Table of Contents (click to expand)
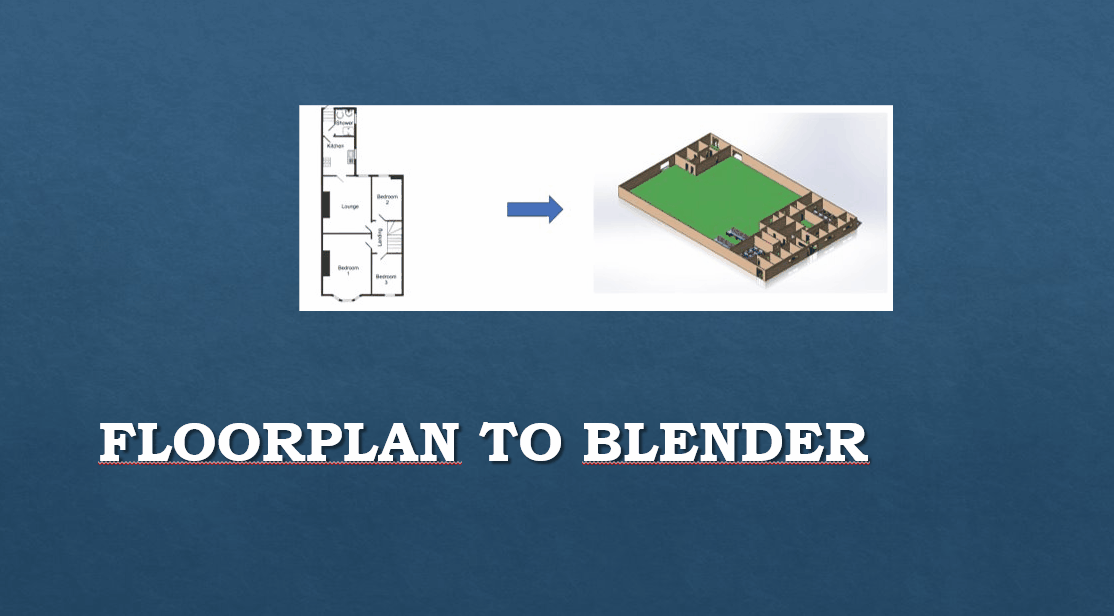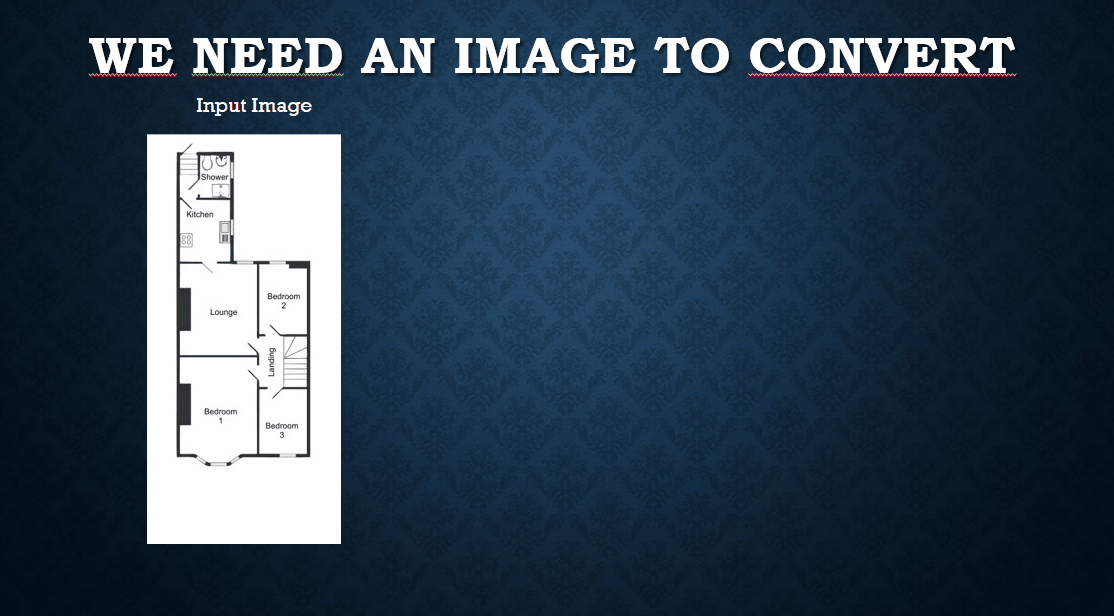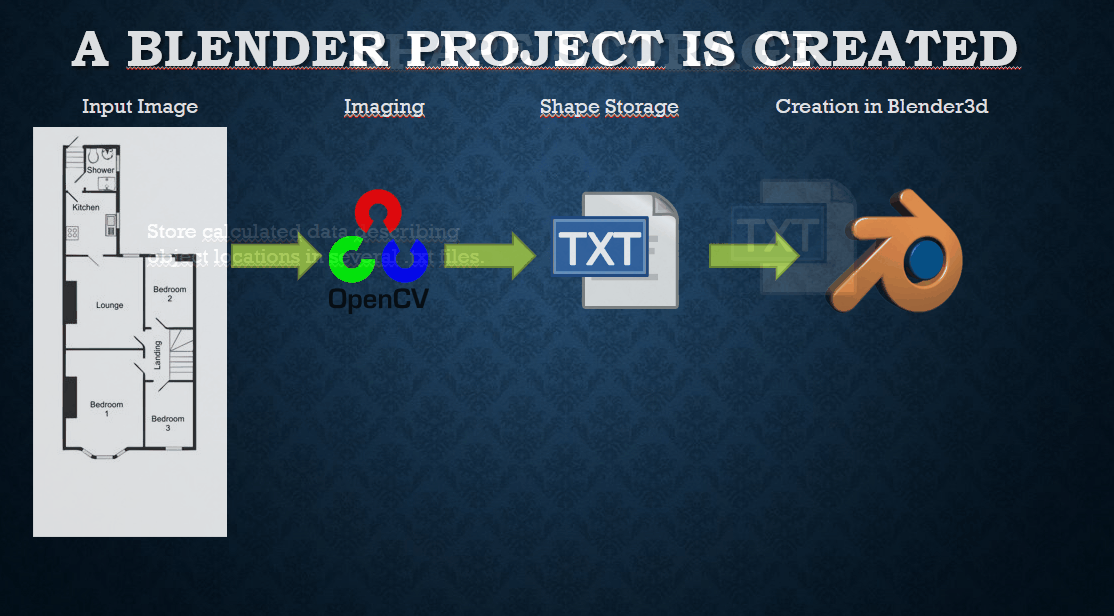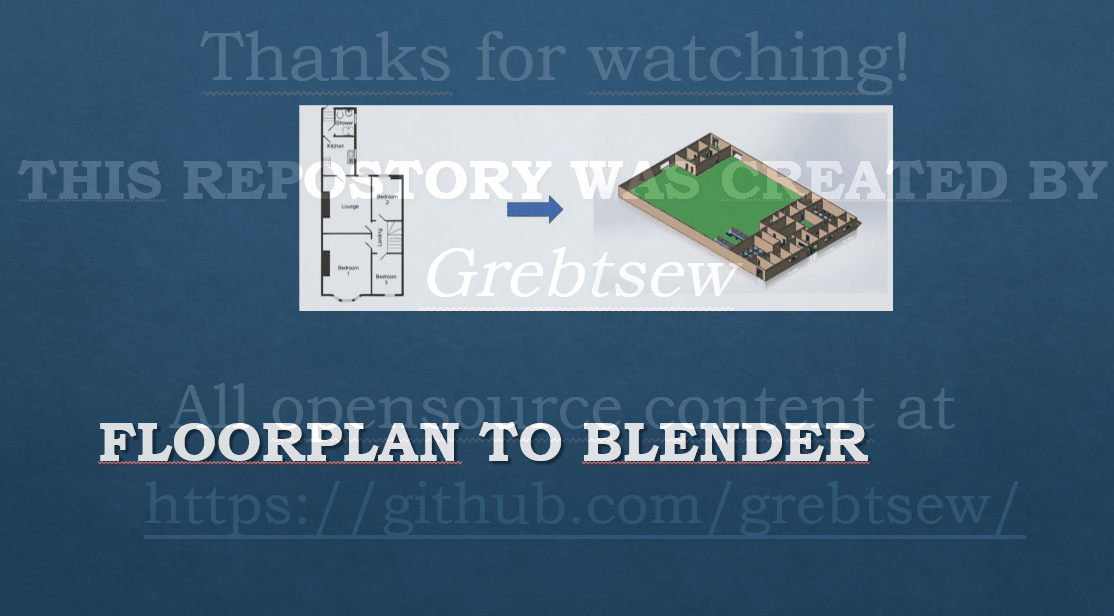
The virtualisation of real life objects has been a hot topic for several years. As I started learning about 3d modelling in Blender3d I thought of the idea to use simple imaging on floorplans to automatically create corresponding 3d models. It is much easier than it sounds and uses a low amount of resources, enabling it to be used on low hardware. By utilizing Blender3d, all created objects will be easy to transfer to any other 3d rendering program. Such as Unity, Unreal Engine or CAD.
This part contains information about how to setup and execute this program.
NOTE: Using other versions of the required programs and libraries than specified in this file might require changes in the implementation. It is only guaranteed that this implementation will work if the assigned versions of all requirements are used. At this time it is known that:
- If a later
Blenderversion is used, several changes has to done in all files in the/Blenderfolder. - If the latest
OpenCVlibrary for python is used, several changes has to be done in the/FloorplanToBlender3d/detect.pyfile. Please create an issue if you encounter any problems with this implementation.
NOTE: To avoid any version related problems use the Docker implementation.
Firstly you need to install a suitable Docker environment on your device.
This project contains a DockerFile which uses the Ubuntu 18.04 image so make sure your docker environment is set to linux containers.
-
Download or clone this repository.
-
Build docker image from DockerFile by running: NOTE: This step can take a long time.
docker build . --tag=floorplan_to_blender:1.0- To start the image run:
docker run -it floorplan_to_blender:1.0 bashThis will take you into your virtual environment where you can safely test the implementation.
- To run the program, enter the container and run:
python3 create_blender_project_from_floorplan.pyBlender is installed on path /usr/local/blender/blender, the path can be changed in the config.ini file with nano inside the container.
The generated .blender file can be retreived with scp or using volumes.
- Some useful docker commands:
# Get into a running container
docker exec -it container_name bash
# Stop all containers
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
# Remove all images
docker rmi $(docker images)This tutorial will describe how to install this implementation directly on your device. If you are a Linux/Ubuntu user, look at DockerFile for better instructions.
These are the programs that are required to run this implementation.
- Blender3d 2.79
Python 3.6.5
If you have Python3 pip installed you can install required packages by running:
pip install -r requirements.txtOr install them manually by running :
pip install
opencv-python==3.4.1.15(OpenCV)numpy==1.16.2configparser==3.5.0future-fstrings==1.2.0imutils==0.5.2pyfiglet==0.7.6
Clone or download this repo:
git clone https://github.com/grebtsew/FloorplanToBlender3d.git
This tutorial takes you through the execution of this program.
- Receive floorplan as image, from pdf or by using other method (for example paint)
- Run python script
create_blender_project_from_floorplan.py - Follow instructions
This tutorial takes you through the execution of this program in examples.
- Receive floorplan as image, from pdf or by using other method (for example paint)
- Set image file path in
Examples/floorplan_to_datafile.py - Run ´floorplan_to_datafile.py´ to create data files for your floorplan.
- Edit path in
floorplan_to_datafile.pyto generated data files. - Start blender
- Open Blender text editor
- Open
floorplan_to_3dObject_in_blender.pyin blender by pressing the text editor, thenalt+oand find the file - Run script
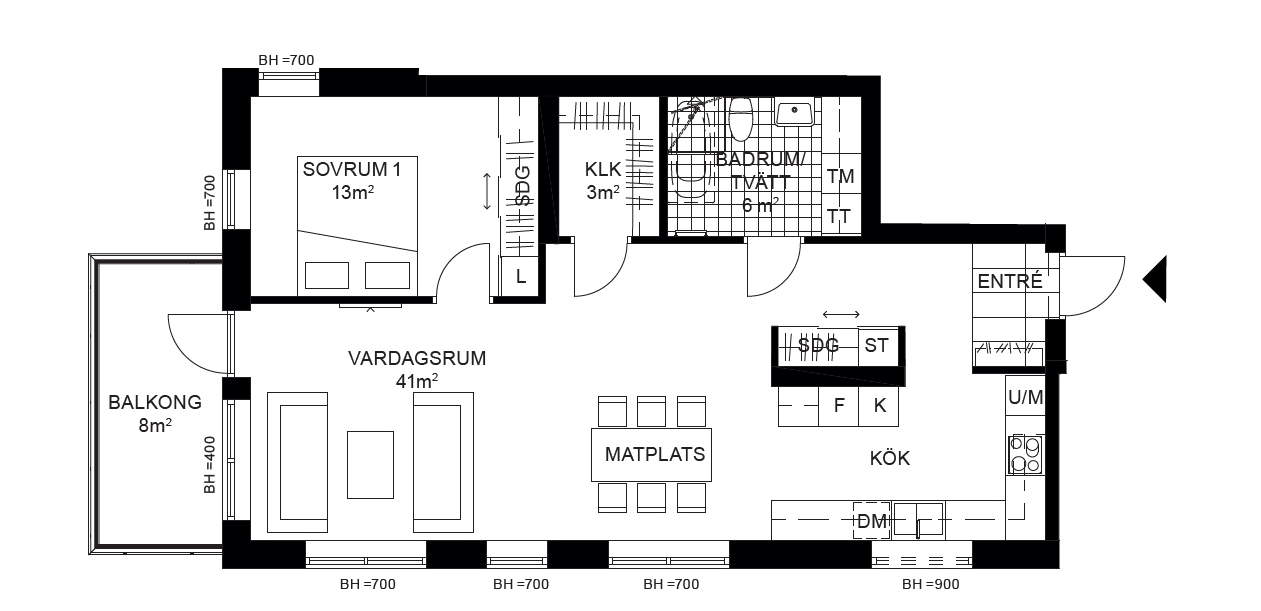
Here we demo the program. First of we need a floorplan image to process.
We use example.png, see below:
Next up we execute our script and answer the questions:
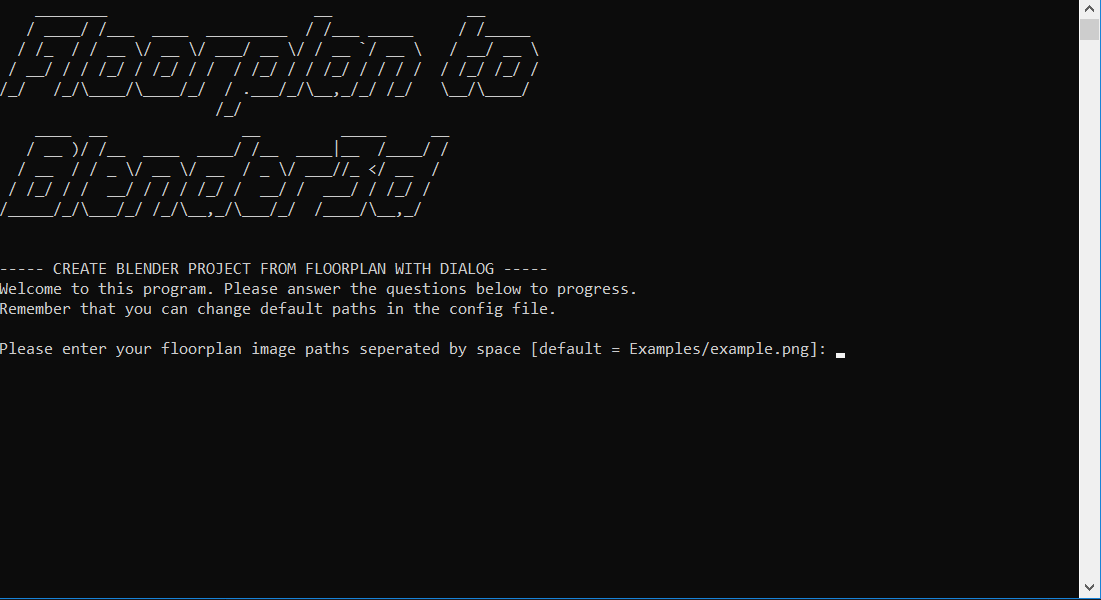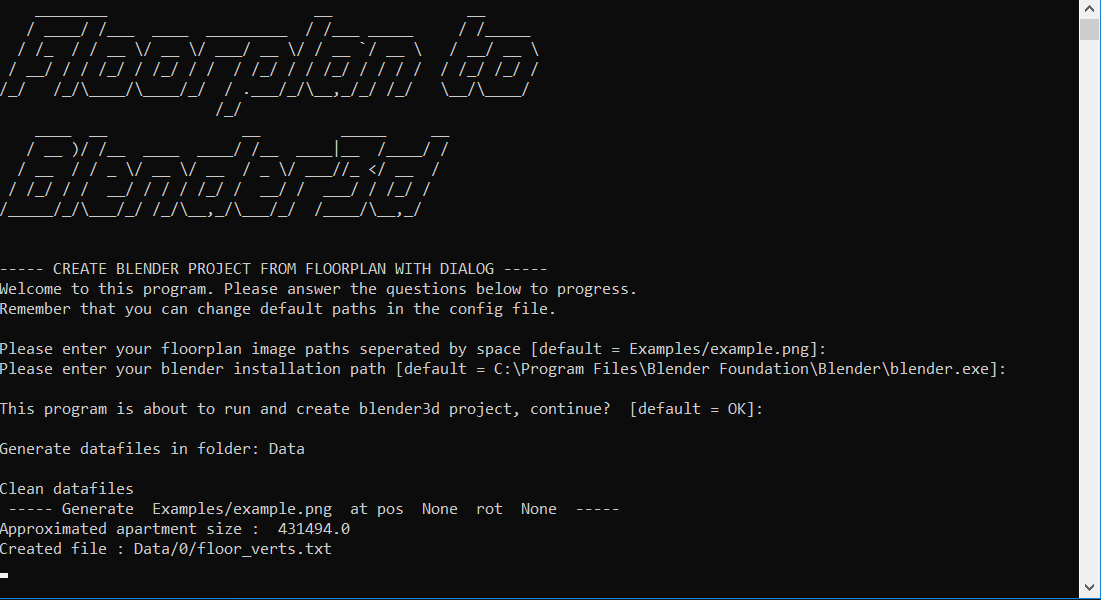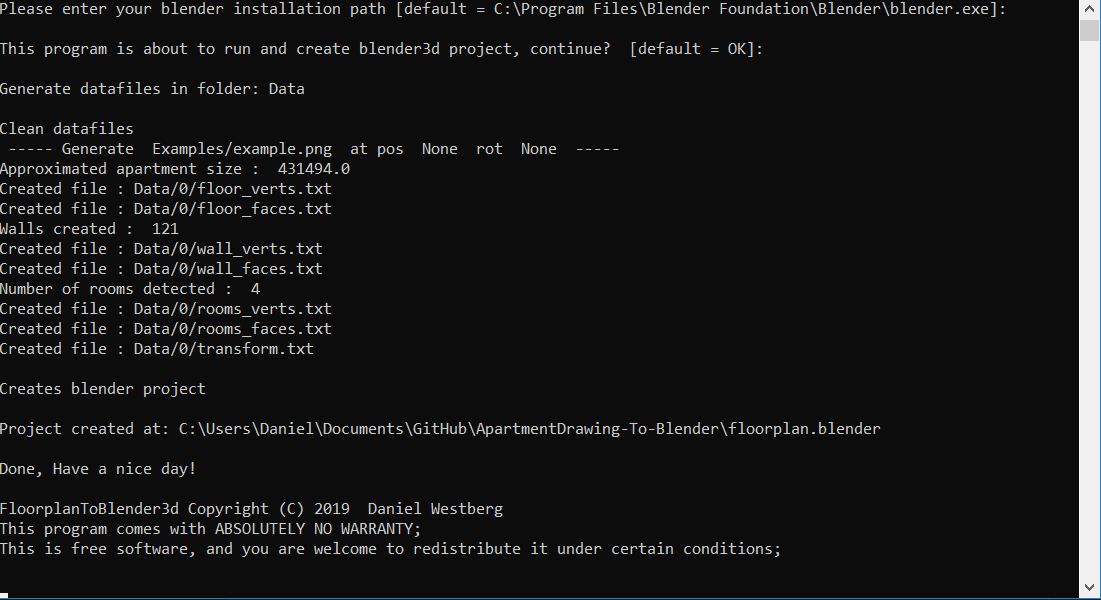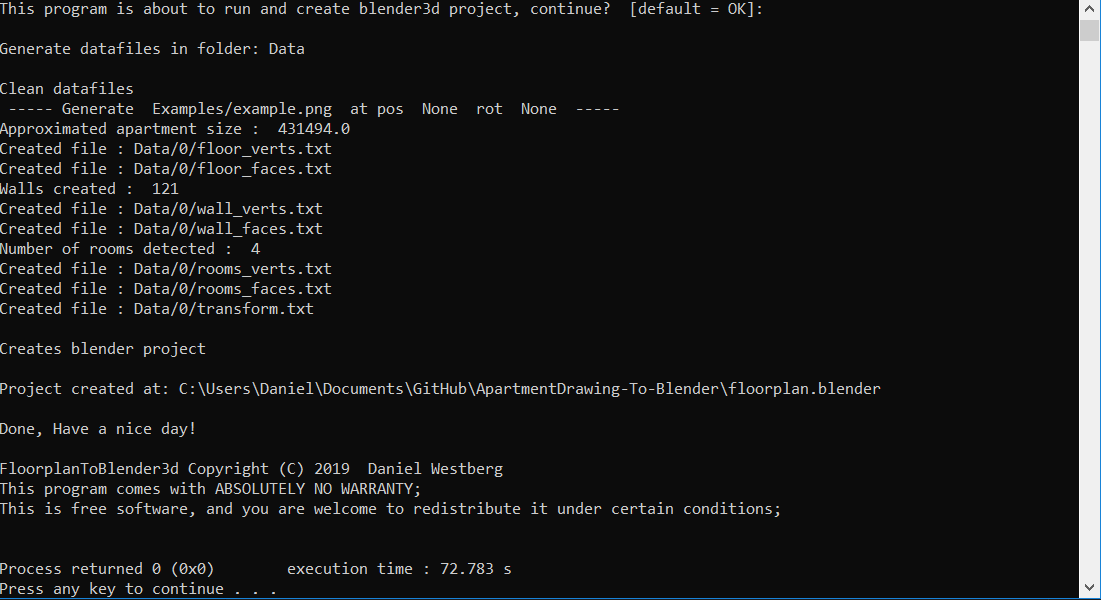
Finally we can open the newly created floorplan.blender file and see the result:
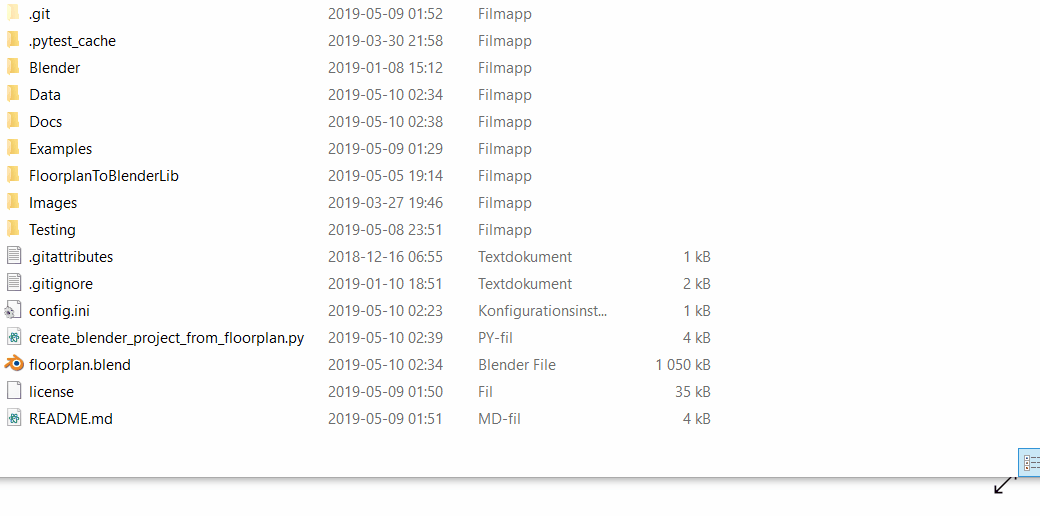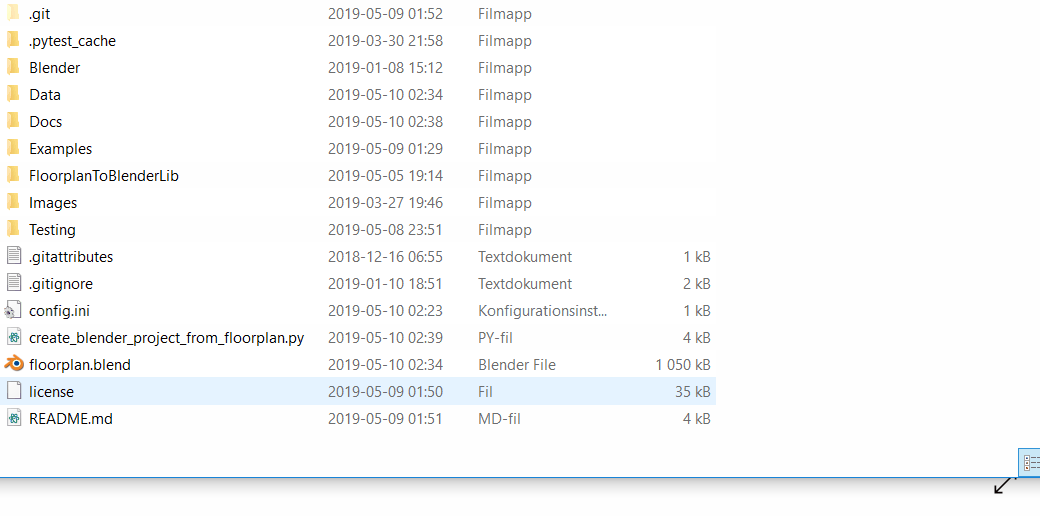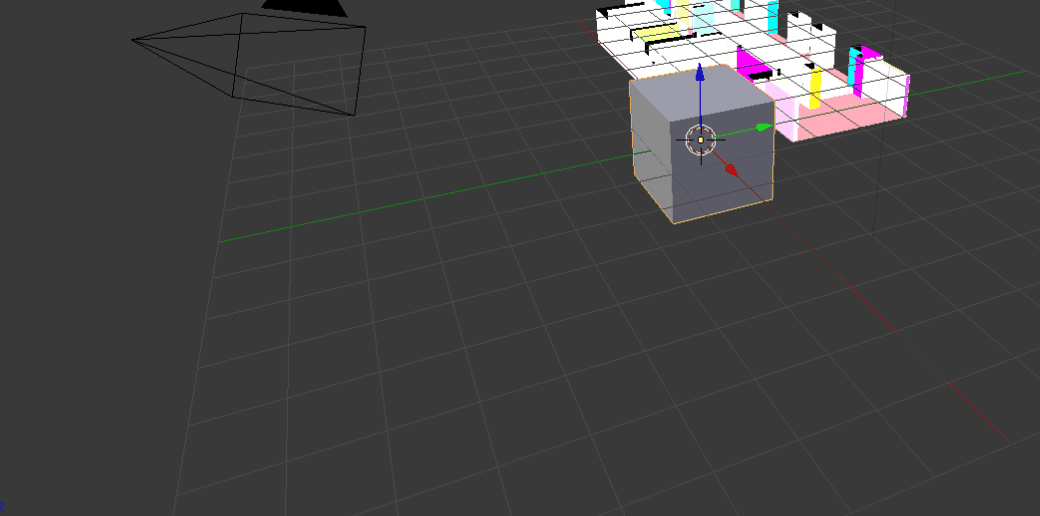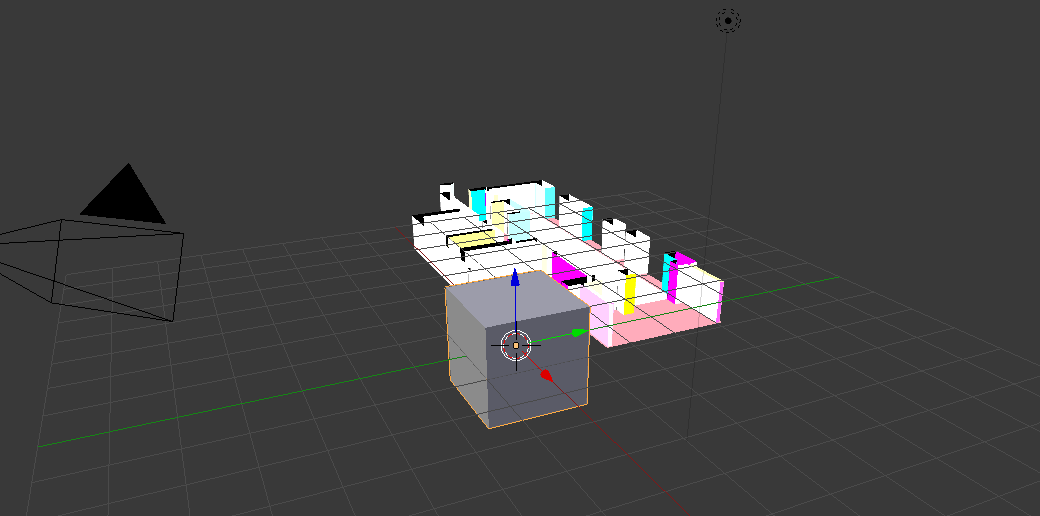
Note: This demo only uses default settings. For instance coloring is by default random.
Vital and core functionality are tested with pytest. To run tests yourself enter "Testing"-folder and run:
pytestDuring the development of this project I have been searching alot and copied code from StackOverflow. I share links to copied code and other contributors here:
- First look at problem : https://mathematica.stackexchange.com/questions/19546/image-processing-floor-plan-detecting-rooms-borders-area-and-room-names-t
- Room detection : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54274610/crop-each-of-them-using-opencv-python
- Watershed : https://docs.opencv.org/3.1.0/d3/db4/tutorial_py_watershed.html
- Shape detection : https://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_feature2d/py_features_harris/py_features_harris.html
- Distance in image : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50930033/drawing-lines-and-distance-to-them-on-image-opencv-python
- Rect contain : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33065834/how-to-detect-if-a-point-is-contained-within-a-bounding-rect-opecv-python
- Line detection : https://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_imgproc/py_houghlines/py_houghlines.html
- Readme tips: https://github.com/matiassingers/awesome-readme
Let me know if you want to contribute to this project, also if you want me to add more functions or answer questions, let me know!
These are some known issues with the current implementation:
- Floorplan images needs to be quite small for detections to work at this time. If you plan on using a large image, consider downscaling it.
- Required programs and libraries might change in future versions, this might require some changes in this implementation for it to work. If you insist on not using the versions specified in this Readme file, a coding effort might be required.
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE Version 3, 29 June 2007
COPYRIGHT @ Grebtsew 2019