- The project is built using typescript, express, prisma, postgres
- Testing: Using jest
- Logger: Using winston and morgan
- Error handling: Using centralized error handling mechanism
- API docs: with swagger-jsdoc and swagger-ui-express
- Dependency managed using Yarn
- Environment variables: Using dotenv and cross-env
- Santizing support: Sanitize request data against xss and query injection
- Docker support: Dev, Test and Production docker support
- Linting: Using ESLint and Prettier
- The server exposes a single endpoint
/v1/worker/:worker_idto get all available shifts as per the requirements specified in the problem statement
- Intialize the db with dummy data by executing:
$ cd seed
$ docker-compose up -d --build
- Install dependencies in root repo:
$ yarn install
- Env file template is provided for reference
.env.example - Need to set the appropriate
DATABASE_URL
- Start server by executing following command in root repo:
In development:
$ yarn dev
In production:
$ yarn dev
This will start development server
-
One can interact with the server by visiting
http://localhost:3000/v1/worker/101This will return the available shifts for the worker with id 101 for e.g. -
One can start the server using docker too
-
View swagger docs by vising
http://localhost:3000/v1/docs/#/
- Make sure the dummy db docker container is stopped, if not follow the following commands:
$ docker stop container_id
$ docker rm container_id
-
The tests covered success and fail cases for workers when trying to query available shifts
-
Start tests:
$ yarn test
- Run all tests in watch mode
yarn test:watch
- We will use locust to monitor RPS performance for our single endpoint
- Used for performance (load and stress) testing the API
- Setup virtual env
$ python3 -m venv venv
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
- Initialise environment
$ source venv/bin/activate
- Execute:
$ ./deploy
-
Open web interface url from console output. The locust server is available at
http://0.0.0.0:8089 -
Paste our server endpoint i.e
http://localhost:3000in theHostfield -
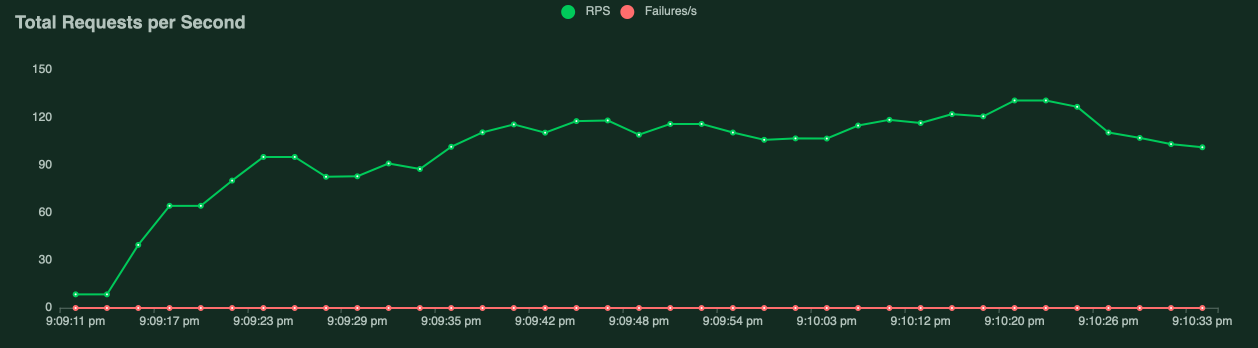
As we can see for 20 simulataneous users, the max RPS we are getting is ~120
- Since
Shifttable has ~2M rows, the performance suffers when we are querying the same - We can speed up already served up queries/workers by using in-memory cache layer such as
redis - Using secondary/slave read-only server for reads, since we are only reading the data
- Depending on how many shifts per facility is available, perhaps it's worthwhile partioning the data using facility_id/profession
- Creating indexes on relevant tables
For e.g. since we are querying
Shifttable with the eligible facility_id, profession of a worker, whether worked_id exists, is_deleted or not, perhaps it's worth trying creating indexes forprofession,facility_id,is_deleted,worked_id - Horizontal scaling: Docker swarm/kubernetes We can create multiple server nodes using docker swarm/kubernetes to distribute the load