Emerging Technologies Module - Lecturer: Ian McLoughlin - 4th Year Software Development
In this lab Emerging Technologies, we look at more tensorflow functionality using the iris dataset Iris Datset if you look down below i will show the workings and the instructions how to run the application
For more: Lab Instructions 1: View Juypter notebook copy 2: View python copy
You will need the following installed to run this project
- Anaconda 3.6 - The version of python you need.
- Jupyter Notebook - To run the ipynb copy of project.
- note if you download Full version of Anaconda Navigator a copy of notebook should be Available.
First if you go to the right and clone this project and unzip the project to a folder of choice.
Cmd in the selected folder (i used git bash )
Now you in if You want to Run the script locally just copy this command below.
python predict.py
Ypuu might get error for Keras package so to fix this go into the Anaconda CMD and type..
pip install keras
now if you need Notebook you will need to run notebook and upload the ipynb file
What is notebook check the link for details Juypter
The Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Uses include: data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning, and much more.
Data Set Information:
This is perhaps the best known database to be found in the pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper is a classic in the field and is referenced frequently to this day. (See Duda & Hart, for example.) The data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the latter are NOT linearly separable from each other.
Predicted attribute: class of iris plant.
This is an exceedingly simple domain.
This data differs from the data presented in Fishers article (identified by Steve Chadwick, spchadwick '@' espeedaz.net ). The 35th sample should be: 4.9,3.1,1.5,0.2,"Iris-setosa" where the error is in the fourth feature. The 38th sample: 4.9,3.6,1.4,0.1,"Iris-setosa" where the errors are in the second and third features.
Attribute Information:
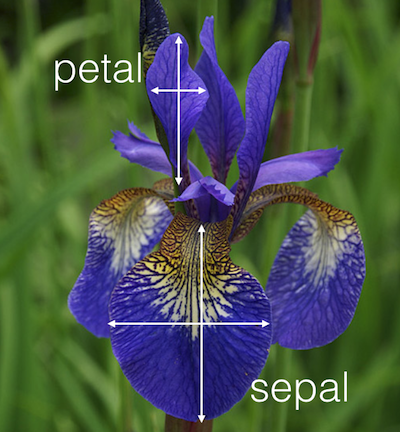
- sepal length in cm
- sepal width in cm
- petal length in cm
- petal width in cm
- class: -- Iris Setosa -- Iris Versicolour -- Iris Virginica
The Keras library in Python makes building and testing neural networks a snap. It provides a simpler, quicker alternative to Theano or TensorFlow–without worrying about floating point operations, GPU programming, linear algebra, etc.
Keras has been around for a while and predates TensorFlow becoming open source. Keras originally supported Theano, which, like TensorFlow, is a framework that supports deep learning. But soon after TensorFlow was open sourced, Keras added support for TensorFlow. You can use Keras with many types of machine learning problems, but it is focused on the needs of neural networks in general and deep neural networks specifically. Also, Keras is expanding to support other frameworks, such as Microsoft CNTK.
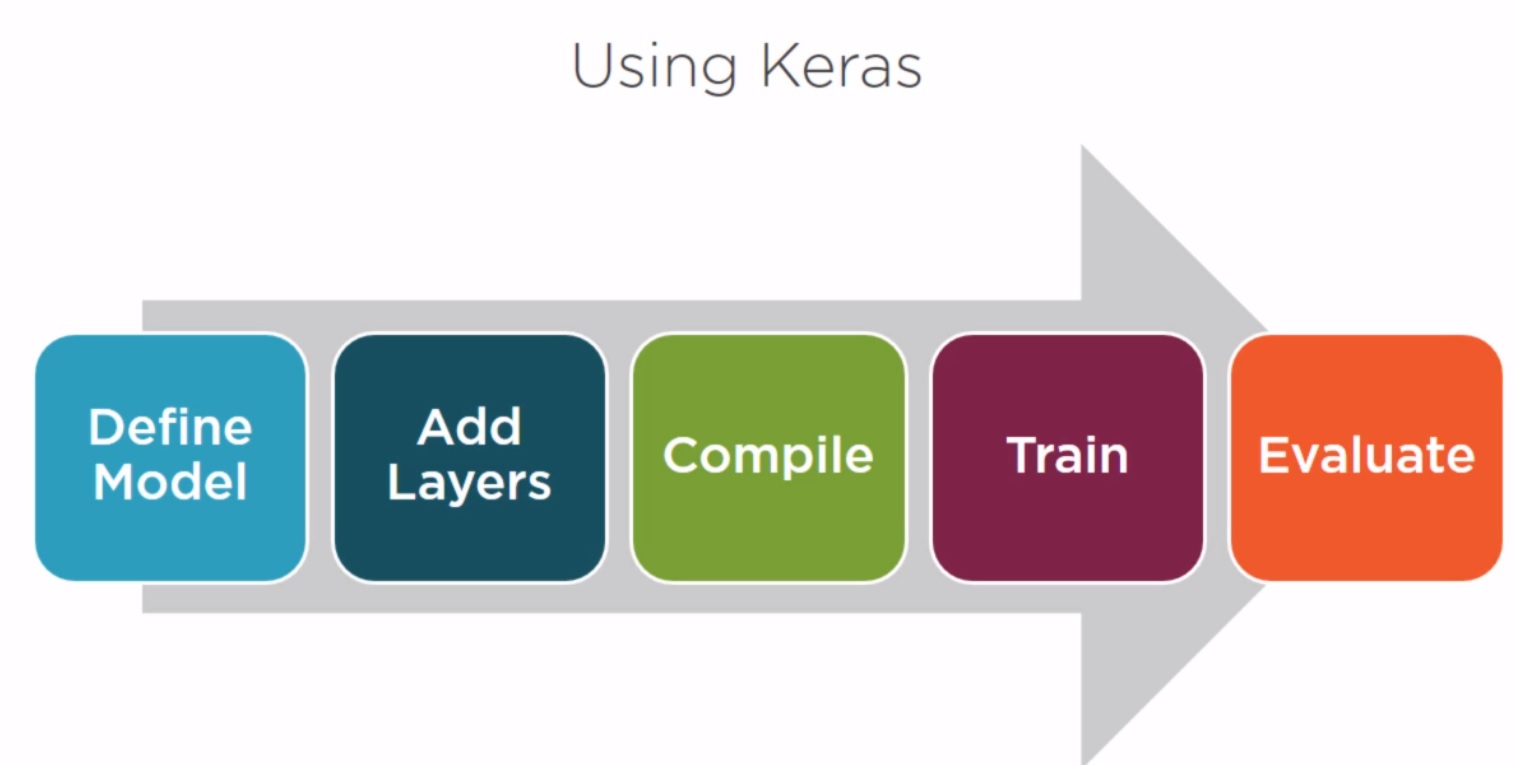
Keras is based on a model object. The model object acts as a framework to which layers are added. There are two primary types of model objects. The first is the sequence, which is a stack of layers where each layer feeds the next. For more complex structures, there is a functional API which lets you create your own relationship between layers. After you create your model object, you add layers to it. As required, you set parameters for each layer. And all of the interconnection between the layers are handled by Keras. Once you have your model object populated with layers, you call the model object's compile method. During this compile process, a TensorFlow graph with appropriate operators and tensors is created. After compiling, fit method is called to train the model. And finally, the evaluate method is called to evaluate the trained model's performance.