Build a Traffic Sign Recognition Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Load the data set (see below for links to the project data set)
- Explore, summarize and visualize the data set
- Design, train and test a model architecture
- Use the model to make predictions on new images
- Analyze the softmax probabilities of the new images
- Summarize the results with a written report
Here I will consider the rubric points individually and describe how I addressed each point in my implementation.
1. Provide a basic summary of the data set and identify where in your code the summary was done. In the code, the analysis should be done using python, numpy and/or pandas methods rather than hardcoding results manually.
The code for this step is contained in the second code cell of the IPython notebook.
I used the pandas library to calculate summary statistics of the traffic signs data set:
- The size of training set is 34799
- The size of test set is 12630
- The shape of a traffic sign image is 32x32x3
- The number of unique classes/labels in the data set is 43
2. Include an exploratory visualization of the dataset and identify where the code is in your code file.
The code for this step is contained in the fourth code cell of the IPython notebook.ß
1. Describe how, and identify where in your code, you preprocessed the image data. What tecniques were chosen and why did you choose these techniques? Consider including images showing the output of each preprocessing technique. Pre-processing refers to techniques such as converting to grayscale, normalization, etc.
The code for this step is contained in the fifth code cell of the IPython notebook. Also I save all those functions in utils.py file since I prefer running model using bash.
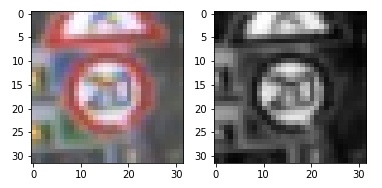
As a first step, I decided to convert the images to grayscale. Here is an example of a traffic sign image before and after grayscaling.
As a last step, I normalized the image data because gradient descent works better when the data is normalized.
2. Describe how, and identify where in your code, you set up training, validation and testing data. How much data was in each set? Explain what techniques were used to split the data into these sets.
- The size of training set is 34799
- The size of validation set is 4410
- The size of test set is 12630
3. Describe, and identify where in your code, what your final model architecture looks like including model type, layers, layer sizes, connectivity, etc.) Consider including a diagram and/or table describing the final model.
The code for my final model is located in the seventh cell of the ipython notebook.
I wrote a class for my neural network model and it could also be found under nnet.py file. The reason is I prefer to run code from command line instead of ipython notebook. You need to reset the tensorflow graph every time you test your code, which is pretty annoying.
My final model consisted of the following layers:
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x1 grayscale image |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, same padding, outputs 32x32x32 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, outputs 16x16x32 |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, same padding, outputs 16x16x64 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, outputs 8x8x64 |
| Fully connected | outputs 1024 |
| Fully connected | outputs 43 |
| Softmax | Cross Entropy |
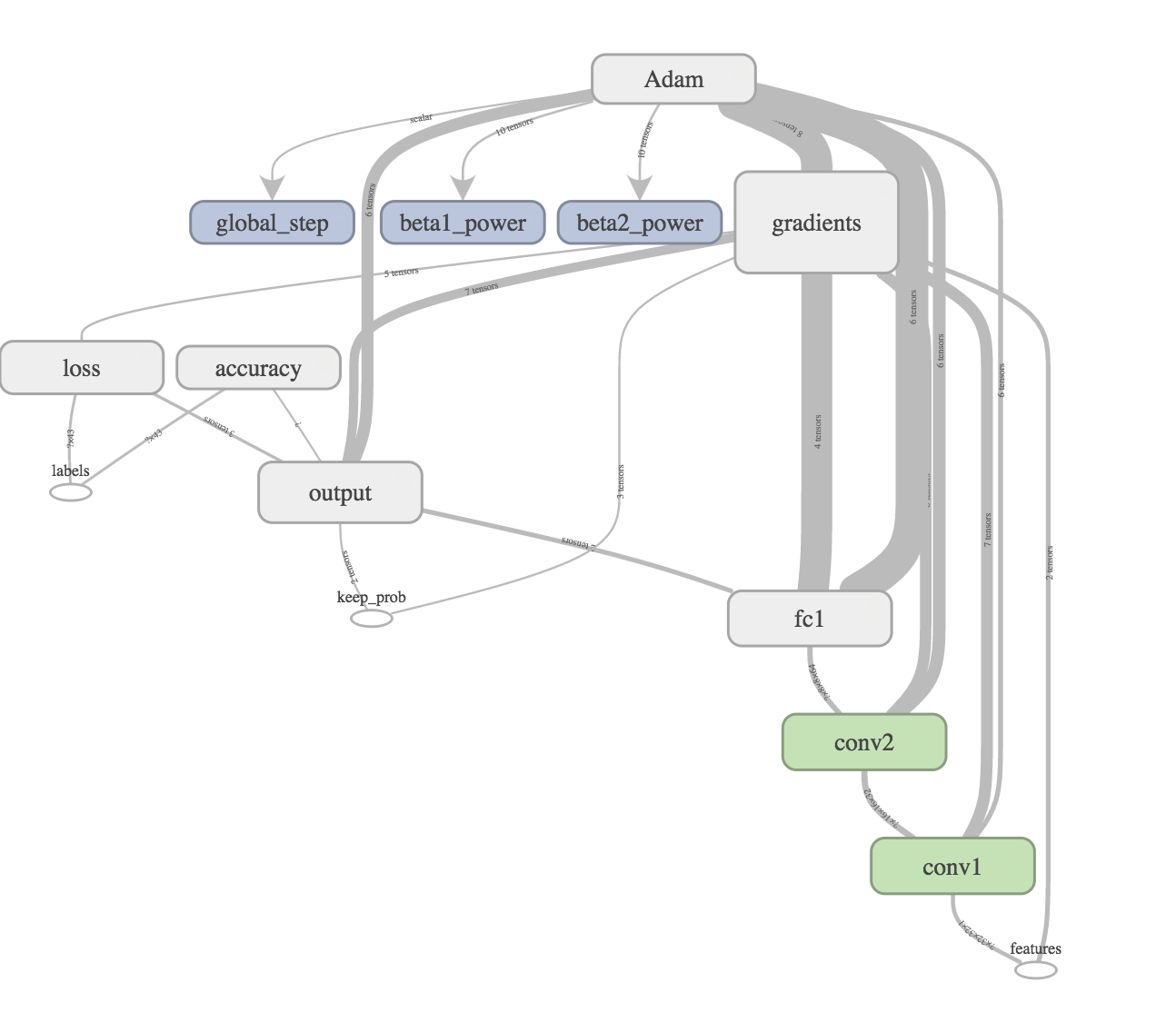
Here is a screenshot I took from Tensorboard.
4. Describe how, and identify where in your code, you trained your model. The discussion can include the type of optimizer, the batch size, number of epochs and any hyperparameters such as learning rate.
The code for training the model is located in the eighth cell of the ipython notebook. The code could also be found under main.py, which is the file I used to run my model.
5. Describe the approach taken for finding a solution. Include in the discussion the results on the training, validation and test sets and where in the code these were calculated. Your approach may have been an iterative process, in which case, outline the steps you took to get to the final solution and why you chose those steps. Perhaps your solution involved an already well known implementation or architecture. In this case, discuss why you think the architecture is suitable for the current problem.
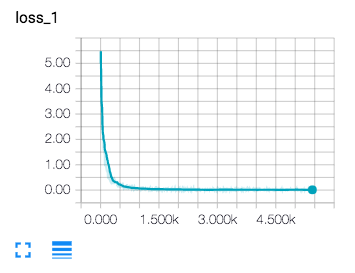
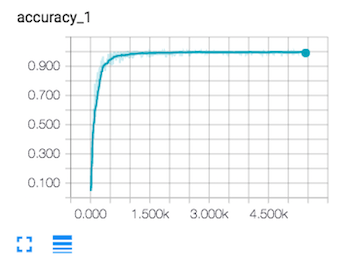
I evaluate my model using the validation set after each epoch and test it out after all 10 epochs. Seem like my model suffers from overfitting and I should probably decrease my dropout probability. It performs almost the same on validation and test data set. I also save my model, including training and testing summaries under runs/ folder so I can easily reload the graph and evaluate using test images.
My final model results were:
- training set accuracy almost equal to 1.
- validation set accuracy of 93.8.
- test set accuracy of 93.3.
1. Choose five German traffic signs found on the web and provide them in the report. For each image, discuss what quality or qualities might be difficult to classify.
Here are five German traffic signs that I found on the web:
2. Discuss the model's predictions on these new traffic signs and compare the results to predicting on the test set. Identify where in your code predictions were made. At a minimum, discuss what the predictions were, the accuracy on these new predictions, and compare the accuracy to the accuracy on the test set (OPTIONAL: Discuss the results in more detail as described in the "Stand Out Suggestions" part of the rubric).
The code for making predictions on my final model is located in the tenth cell of the Ipython notebook.
Here are the results of the prediction:
| Image | Prediction |
|---|---|
| Speed limit (50km/h) | Speed limit (50km/h) |
| Stop | Stop |
| No entry | No entry |
| Road work | Road work |
| Ahead only | Ahead only |
The results turned out to be impossibly well and it reaches 100%. Definitely we can't trust this result since it is a very small sample set.
Actually I trained two models, one with RGB images and the other one with grayscale. It seems like the grayscale one outperforms the RGB one on the five test images.