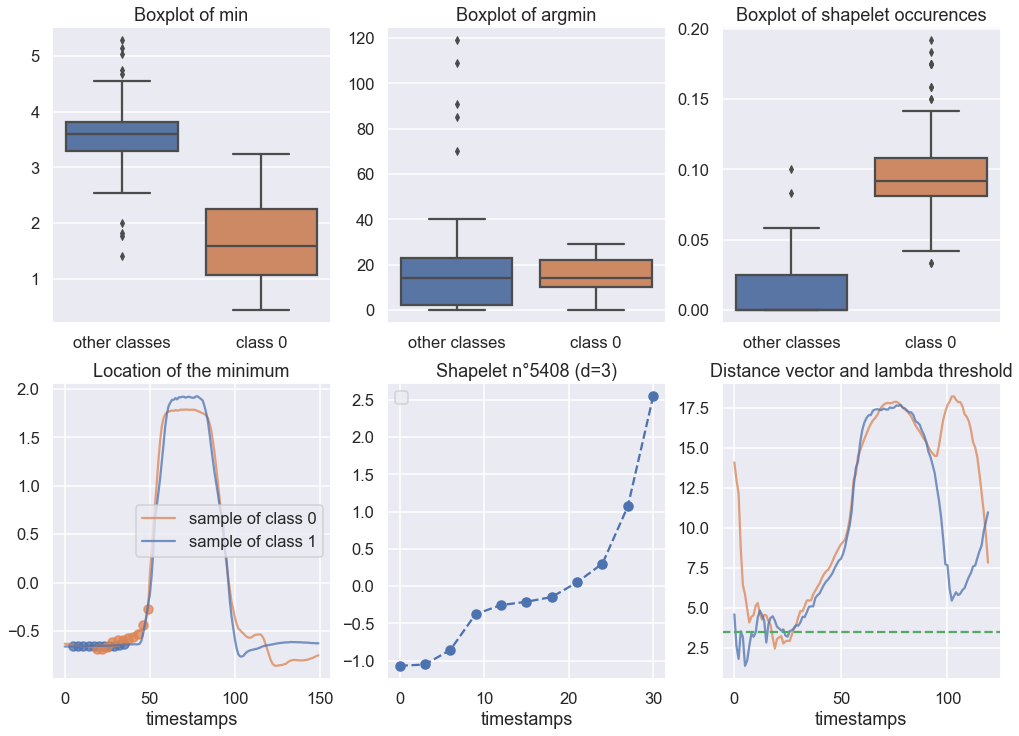
print("Accuracy Score for RDST : {}".format(rdst_e.score(X_test, y_test)))You can also visualize a shapelet using the visualization tool to obtain such visualization :
To know more about all the interpretability tools, check the documentation on readthedocs.
RDST support the following type of time series:
- Univariate and same length
- Univariate and variable length
- Multivariate and same length
- Multivariate and variable length
We use the standard scikit-learn interface and expect as input a 3D numpy array of shape (n_samples, n_features, n_timestamps). For variable length input, we expect a (python) list of numpy arrays, or a numpy array with object dtype.
Multiple scripts are available under the PaperScripts folder. It contains the exact same scripts used to generate our results, notably the test_models.py file, used to generate the csv results available in the Results folder of the archive.
If you are experiencing bugs in the RDST implementation, or would like to contribute in any way, please create an issue or pull request in this repository. For other question or to take contact with me, you can email me at antoine.guillaume45@gmail.com
If you use our algorithm or publication in any work, please cite the following paper (ArXiv version https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.13514):
@InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-031-09037-0_53,
author="Guillaume, Antoine
and Vrain, Christel
and Elloumi, Wael",
title="Random Dilated Shapelet Transform: A New Approach for Time Series Shapelets",
booktitle="Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence",
year="2022",
publisher="Springer International Publishing",
address="Cham",
pages="653--664",
abstract="Shapelet-based algorithms are widely used for time series classification because of their ease of interpretation, but they are currently outperformed by recent state-of-the-art approaches. We present a new formulation of time series shapelets including the notion of dilation, and we introduce a new shapelet feature to enhance their discriminative power for classification. Experiments performed on 112 datasets show that our method improves on the state-of-the-art shapelet algorithm, and achieves comparable accuracy to recent state-of-the-art approaches, without sacrificing neither scalability, nor interpretability.",
isbn="978-3-031-09037-0"
}To cite the RDST Ensemble method, you can cite the PhD thesis where it is presented as (soon to be available, citation format may change):
@phdthesis{Guillaume2023,
author="Guillaume, Antoine",
title="Time series classification with Shapelets: Application to predictive maintenance on event logs",
school="University of Orléans",
year="2023",
url="https://www.theses.fr/s265104"
}- Finish Numpy docs in all python files
- Update documentation and examples
- Enhance interface for interpretability tools
- Add the Generalised version of RDST
- Continue unit tests and code coverage/quality
Here are the code-related citations that were not made in the paper
[2]: The Numpy development team, "Array programming with NumPy", Nature 2020


.png)