What are you sinking about?
Sinker is middleware that synchronizes relational data from a Postgres database to Elasticsearch. It is simple to operate, requires minimal RAM, and handles arbitrarily complex schemas. Sinker is built by Paradigm, and is licensed under the Apache and MIT licenses.
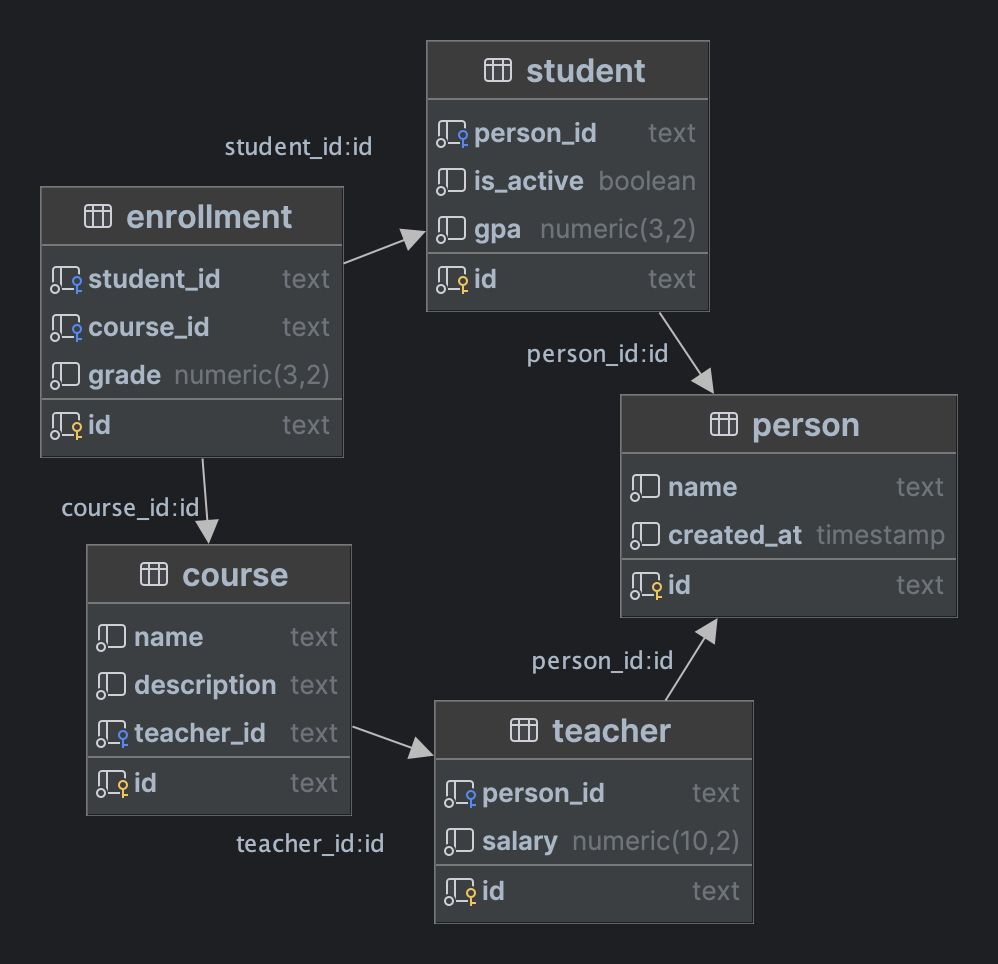
In Postgres, you might have a normalized schema like this:
- A Student and a Teacher refer to a Person
- A Course is taught by a Teacher
- Students have and belong to many Courses through the Enrollment join table
In Elasticsearch, you might want to index the Course data in an index called courses like this:
{
"name": "Reth",
"description": "How to build a modern Ethereum node",
"teacher": {
"salary": 100000.0,
"person": {
"name": "Prof Georgios"
}
},
"enrollments": [
{
"grade": 3.14,
"student": {
"gpa": 3.99,
"person": {
"name": "Loren"
}
}
},
{
"grade": 3.50,
"student": {
"gpa": 4.00,
"person": {
"name": "Abigail"
}
}
}
]
}Now you can easily query Elasticsearch for courses taught by Prof Georgios, or students with high GPAs named Loren. To do this, you need to do two things reliably:
- Denormalize the normalized data from the five Postgres tables into a single Elasticsearch document with the Course as the parent and the other four tables nested appropriately inside it.
- Keep the Elasticsearch document in sync with the Postgres data, so that if Abigail changes her name in the database
to Abby, it's reflected in the
Course->Enrollments->Student->Person.namefield.
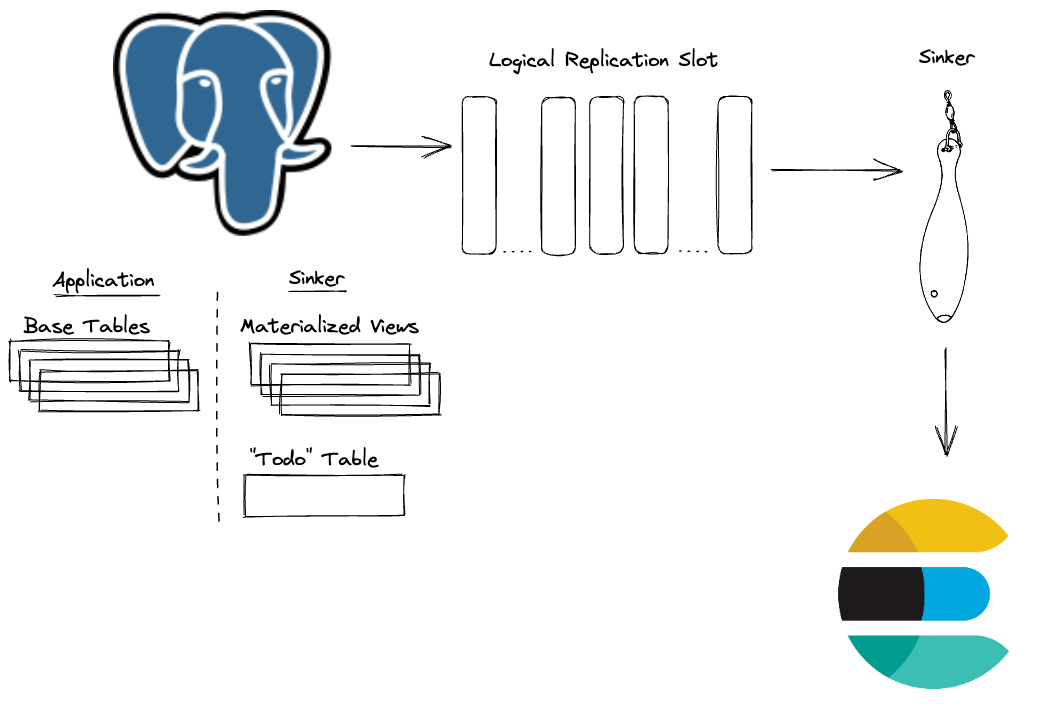
Sinker transforms the normalized Postgres data into JSON documents stored in a simple key-value materialized view where the key is the Elasticsearch document ID and the value is the JSON document to be stored in Elasticsearch.
Sinker creates triggers on the Postgres tables that you want to synchronize (e.g., the five tables in the example above). When a row is inserted, updated, or deleted in any of these tables, the trigger schedules the materialized view to be refreshed at the next interval.
The changes to the materialized view are sent to a logical replication slot. Sinker reads from this slot and indexes the documents in Elasticsearch.
You define the query behind the materialized view, so you can denormalize the data however you want, filter out unwanted documents, transform some fields, etc. If you can express it in SQL, you can build your materialized view around it.
You also configure the Elasticsearch index settings and mappings however you like.
pip install sinkerHere are some of the environment variables that you'll want to set:
| Environment Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| SINKER_DEFINITIONS_PATH | . |
| SINKER_SCHEMA | public |
| SINKER_POLL_INTERVAL | 10 |
| SINKER_LOG_LEVEL | DEBUG |
| PGPASSWORD | secret! |
| PGHOST | localhost |
| PGUSER | dev |
| PGDATABASE | dev_db |
| ELASTICSEARCH_HOST | localhost |
| ELASTICSEARCH_SCHEME | http |
See sinker/settings.py for the full list.
Sinker's main configuration file views_to_indices.json specifies the mapping between the root Postgres materialized
view names and the Elasticsearch indexes that will get populated by them, e.g.:
{
"person_mv": "people",
"course_mv": "courses"
}This tells Sinker to define a Postgres materialized view called person_mv based on the query in the person_mv.sql
file and an Elasticsearch index called people based on the settings and mappings in the people.json file. It will
then populate the people index with the documents from the person_mv materialized view. It will then do the same for
the course_mv materialized view and the courses index.
The person_mv materialized view is defined by the SQL in the person_mv.sql file, e.g.:
select id, json_build_object('name', "name") as "person"
from "person"The course_mv SQL is more complex, but you can see how it denormalizes the data from the five tables into a single
JSON document:
select id,
json_build_object(
'name',
"name",
'description',
"description",
'teacher',
(select json_build_object(
'salary',
"salary",
'person',
(select json_build_object('name', "name")
from person
where person.id = person_id)
)
from teacher
where teacher.id = teacher_id),
'enrollments',
(select json_agg(
json_build_object(
'grade',
"grade",
'student',
(select json_build_object(
'gpa',
"gpa",
'person',
(select json_build_object('name', "name")
from person
where person.id = person_id)
)
from student
where student.id = student_id)
)
)
from enrollment
where enrollment.course_id = course.id)
) as "course"
from "course";The Elasticsearch index configurations are stored in the people.json and courses.json files, e.g.:
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
}
}
}Using strict mappings helps ensure the JSON document structure from the materialized view matches what Elasticsearch
expects in the index.
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"enrollments": {
"properties": {
"grade": {
"type": "float"
},
"student": {
"properties": {
"gpa": {
"type": "float"
},
"person": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"teacher": {
"properties": {
"person": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"salary": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
}
}
}Before running sinker, do a dry run on one of your view-index mappings to verify everything is defined correctly:
- Execute the SQL query with
LIMIT 1in the materialized view definition file to see what a sample JSON record will look like. - Create the destination Elasticsearch index with the settings and mappings in the index configuration file.
- In Kibana or via cURL,
PUTthe sample JSON record into the Elasticsearch index. - Verify the record is indexed as you expect in Elasticsearch.
Once you have the environment variables and configuration files set up, you can run Sinker with:
sinkerOnce you have Sinker running, you may well want it to run faster. Here are some things you can do to improve performance:
- Decrease
SINKER_POLL_INTERVAL. This will make Sinker refresh the materialized views more frequently (and thus keep Elasticsearch in closer sync), but it will also increase the load on the database. Note that the materialized views are only refreshed when one of the underlying tables has changed, so this won't increase the load on the database if there are no changes. - Increase the
PGCHUNK_SIZE. This will make Sinker read more rows from the logical replication slot at a time, which will reduce the number of round trips to the database. However, it will also increase the memory usage of Sinker. - Increase the
ELASTICSEARCH_CHUNK_SIZE. This will make Sinker index more documents in a single Elasticsearch bulk request, which will reduce the number of round trips to Elasticsearch. However, it will also increase the memory usage of Sinker and the CPU load on the Elasticsearch cluster. - Run
EXPLAIN ANALYZEon your materialized view queries to see if you can optimize them (e.g., by adding indexes on the foreign keys).
Before getting started, make sure you have poetry
and docker-compose installed.
% docker-compose --version
Docker Compose version v2.15.1
% poetry --version
Poetry (version 1.4.0)Clone the repo:
git clone git@github.com:paradigmxyz/sinker.git
cd sinkerInstall dependencies:
poetry installSpin up Postgres and Elasticsearch:
docker-compose --env-file=.env.test up -dRun tests:
poetry run pytest -sTo run Sinker as a Docker container, you can use the docker/ files in this repo as a starting point.
Bundle your views and indices configuration files into the Docker image, set up your environment variables, and deploy.
Setting up monitoring and alerting will give you confidence that Sinker is functioning properly. For instance, you can periodically check that the row counts in Postgres match the expected document counts in Elasticsearch.
Contributions are welcome! Please open an issue or submit a pull request.
Sinker was inspired by pgsync and debezium. Each project takes a different approach to the problem, so check them out to see which one is best for you.