This project provides an EVM bytecode disassembler and Control Flow Graph (CFG) generator.
The disassembler should support the latest opcodes like PUSH0, EIP-3855, and is ready for RJumps (experimental, not tested), EIP-4200.
The disassembler takes as an input some binary representation, EVM bytecode, and produces a readable version of it.
For instance the following binary string, prog :
60015f5b600a81106014575060405260206040f35b905f5b600a8110602c57506001600a91019190506003565b9060020290601756
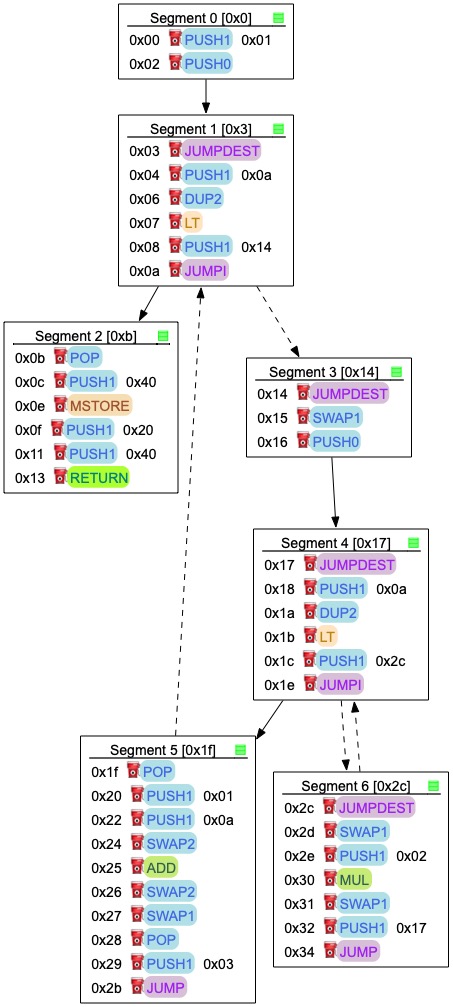
is disassembled into the more readable (but arguably still opaque!) EVM assembly code, left-hand side below, and the CFG is depicted on the right-hand side.
The CFG generator outputs a DOT representation of the graph. Hovering some items (segments) reveals some information about the instructions, their gas cost, and for the segment about their stack effects.
The generator uses a combination of abstract interpretation, loop folding (using weakest pre-conditions) and automata minimisation. It can re-construct CFGs with nested loops, function calls.
Examples of CFGs in DOT format and SVG format are available in the test folder.
A front end is provided at https://bytespector.org or alternatively,
you can use the Graphviz-Online tool to visualise the dot files.
The input to the disassembler and CFG generator is the deployed (bin-runtime) part of the compiled code if you compile Solidity with solc.
For the examples in the repo I have used Yul and solc --yul to get a text representation of the Yul code that includes the binary representation hexadecimal string.
The CFGs can be formally verified using a Dafny proof object.
The project is written in Dafny but Dafny's backends can be used to generate some target code in several languages. To begin with we have generated artefacts in Python, Java, JS and C# (Dotnet) code.
So you don't need to install Dafny to use the disassembler, you can run the Python or java versions provided in the build/libs.
The Python disassembler is in build/driver-py.
It can be used with an input string as follows:
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ python3 build/libs/driver-py/__main__.py
Not enough arguments
usage: <this program> [--help] [--dis] [--proof] [--segment] [--lib] arg0 [--cfg] arg0 [--raw] [--size] arg0 [--notable] [--title] arg0 [--info] <string>
options
--help [-h] Display help and exit
--dis [-d] Disassemble <string>
--proof [-p] Generate proof object to verify the CFG for <string>
--segment [-s] Print segment of <string>
--lib [-l] The path to the Dafny-EVM source code. Used to add includes files in the proof object.
--cfg [-c] Max depth. Control flow graph in DOT format
--raw [-r] Display non-minimised and minimised CFGs
--size [-z] The max size of segments. Default is upto terminal instructions or JUMPDEST.
--notable [-n] Don't use tables to pretty-print DOT file. Reduces size of the DOT file.
--title [-t] The name of the program.
--info [-i] The stats of the program (size, segments).
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ python3 build/libs/driver-py/__main__.py "6040"
PUSH1 0x40To parse a binary representation from a file file.evm use:
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ python3 build/libs/driver-py/__main__.py $(<file.evm)
PUSH1 0x40To generate a Dafny proof object (only usable with the Dafny-EVM):
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ python3 build/libs/driver-py/__main__.py -p "6040"
/** Code starting at 0x0 */
function ExecuteFromTag_0(s0: EvmState.ExecutingState): (s': EvmState.State)
requires s0.PC() == 0x0 as nat
requires s0.Operands() >= 0
requires s0.Capacity() >= 1
{
ValidJumpDest(s0);
var s1 := Push1(s0, 0x40);
s1
}The java disassembler is the file evmdis.jar in build/libs/Driver-java.
It can be used with an input string as follows:
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ java -jar build/libs/Driver-java/evmdis.jar
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ dotnet build/libs/driver.dll
evm-dis git:(main) ✗ node build/driver.jsThe disassembler and CFG generator is written in Dafny a verification-friendly programming language.
Some code (e.g. the definition of EVMOpcodes, Int) is adapted from the Dafny-EVM project.
The disassembler/CFG generator is a useful tool but not the ultimate goal of this project.
The main component, Disassemble, builds a representation of the binary as a sequence of Instructions.
This representation can be printed out (this is how the disassembler generates the readable code), but also used to generate proof objects that are Dafny programs that can be verified using the Dafny-EVM.
As an example, the following Yul code (the same can be done with Solidity code):
object "Runtime" {
code {
function checked_add_t_uint256(x, y) -> sum {
sum := add(x, y)
if gt(x, sum) { revert(0, 0) }
}
let x := 8
let y := 56
let z := checked_add_t_uint256(x, y)
}
}can be compiled using solc --yul into an (EVM) binary representation, and the result is the string prog given above.
The disassembler we build here will ultimately be used to generate a Dafny program to verify some properties of the previous code.
From the binary representation prog we want to automatically build a Dafny-EVM friendly program similar to the OverFlowCheckerBytecode below.
This program can be used to reason about the bytecode, thanks to the formal semantics provided by the Dafny-EVM and the verification engine embedded in Dafny.
module OverFlowCheckerBytecode {
import opened Int
import EvmState
import opened Bytecode
/**
* The labels (JUMPDEST) in the bytecode.
*/
const tag_1: u8 := 0x0c
const tag_2: u8 := 0x0d
const tag_3: u8 := 0x18
const tag_4: u8 := 0x17 // this one is not a JUMPDEST
/**
* When a JUMP or JUMPI is executed we need to make sure the target location
* is a JUMPDEST.
* This axiom enforces it.
*/
lemma {:axiom} ValidJumpDest(s: EvmState.ExecutingState)
ensures s.IsJumpDest(tag_1 as u256)
ensures s.IsJumpDest(tag_2 as u256)
ensures s.IsJumpDest(tag_3 as u256)
/**
* Code starting at PC == 0.
*/
function ExecuteFromZero(st: EvmState.ExecutingState): (s': EvmState.State)
requires st.Capacity() >= 4
requires st.Operands() >= 0
requires st.PC() == 0 as nat
ensures s'.EXECUTING?
ensures s'.PC() == tag_1 as nat
{
/*
00000000: PUSH1 0xa // tag_2
00000002: PUSH1 0x8
00000004: PUSH1 0x38
00000006: SWAP1
00000007: PUSH1 0xc // tag_1
00000009: JUMP
*/
ValidJumpDest(st);
var s1 := Push1(st, tag_2);
var s2 := Push1(s1, 0x08);
var s3 := Push1(s2, 0x38);
var s4 := Swap(s3, 1);
assert s4.Peek(2) == tag_2 as u256;
var s5 := Push1(s4, tag_1);
assert s5.Peek(3) == tag_2 as u256;
var s6 := Jump(s5);
s6
}
/**
* Code staring at tag_2
*/
function ExecuteFromTag2(st: EvmState.ExecutingState): (s': EvmState.State)
requires st.Capacity() >= 0
requires st.Operands() >= 0
requires st.PC() == tag_2 as nat
ensures s'.RETURNS?
ensures |s'.data| == 0
{
/*
0000000b: STOP
*/
var s6 := Stop(st);
s6
}
/**
* Code staring at tag_1
*/
function ExecuteFromTag1(st: EvmState.ExecutingState): (s': EvmState.State)
requires st.Capacity() >= 1
requires st.Operands() >= 3
requires st.PC() == tag_1 as nat
requires st.Peek(2) == tag_3 as u256
ensures s'.EXECUTING?
ensures s'.Operands() == st.Operands() - 1
ensures s'.Peek(0) == st.Peek(2)
ensures s'.Peek(1) as nat == (st.Peek(0) as nat + st.Peek(1) as nat) % TWO_256
ensures s'.PC() == if st.Peek(0) > ((st.Peek(0) as nat + st.Peek(1) as nat) % TWO_256) as u256 then tag_3 as nat else tag_4 as nat
{
/*
0000000c: JUMPDEST // tag_1
0000000d: SWAP2
0000000e: SWAP1
0000000f: DUP3
00000010: ADD
00000011: DUP1
00000012: SWAP3
00000013: GT
00000014: PUSH1 0x18 // tag_3
00000016: JUMPI
*/
ValidJumpDest(st);
var s1 := JumpDest(st); // x, y, z
var s2 := Swap(s1, 2); // z, y, x
var s3 := Swap(s2, 1); // y, z, x
var s4 := Dup(s3, 3); // x, y, z, x
var s5 := Add(s4); // x + y, z, x
var s6 := Dup(s5, 1); // x + y, x + y, z, x
var s7 := Swap(s6, 3); // x, x + y, z, x + y
assert s7.Peek(0) == st.Peek(0);
var s8 := Bytecode.Gt(s7); // x > x + y, z, x + y
var s9 := Push1(s8, tag_3); // tag_3, x > x + y, z, x + y
var s10 := JumpI(s9); // z, x + y
s10
}
/**
* Code staring at tag_3
*/
function ExecuteFromTag3(st: EvmState.ExecutingState): (s': EvmState.State)
requires st.Operands() >= 0
requires st.Capacity() >= 2
requires st.PC() == tag_3 as nat
ensures s'.ERROR?
{
/*
00000018: JUMPDEST // tag_3
00000019: PUSH0
0000001a: DUP1
0000001b: REVERT
*/
ValidJumpDest(st);
var s1 := JumpDest(st);
var s2 := Push0(s1);
var s3 := Dup(s2, 1);
var s4 := Revert(s3);
s4
}
/**
* Code staring at tag_3
*/
function ExecuteFromTag4(st: EvmState.ExecutingState): (s': EvmState.State)
requires st.Operands() >= 1
requires st.Capacity() >= 0
requires st.PC() == tag_4 as nat
requires st.Peek(0) in {tag_1 as u256, tag_2 as u256, tag_3 as u256}
ensures s'.EXECUTING?
ensures s'.PC() == st.Peek(0) as nat
ensures s'.Operands() == st.Operands() - 1
{
/*
00000017: JUMP
*/
ValidJumpDest(st);
// assume st.IsJumpDest(st.Peek(0));
Jump(st)
}
}