This is the official code repository for the paper, "Feature Interaction Interpretability: A Case for Explaining Ad-Recommendation Systems via Neural Interaction Detection".
Example Explanations
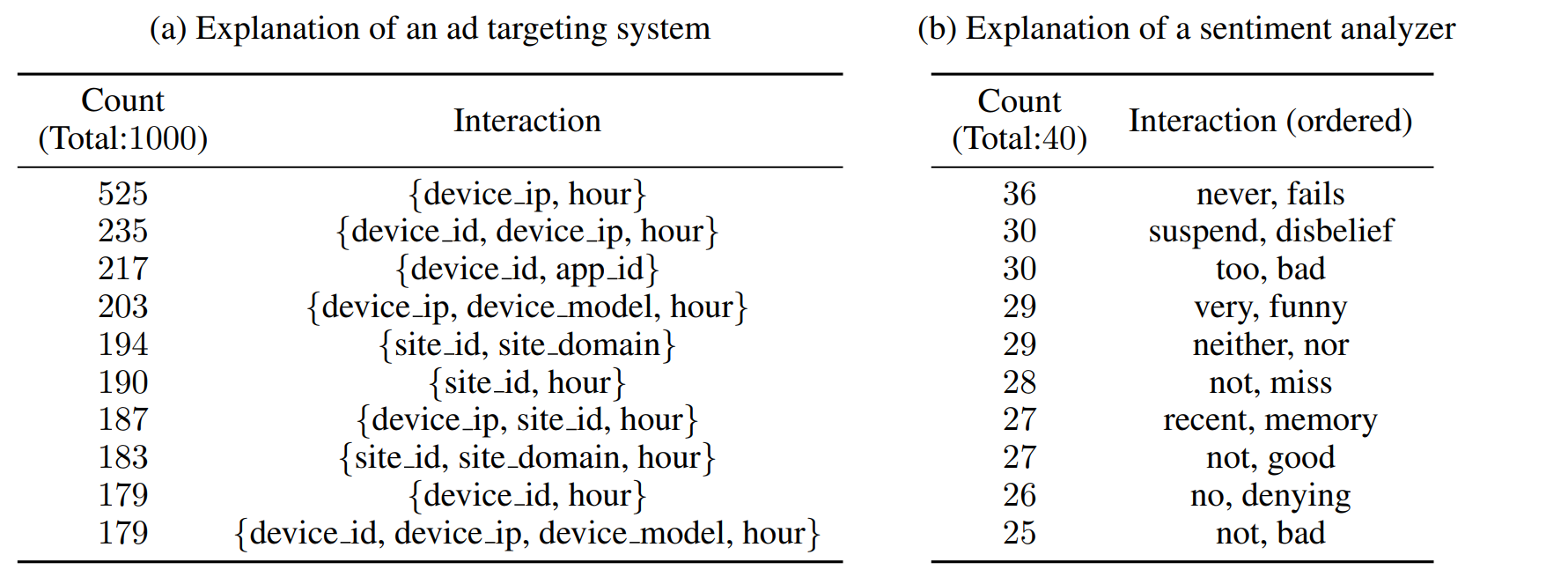
- Global Interpretations
- Local Interpretations (of ResNet classifications)
Michael Tsang, Dehua Cheng, Hanpeng Liu, Xue Feng, Eric Zhou, Yan Liu, Feature Interaction Interpretability: A Case for Explaining Ad-Recommendation Systems via Neural Interaction Detection, ICLR 2020.
Neural Interaction Detection:
Michael Tsang, Dehua Cheng, Yan Liu, Detecting Statistical Interactions from Neural Network Weights, ICLR 2018.
In a linux environment with Python 3.6:
pip install -r requirements.txtWe require CUDA 10 support to use GLIDER.
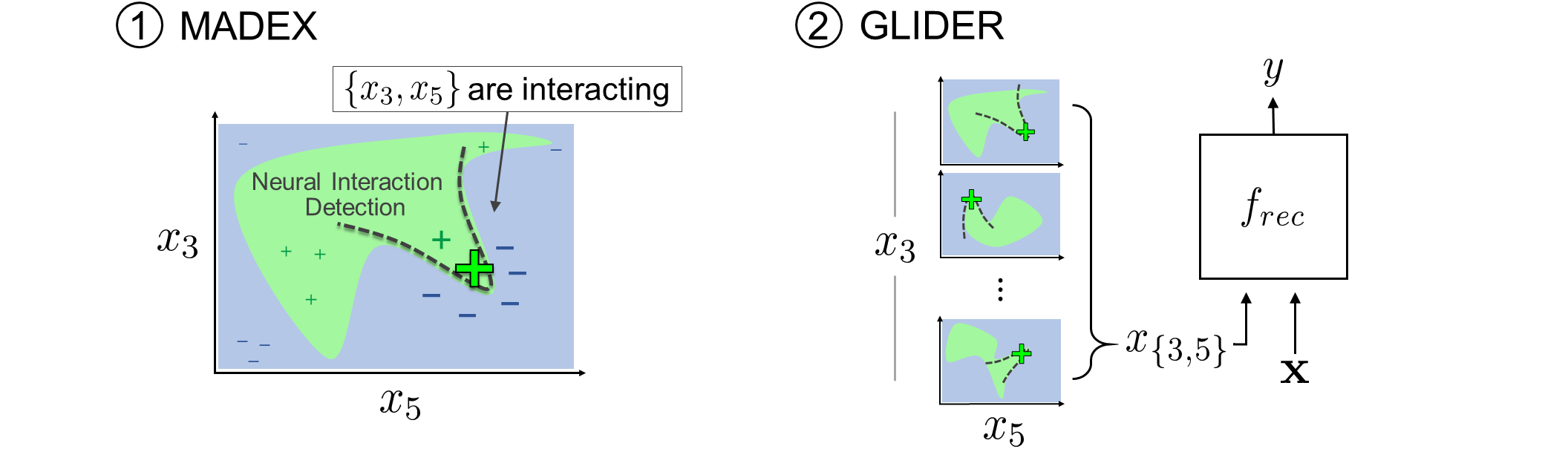
MADEX (Model-Agnostic Dependency EXplainer) is a method for interpreting feature interactions from a black-box prediction model per data instance. It contains two versions of Neural Interaction Detection (NID): the original NID and GradientNID. NID is a fast and accurate method to detect arbitrary-order interactions in polynomial time, whereas GradientNID exactly detects interactions from an explainer MLP. The following domains are showcased: DNA, graph, image, and text modeling.
Show instructions
cd 1.\ madex/The following notebooks are available to demo MADEX:
madex_example_dna.ipynbmadex_example_graph.ipynbmadex_example_image.ipynbmadex_example_text.ipynb
GLIDER (GLobal Interaction Detection and Encoding for Recommendation) takes MADEX beyond model interpretation on recommendation tasks (or tablular data modeling). GLIDER detects feature interactions that reoccur across data instances from a source recommender model, then explicitly encodes the interactions in a target recommender model. This process is a form of automatic feature engineering.
Show instructions
cd 2.\ glider/Please follow instructions in the AutoInt repo for how to prepare data splits.
The same code is also provided in this repo and follows the same series of commands. The Criteo dataset is found here. Place it in the path data/autoint/criteo.
mkdir data/autoint/criteo
python data/initial_data_prep/criteo/preprocess.py
python data/initial_data_prep/Kfold_split/stratifiedKfold.py
python data/initial_data_prep/criteo/scale.pyFirst, train a baseline AutoInt model.
python models/autoint/train.py --exp baseline --data data/autoint/criteo --save_path experiments/autoint/criteo/baseline/ --run_times 1 --gpu 0 Then, run global interaction detection on this model.
python detect_global_interactions.py --save_path experiments/autoint/criteo/baseline/1/ --data criteousing defaul arguments instead
par_batch_sizeis the number of data instances to process in parallel. Set this based on the number of CPU processes and GPU memory available.SAVEIDshows up again later. Use a descriptive identifier.
This is where I cannot progress past
To generate cross features:
python make_cross_feature_data.py --data_file experiments/detected_interactions_criteo_SAVEID.pickle --exp cross_K40 --K 40 --data criteo --autoint_save_path data/autoint/criteo --deepctr_save_path data/deepctr/criteo --save_base_data true- Wide&Deep:
WDL - DeepFM:
DeepFM - Deep&Cross:
DCN - xDeepFM:
xDeepFM
Baseline:
python train_deepctr.py --model WDL --ds criteo --exp baseline --patience 5 --test_id baseline_experiment --gpu 0Baseline + GLIDER (distillation):
python train_deepctr.py --model WDL --ds criteo --exp cross --patience 5 --test_id cross_experiment --gpu 0 --d_cross_exp cross_K40 --n_cross 40Baseline + GLIDER (enhancement):
python models/autoint/train.py --exp cross --data data/autoint/criteo --save_path experiments/autoint/criteo/cross/ --gpu 0 --cross_exp cross_K40@inproceedings{tsang2020feature,
title={Feature Interaction Interpretability: A Case for Explaining Ad-Recommendation Systems via Neural Interaction Detection},
author={Michael Tsang and Dehua Cheng and Hanpeng Liu and Xue Feng and Eric Zhou and Yan Liu},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2020},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=BkgnhTEtDS}
}
Neural Interaction Detection:
@article{tsang2017detecting,
title={Detecting Statistical Interactions from Neural Network Weights},
author={Michael Tsang and Dehua Cheng and Yan Liu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.04977},
year={2017}
}