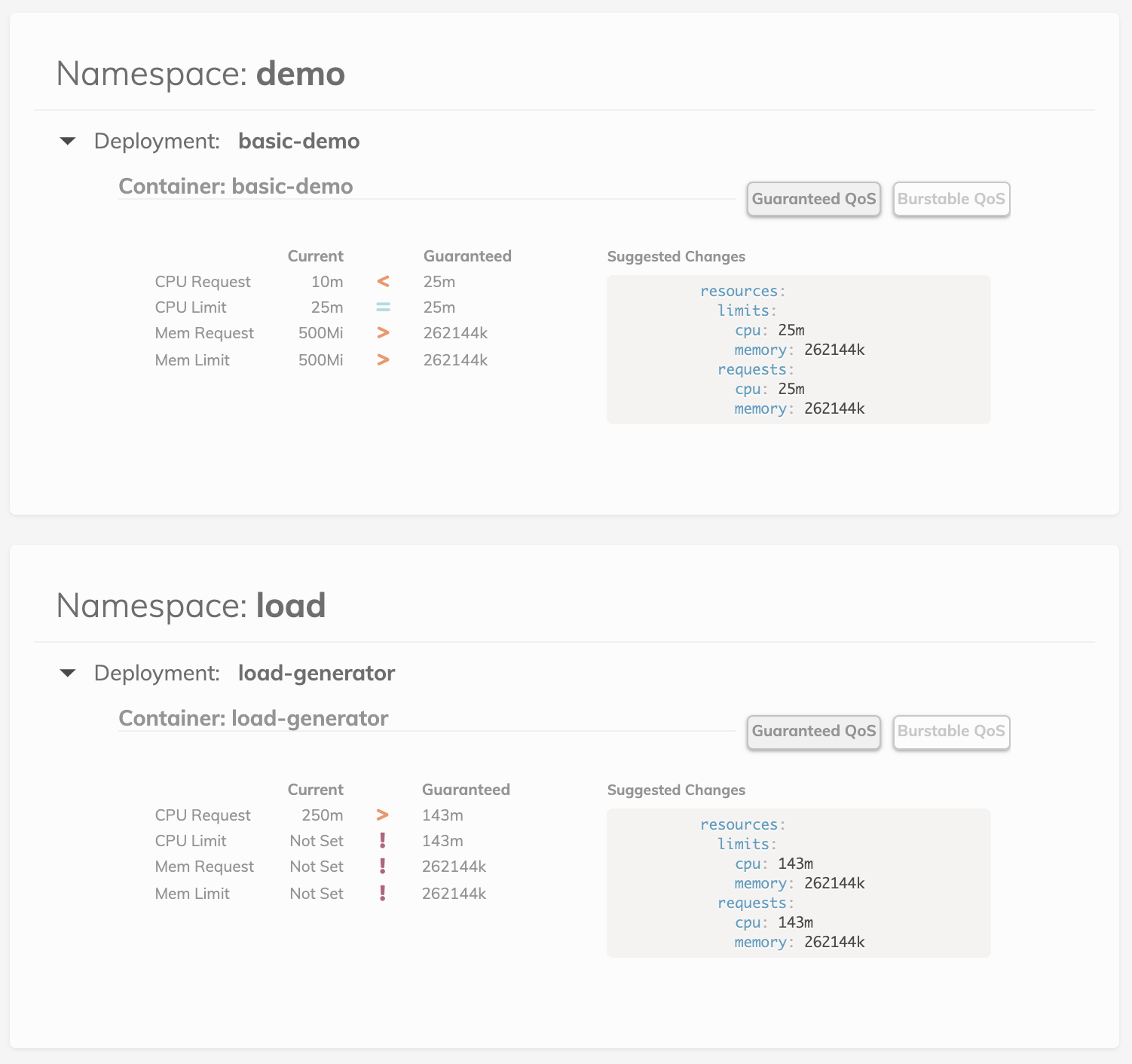
By using the kubernetes vertical-pod-autoscaler in recommendation mode, we can see a suggestion for resource requests on each of our apps. This tool creates a VPA for each deployment in a namespace and then queries them for information.
Once your VPAs are in place, you'll see recommendations appear in the Goldilocks dashboard:
Want to learn more? Reach out on the Slack channel (request invite), send an email to opensource@fairwinds.com, or join us for office hours on Zoom
- kubectl
- vertical-pod-autoscaler configured in the cluster
- some deployments with pods
- metrics-server (a requirement of vpa)
- golang 1.11+
There are multiple ways to install VPA for use with Goldilocks:
- Install using the
hack/vpa-up.shscript from the vertical-pod-autoscaler repository - Set the value
installVPA=truewhen doing the Helm chart installation of Goldilocks. This will run the script from VPA in your cluster.
The full VPA install includes the updater and the admission webhook for VPA. Goldilocks only requires the recommender. An admission webhook can introduce unexpected results in a cluster if not planned for properly. We recommend installing using the chart v2.0.0 or higher, which will only install the parts of VPA necessary for Goldilocks to function.
VPA does not require the use of prometheus, but it is supported.
Google has provided the vertical pod autoscaler as a beta feature in GKE. You can see the docs here, or just enable it like so:
gcloud beta container clusters update [CLUSTER-NAME] --enable-vertical-pod-autoscaling
NOTE: This does not support using prometheus as a data backend.
First, make sure you satisfy the requirements above.
helm repo add fairwinds-stable https://charts.fairwinds.com/stable
helm install --name goldilocks --namespace goldilocks fairwinds-stable/goldilocks
The hack/manifests directory contains collections of Kubernetes YAML definitions for installing the controller and dashboard components in cluster.
kubectl create namespace goldilocks
kubectl -n goldilocks apply -f hack/manifests/controller
kubectl -n goldilocks apply -f hack/manifests/dashboard
Pick an application namespace and label it like so in order to see some data:
kubectl label ns goldilocks goldilocks.fairwinds.com/enabled=true
After that you should start to see VPA objects in that namespace.
The default installation creates a ClusterIP service for the dashboard. You can access via port forward:
kubectl -n goldilocks port-forward svc/goldilocks-dashboard 8080:80
Then open your browser to http://localhost:8080
The CLI was originally developed to test the features of Goldilocks. While the CLI is still present and somewhat functional, we do not generally recommend using it. The CLI is scoped to a single namespace per run (meaning you would have to run it multiple times), and it will not automatically clean up any VPA objects that are created. The controller is a much better option, as it will monitor for changes and keep the list of VPA objects up-to-date. In addition, the controller will allow keeping multiple namespaces up to date.
The CLI summary function shoul still be useful. It runs the same summary output that the dashboard uses, and can generate a JSON object that can be used elsewhere.
A tool for analysis of kubernetes deployment resource usage.
Usage:
goldilocks [flags]
goldilocks [command]
Available Commands:
controller Run goldilocks as a controller inside a kubernetes cluster.
create-vpas Create VPAs
dashboard Run the goldilocks dashboard that will show recommendations.
delete-vpas Delete VPAs
help Help about any command
summary Genarate a summary of the vpa recommendations in a namespace.
version Prints the current version of the tool.
Flags:
--alsologtostderr log to standard error as well as files
-h, --help help for goldilocks
--kubeconfig string Kubeconfig location. [KUBECONFIG] (default "$HOME/.kube/config")
--log_backtrace_at traceLocation when logging hits line file:N, emit a stack trace (default :0)
--log_dir string If non-empty, write log files in this directory
--log_file string If non-empty, use this log file
--log_file_max_size uint Defines the maximum size a log file can grow to. Unit is megabytes. If the value is 0, the maximum file size is unlimited. (default 1800)
--logtostderr log to standard error instead of files (default true)
--master string The address of the Kubernetes API server. Overrides any value in kubeconfig. Only required if out-of-cluster.
--skip_headers If true, avoid header prefixes in the log messages
--skip_log_headers If true, avoid headers when opening log files
--stderrthreshold severity logs at or above this threshold go to stderr (default 2)
-v, --v Level number for the log level verbosity
--vmodule moduleSpec comma-separated list of pattern=N settings for file-filtered logging
Use "goldilocks [command] --help" for more information about a command.
This starts the goldilocks controller. Used by the Docker container, it will create vpas for properly labelled namespaces.
You can set the default behavior for VPA creation using some flags. When specified, labels will always take precedence over the command line flags.
--on-by-default- create VPAs in all namespaces--include-namespaces- create VPAs in these namespaces, in addition to any that are labeled--exclude-namespaces- when--on-by-defaultis set, exclude this comma-separated list of namespaces
Namespaces are considered enabled or managed by goldilocks when the Namespace has the enabled label set to "true", for example:
kubectl label ns goldilocks goldilocks.fairwinds.com/enabled=true
Note: This feature is for advanced usage only and is not recommended nor the default!
VPAs created for Deployments in a Namespace have an update mode of "off" by default, meaning the VPAs only report recommendations and do not actually auto-scale the Pods.
The update mode can be changed for a namespace by labels as well, for example:
kubectl label ns goldilocks goldilocks.fairwinds.com/vpa-update-mode="auto"
If you want a specific Deployment to have a VPA in a specific update mode,
then you can annotate the Deployment with goldilocks.fairwinds.com/vpa-update-mode=<mode>
to control the update mode for a specific Deployment in a Namespace (regardless of labeling on the Namespace).
goldilocks create-vpas -n some-namespace
This will search for any deployments in the given namespace and generate a VPA for each of them. Each vpa will be labelled for use by this tool.
This will delete all vpa objects in a namespace that are labelled for use by this tool.
goldilocks dashboard
Runs the goldilocks dashboard server that will display recommendations. Listens on port 8080 by default.
goldilocks summary
Queries all the VPA objects that are labelled for this tool across all namespaces and summarizes their suggestions into a JSON object.
The dashboard and summary commands can exclude recommendations for a list of comma separated container names using the --exclude-containers argument. This option can be useful for hiding recommendations for sidecar containers for things like Linkerd and Istio.
Containers can be excluded for individual deployments by applying a label to any deployment. The label value should be a list of comma separated container names. The label value will be combined with any values provided through the --exclude-containers argument.
Example label:
kubectl label deployment myapp goldilocks.fairwinds.com/exclude-containers=linkerd-proxy,istio-proxy