- A curriculum vitae (CV) is a brief description which shows an overview of an individual's Qualificaions, Skills and Work experience (if they do).
- We are creating an application which will be able to receive CVs from job applicants and be able to store data in a database.
-
The first thing we need to be creat is a
Json data structurewhich shows an overview of how the data will be recieved. The Json data structure will be inmycv.py -
The second step will about creating a
model data structureof how the data entered by an applicant will be stored in a database and this will be put in a file calledmodel.py. The data will be stored in tables which have been defined as class instances in the model file.
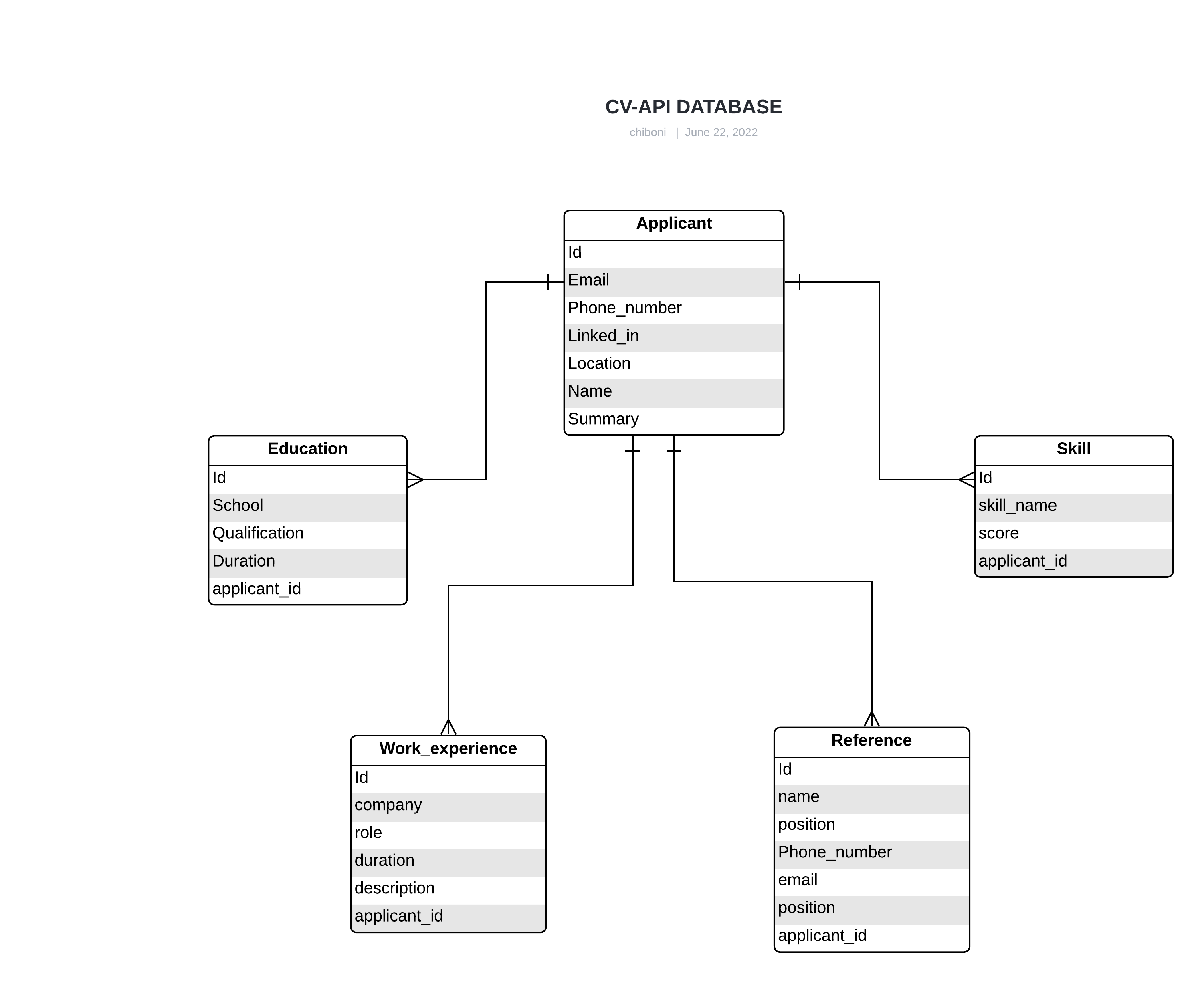
The diagram below outlines the database structure for the CV application.
-
Below is a simple example of a Model class
class Applicant(Base): __tablename__ = "applicant" id = column(string(64)) email = column(string(64)) Phone_number = column(String(64)) linked_in = column(String(64)) location = column(String(64)) name = column(String(64))
- The third step will about posting data in the database and this will be done using the
create.pyfile. In this file there are functions which are used to fill in data in the database.
-
Before adding the data from the model to the database, you frist need to import the classes from the
model.pyfrom sqlalchemy.exc import IntegrityError from model import Applicant, Education, Skill, Work_experience, Reference, dbconnect from sqlalchemy.orm.exc import NoResultFound -
Below is a simple example of the function which add data to the applicant table in a database.
-
You need to create a function with param
aplicant_dictwhich allows us to get the Json data from themycv.py -
The
applicant = Applicant()allows us to hold an empty instance of the applicant class.def addApplicant(applicant_dict): applicant = Applicant()
-
-
Then the following codes are adding the attirbutes to the empty instance
# Add attributes applicant.name = applicant_dict["name"] applicant.email = applicant_dict["email"] applicant.phone_number = applicant_dict["phone_number"] applicant.linked_in = applicant_dict["linked_in"] applicant.location = applicant_dict["location"] applicant.summary = applicant_dict["summary"] return applicant
- The fourth step is creating a file called
read.pywhich helps in retrieving data from the database. Below is an example:
-
Before retrieving the data from the model to the database, you frist need to import the classes from the
model.py, flask, sqlalchemyfrom model import Applicant, dbconnect from flask import Flask, jsonify from sqlalchemy.orm.exc import NoResultFound -
Then a connection to the database will be held in a session variable.
session = dbconnect() -
The function below is used to get data from the applicant table in the database
def get_applicant(session,applicant_dict): applicant = session.query(Applicant).where(Applicant.id == applicant_dict['id']).first() print (applicant)
- The fifth step is creating
Application Programming Interface (API)which will be used to send and retrieve data from the database.
-
Before writing the function which send and retrieves data from the database, it is important to import the classes from the model file
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify from model import Applicant, Education, Skill, Reference, Work_experience, dbconnect from create import addApplicant, addEducation, addReference, addSkill, addWorkExperience import json from readcv import get_applicant -
Below is a simple example of an
APIsaved in anapi.pyfileif request.method == 'POST': applicantInstance = addApplicant(request.json) session.add(applicantInstance) for educationDict in request.json['Education']: educationInstance = addEducation(educationDict) educationInstance.applicant = applicantInstance session.add(educationInstance) session.commit()