cniic (pronounced "C"-nic) is a Compilation of Naive Ideas for Image Compression.
Have you ever asked yourself the following question?
If I didn't know about the existing efficient image compression techniques and formats, how would I go about compressing an image?
Well, I did. And this is my attempt at an answer.
This repo implements a number of naive solutions to the general problem of image compression and measures their performance.
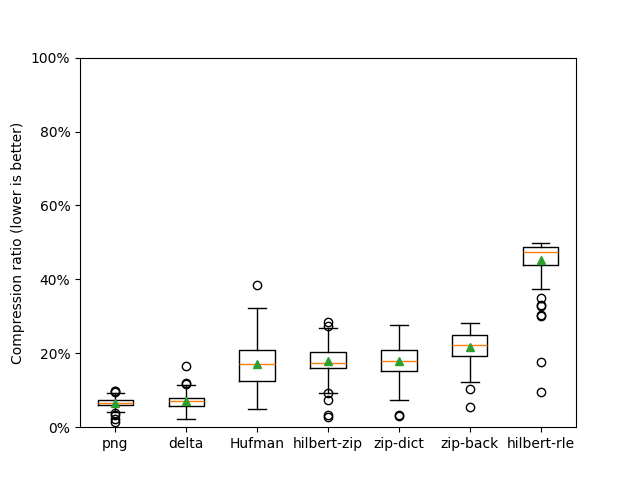
Legend:
png: The lossless PNG codec with default parametersHufman: Hufman-coding the pixel colorszip-dict: Zip-inspired online dictionary buildingzip-back: Zip-inspired lookback compressionhilbert-rle: Run-Length Encoding on a Hilbert curve traversalhilbert-zip:zip-dicton a Hilbert curve traversaldelta: Hufman encode neighbouring pixel differences
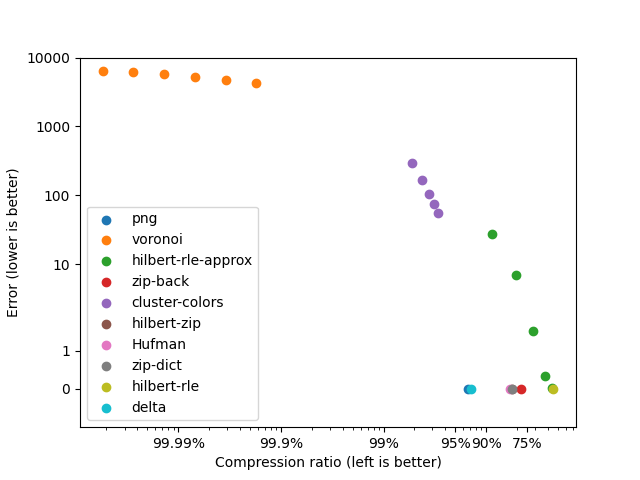
The error is computed as the mean square error of each pixel in every image.
Legend:
png: The lossless PNG codec with default parametersHufman: Hufman-coding the pixel colorscluster-colors: cluster the image colors using K-means, then apply Hufman-coding- results are shown for 16 colors (top-left), 32, 64, 128 and 256 (bottom-right)
voronoi: cluster the pixels using K-means (position + color). Store only the clusters and reconstruct the image as a Voronoi diagram.- results are shown for 64 centroids (left), 128, 256, 512, 1024 and 2048 (right)
zip-dict: Zip-inspired online dictionary buildingzip-back: Zip-inspired lookback compressionhilbert-rle: Run-Length Encoding on a Hilbert curve traversalhilbert-rle-approx: Approximate Run-Length Encoding on a Hilbert curve traversal- running average with an allowed color distance of 1 (bottom right), 2, 4, 8, 16 (top left)
hilbert-zip:zip-dicton a Hilbert curve traversaldelta: Hufman encode neighbouring pixel differences
Who doesn't love ASCII art? In this section, it's used to help explain the various codecs listed above.
input: 0x01 0x02 0x01 0x02 0x01 0x02 0x0001 -> 0x01
| | ^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^ ...
| | | | 0x00ff -> 0xff
v v v v +...> 0x0100 -> 0x01 0x02
output: 0x0001 0x0002 0x0100 0x0100 : 0x0101 -> 0x0100 0x0100
^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ : ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^
+............................+ = 0x01 0x02 0x01 0x02
.................................
v v v v :
:
................. :
v v v v : :
input: 0x01 0x01 0x02 0x02 0x01 0x02 0x01 0x01
[^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^][^^^^^^^^^][^^^^^^^^^]
output: | | |
1. Write the sequence: ---+ | |
0x01 0x01 0x02 0x02 | |
2. Go back 3 bytes ----------------------+ |
Copy 2 bytes |
3. Go back 6 bytes ----------------------------------+
Copy 2 bytes
Hilbert input
traversal image
+----------+
5--6 9--a |6 8 7 7|
| | | | | |
4 7--8 b |6 8 7 8|
| | | |
3--2 d--c |7 5 9 9|
| | | |
0--1 e--f |3 3 8 9|
+----------+
| |
+---------+---------+
|
v
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
+-------------------------------+
|3 3 5 7 6 6 8 8 7 7 7 8 9 9 8 9|
+-------------------------------+
|
+--> hilbert-rle
|
| [3 3] [5] [7] [6 6] [8 8] [7 7 7] [8] [9 9] [8] [9]
| | | ...
| v v
| 2x3 1x5 1x7 2x6 2x8 3x7 1x8 2x9 1x8 1x9
|
|
+--> hilbert-rle-approx
| assuming allowance = 1
|
| idx value distance output running-avg
| 0 3 no 3
| 1 3 abs(3 - 3) = 0 < 1 no 3
| 2 5 abs(3 - 5) = 2 > 1 2x3 5
| 3 7 abs(5 - 7) = 2 > 1 1x5 7
| 4 6 abs(7 - 6) = 1 no 6.5
| 5 6 abs(6.5-6) = .5 < 1 no 6.33
| 6 8 1.66 > 1 3x6 8
| .
| .
| .
|
| output: 2x3 1x5 3x6 6x8 4x9
|
|
+--> hilbert-zip
3 3 5 7 6 6 8 8 7 7 7 8 9 9 8 9
|
zip-dict
|
v
0x0003 0x0003 0x0005 0x0007 0x0006 ...
Hilbert input
traversal image
+----------+
5--6 9--a |6 8 7 7|
| | | | | |
4 7--8 b |6 8 7 8|
| | | |
3--2 d--c |7 5 9 9|
| | | |
0--1 e--f |3 3 8 9|
+----------+
| |
+---------+---------+
|
v
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
+------------------------------------------------+
| 3 3 5 7 6 6 8 8 7 7 7 8 9 9 8 9 |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
difference with previous
|
v
+------------------------------------------------+
| 3 0 2 2 -1 0 2 0 -1 0 0 1 1 0 -1 1 |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
Hufman encoding -----------v
| *
| 0 / \ 1
| / \
| 0 *
| 0 0 / \ 1
| / \
| * *
| 0 / \ 1 0 / \ 1
| / \ / \
| -1 1 2 3
| 100 101 110 111
|
v
output: 111 0 110 110 100 0 110 0 100 0 0 101 101 0 100 101