A command line tool for easily doing prebuilds for multiple version of node/iojs on a specific platform.
$ npm install -g prebuild
- Builds native modules for any version of node/iojs, without having to switch between different versions of node/iojs to do so. This works by only downloading the correct headers and telling
node-gypto use those instead of the ones installed on your system. - Upload (
--upload) prebuilt binaries to GitHub. - Installs (
--install) prebuilt binaries from GitHub by default or from a host of your choice. The url format can be customized as you see fit. - Installed binaries are cached in
~/.npm/_prebuilds/so you only need to download them once. - Support for stripping (
--strip) debug information.
Building is only required for targets with different ABI versions. To build for all supported abi versions greater than 0.8 (example from leveldown):
prebuild --all
Alternatively, to build for some specific versions you can do:
prebuild -b 0.10.42 -b 0.12.10 -b 4.3.0
Optionally, to always build for the above versions, add the following to a .prebuildrc file in the project root:
prebuild[] = 0.10.42
prebuild[] = 0.12.10
prebuild[] = 4.3.0See targets.js for currently available versions.
For more options run prebuild --help. The prebuilds created are compatible with node-pre-gyp
prebuild supports uploading prebuilds to GitHub releases. If the release doesn't exist, it will be created for you. To upload prebuilds simply add the -u <github-token> option:
$ prebuild --all -u <github-token>
If you don't want to use the token on cli you can also stick that in e.g. ~/.prebuildrc:
{
"upload": "<github-token>"
}rc supports .ini format so you can write the same file as:
upload = <github-token>Note that --upload will only upload the targets that was built and stored in ./prebuilds, so prebuild -u <github-token> -b 4.3.0 will only upload the binary for the 4.3.0 target.
You can use prebuild --upload-all to upload all files from the ./prebuilds folder.
prebuild supports installing prebuilt binaries from GitHub by default. To install for your platform, use the --install flag.
$ prebuild --install
If no suitable binary can be found, prebuild will fallback to node-gyp rebuild. Native modules that have a javascript fallback can use --no-compile to prevent this.
Once a binary has been downloaded prebuild will require() the module and if that fails it will also fallback to building it.
Installed binaries are cached in your npm cache meaning you'll only have to download them once.
Add prebuild --install to your package.json so the binaries will be installed when the module is installed
{
"name": "a-native-module",
"scripts": {
"install": "prebuild --install"
},
"dependencies": {
"prebuild": "^4.0.0"
}
}If you are hosting your binaries elsewhere you can provide a host to the --install flag. The host string can also be a template for constructing more intrinsic urls. Install from example.com with a custom format for the binary name:
$ prebuild --install https://example.com/{name}-{version}-{abi}-{platform}-{arch}.tar.gz
--install will download binaries when installing from npm and compile in other cases. If you want prebuild to always download binaries you can use --download instead of --install. Either way, if downloading fails for any reason, it will fallback to compiling the code.
There's also support for node-pre-gyp style by utilizing the binary property in package.json.
The following placeholders can be used:
{name}or{package_name}: the package name taken frompackage.json{version}: package version taken frompackage.json{major}: major version taken fromversion{minor}: minor version taken fromversion{patch}: patch version taken fromversion{prerelease}: prelease version taken fromversion{build}: build version taken fromversion{abi}or{node_abi}: ABI version of node/iojs taken from current--targetorprocess.versionif not specified, seeABIsection below for more information{platform}: platform taken from--platformorprocess.platformif not specified{arch}: architecture taken from--archorprocess.archif not specified{configuration}:'Debug'if--debugis specified, otherwise'Release'{module_name}: taken frombinary.module_nameproperty frompackage.json
A GitHub token is needed for two reasons:
- Create a GitHub release (leveldown example)
- Upload the prebuilt binaries to that release
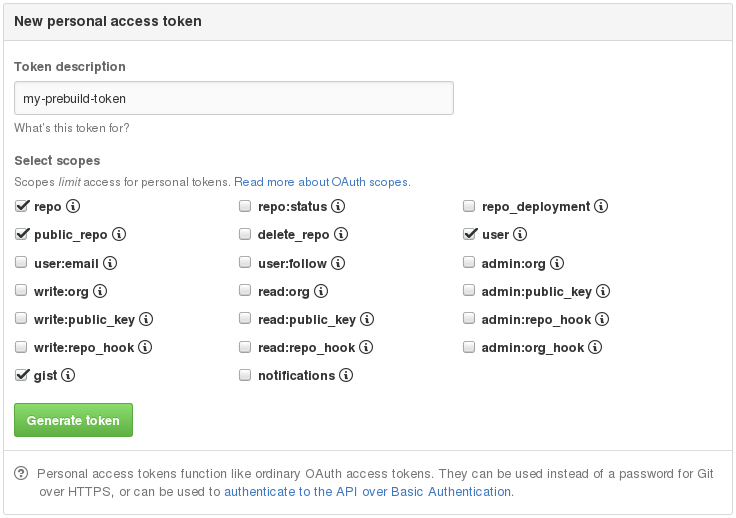
To create a token:
- Go to this page
- Click the
Generate new tokenbutton - Give the token a name and click the
Generate tokenbutton, see below
The default scopes should be fine.
$ prebuild -h
prebuild [options]
--path -p path (make a prebuild here)
--target -t version (version to build or install for)
--prebuild -b version (version to prebuild against)
--all (prebuild for all known abi versions)
--install (download when using npm, compile otherwise)
--download -d [url] (download prebuilds, no url means github)
--upload -u [gh-token] (upload prebuilds to github)
--upload-all -u [gh-token] (upload all files from ./prebuilds folder to github)
--preinstall -i script (run this script before prebuilding)
--compile -c (compile your project using node-gyp)
--no-compile (skip compile fallback when downloading)
--abi (use provided abi rather than system abi)
--backend (specify build backend, default is 'node-gyp')
--strip (strip debug information)
--debug (set Debug or Release configuration)
--verbose (log verbosely)
--version (print prebuild version and exit)
var prebuild = require('prebuild')Options:
.pkgthe parsedpackage.json.log(optional).nolocalDon't check for cached builds (optional).updateNameFunction to update the binary name (optional).pathLocation of the module (default:".").abiNode ABI version (default:process.versions.modules).platformOS platform (default:process.platform).downloadPrecomputed url to download the binary from (optional).all(default:false).force(default:false).proxy(default:process.env['HTTP_PROXY']).https-proxy(default:process.env['HTTP-PROXY'])`
Example:
prebuild.download({
pkg: require('./package.json')
}, function (err) {
// ...
})Options:
.log(optional).preinstall(optional).gypProvide a customnode-gypinstance (optional).backendProvide a customnode-gypinstance via string. Alternatives are'node-gyp'and'node-ninja'(optional, defaults to'node-gyp').argsAdditional command line arguments tonode-gyp(optional).debugPass in--debugon command line to gyp backend (optional)
Example:
prebuild.build({}, version, function (err) {
// ...
}).debugDownload or build a debug build (default:false).archProcessor architecture (default:process.arch)
If you want to hack on prebuild you need an environment to play around with. We recommend a setup similar
to the following:
- A fork of
prebuild - A GitHub token (see above)
- A native node module
$ git clone git@github.com:<your-nick>/prebuild
$ cd prebuild && npm link && cd ..
$ git clone git@github.com:<your-nick>/some-native-moduleSince you did npm link on prebuild it will be installed globally. Now you can go ahead and try things out.
$ cd some-native-module
$ prebuild --all --strip -u <github-token>This command would:
- Build
some-native-modulefor all targets listed intargets.jsand store them in./prebuilds/ - Strip binaries from debug information
- Create a release on GitHub, if needed
- Upload all binaries to that release, if not already uploaded
Before you commit your changes and send us a pull request, do run npm test.
MIT