Based on Jake Wharton's excellent pidcat which filters adb
result by application package name.
Basic usage:
pidcat-ex com.oprah.bees.androidOn top of the original pidcat, this fork provides these additional features
--timestamp Prepend each line of output with the current time.
--extra-header-width N
Width of customized log header. If you have your own
header besides Android log header, this option will
further indent your wrapped lines with additional
width
--grep WORD_LIST_TO_GREP
Filter lines with words in log messages. The words are
delimited with '|', where each word can be tailed with
a color initialed with '\'. If no color is specified,
'RED' will be the default color. For example, option
--grep='word1|word2\CYAN' means to filter out all
lines containing either 'word1' or 'word2', and
'word1' will appear in default color 'RED', while
'word2' will be in the specified color 'CYAN'.
Supported colors (case ignored): {BLACK, RED, GREEN,
YELLOW, BLUE, MAGENTA, CYAN, WHITE, BG_BLACK, BG_RED,
BG_GREEN, BG_YELLOW, BG_BLUE, BG_MAGENTA, BG_CYAN,
BG_WHITE, NONE}. The color with prefix 'BG_' is
background color. And color 'NONE' means NOT
highlighting with color. You can have multiple '--
grep' options in the command line, and if so, the
command will grep all of the key words in all '--grep'
options. Escape '|' with '\|', and '\' with '\\'.
--hl WORD_LIST_TO_HIGHLIGHT
Words to highlight in log messages. Unlike '--grep'
option, this option will only highlight the specified
words with specified color but does not filter any
lines. Except this, the format and supported colors
are the same as '--grep'. You can have multiple '--hl'
options in the command line, and if so, the command
will highlight all of the key words in all '--hl'
options
--grepv WORD_LIST_TO_EXCLUDE
Exclude lines with words from log messages. The format
and supported colors are the same as '--grep'. Note
that if both '--grepv' and '--grep' are provided and
they contain the same word, the line will always show,
which means '--grep' overwrites '--grepv' for the same
word they both contain. You can have multiple '--
grepv' options in the command line, and if so, the
command will exclude the lines containing any keywords
in all '--grepv' options
--igrep WORD_LIST_TO_GREP
The same as '--grep', just ignore case
--ihl WORD_LIST_TO_HIGHLIGHT
The same as '--hl', just ignore case
--igrepv WORD_LIST_TO_EXCLUDE
The same as '--grepv', just ignore case
--rgrep REGEX_LIST_TO_GREP
The same as '--grep', just using regular expressions
in python style as described in
'https://docs.python.org/2/library/re.html'. In the
regular expression, make sure to escape '|' with '\|',
and '\' with '\\'
--rhl REGEX_LIST_TO_HIGHLIGHT
The same as '--hl', just using regular expressions in
python style as described in
'https://docs.python.org/2/library/re.html'. In the
regular expression, make sure to escape '|' with '\|',
and '\' with '\\'
--rgrepv REGEX_LIST_TO_EXCLUDE
The same as '--grepv', just using regular expressions
in python style as described in
'https://docs.python.org/2/library/re.html'. In the
regular expression, make sure to escape '|' with '\|',
and '\' with '\\'
--keep-all-errors Do not filter any error or fatal logs from 'pidcat-ex'
output. This is quite helpful to avoid ignoring
information about exceptions, crash stacks and
assertion failures
--tee FILE_NAME Besides stdout output, also output the filtered result
(after grep/grepv) to the file
--tee-pidcat PIDCAT_FILE_NAME
Besides stdout output, also output the unfiltered
original pidcat-ex result (all pidcat-ex formatted
lines) to the file
--tee-adb ADB_OUTPUT_FILE_NAME
Output original adb result (raw adb output) to the
file
--pipe TERMINAL_WIDTH_FOR_PIPE_MODE
Note: you need to give terminal width as the value,
just put `tput cols` here. When running in pipe mode,
the script will take input from 'stdin' rather than
launching adb itself. The usage becomes something like
"adb -d logcat | pidcat-ex --pipe `tput cols`
com.testapp". This is very useful when you want to
apply any third-party scripts on the adb output before
pidcat-ex cutting each line, like using 3rd-party
scripts to grep or hilight with colors (such as using
'ack' or 'h' command) to keywords. For example, "adb
-d logcat | h -i 'battery' | pidcat-ex --pipe `tput
cols` com.testapp"
--hide-header HIDE_HEADER_REGEX
Remove the header in each line that matches the
regular expression. Note that Android adb header is
NOT considered here. The parameter is regular
expression. When this option provided, the script will
match the head of each log line (not including the
Android adb header) with the regular expression, and
remove the matched header in the output. This is
useful when your own log has big long headers in each
line which you don't care and want to hide them from
the output. The regular expression syntax is in python
style as described in
'https://docs.python.org/2/library/re.html'. You can
specify multiple '--hide-header' options and if the
header matches any of them, it will be removed from
output
--addr2line-tool ADDR2LINE_TOOL_PATH
This option along with '--addr2line-bin' (you have to
give values to both these parameters) will help you
automatically symbolicate the native crash addresses
found in the log that match your native code binary
file with debug information, such as '.so' lib file.
'ADDR2LINE_TOOL_PATH' is the path to the 'xxx-
addr2line', which should be found in your Android SDK
directory.
--addr2line-bin NATIVE_DEBUG_BIN_FILE_PATH
This option along with `--addr2line-tool` (you have to
give values to both these parameters) will help you
automatically symbolicate the native crash addresses
found in the log that match your native code binary
file with debug information, such as '.so' lib file.
'NATIVE_DEBUG_SO_LIB_FILE_PATH' is the file path to
your debug version native binary file with debug
symbols in it. You can provide multiple '--addr2line-
bin' options to symbolicate crashes of multiple native
binary files. The script can automatically match the
correct binary file for each crash log line. Note that
your 'NATIVE_DEBUG_SO_LIB_FILE_PATH' version has to
match the addresses in the crash log, otherwise, the
symbolicated result would not be correct
If you want to use the grep, highlight and any other functions
as a stand-alone tool so as to use it with other files or tools,
you can check this one hl (A Text Highlighting Tool)
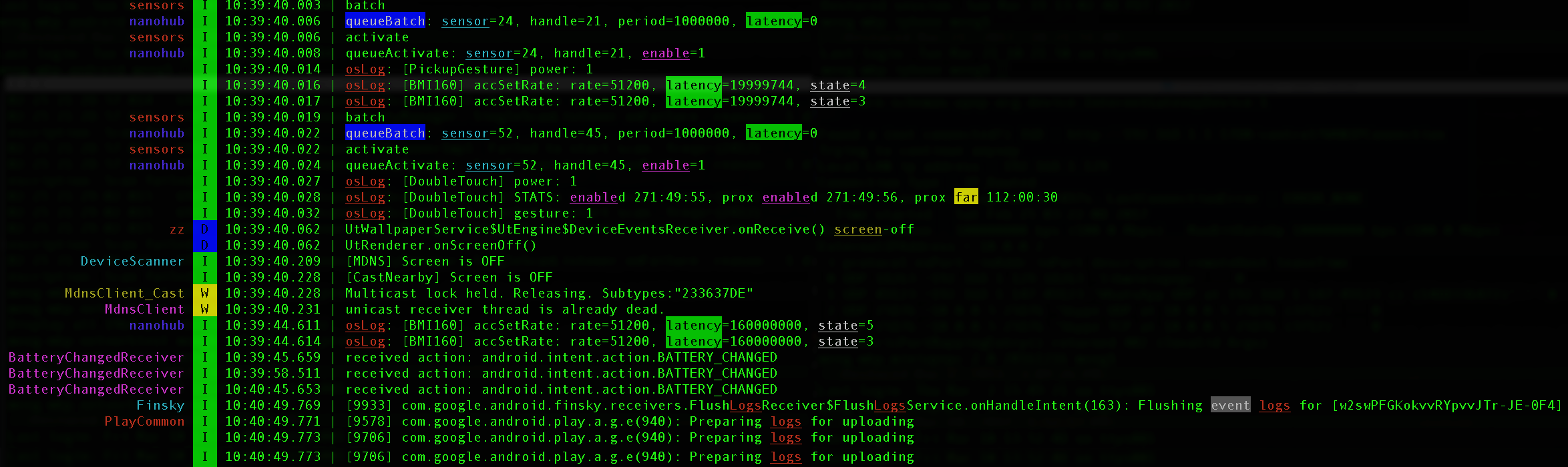
Here is an example of the output of the following command:
pidcat-ex --timestamp --ihl='oslog|logs|sensor\cyan|queuebatch\bg_blue|state\white|latency\bg_green|enable\magenta' --hl='screen\yellow|far\bg_yellow|event\bg_ack'Another example using pipe mode with 3rd-party h tool:
adb logcat | h group android call Status Layout system pid event | pidcat-ex --pipe=`tput cols`You could notice that
- The words are highlighted in specified colors, even the cut words due to line wrapping (
--hl); - Timestamps are headed in each line (
--timestamp); - Additional indentation spaces are added to align the wrapped lines to the right of timestamp headers (
--header-width);
Get the script:
- Download the
pidcat-ex.pyand place it on your PATH.
Make sure that adb from the Android SDK is on your PATH. This script will
not work unless this is that case. That means, when you type adb and press
enter into your terminal something actually happens.
To include adb and other android tools on your path:
export PATH=$PATH:<path to Android SDK>/platform-tools
export PATH=$PATH:<path to Android SDK>/toolsInclude these lines in your .bashrc, .zshrc or .bash_profile.
Note: <path to Android SDK> should be absolute and not relative.