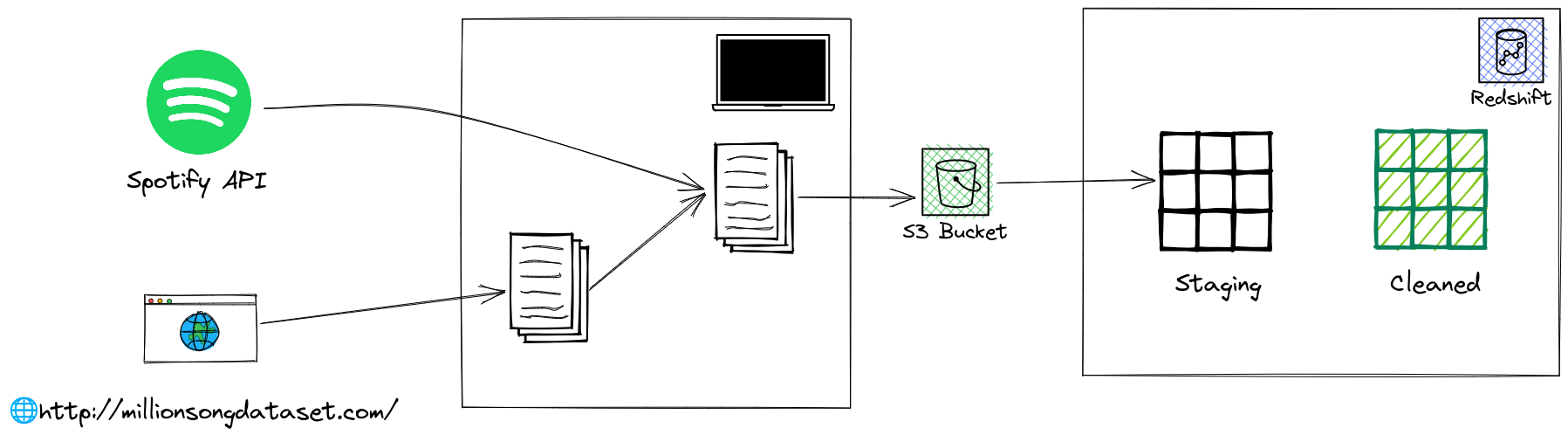
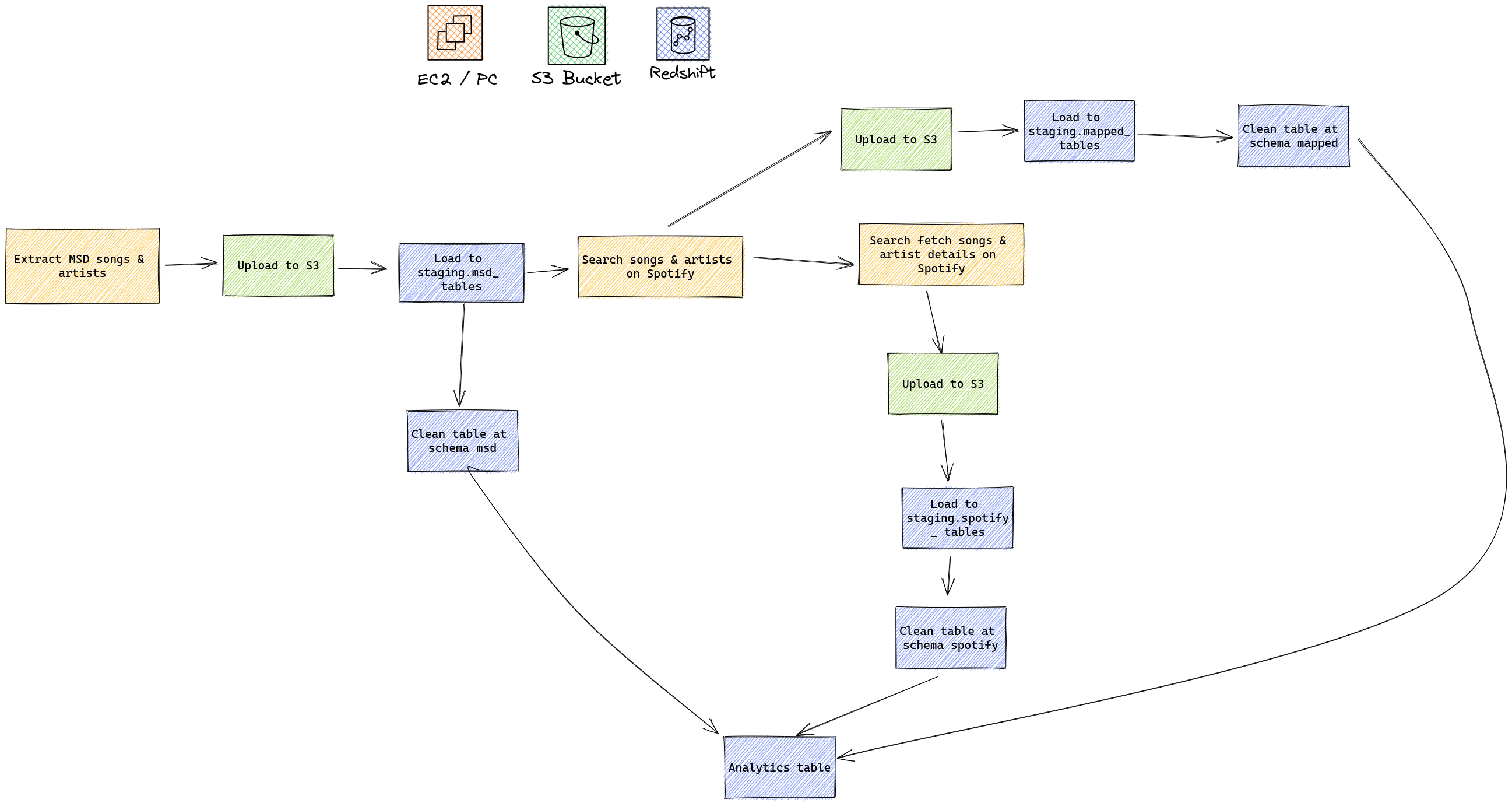
With this project, I aim to combine the real Million Song Dataset with data coming from Spotify API. With this pipeline, new researchers that are already familiar with the old Million Song Dataset to get new information for all the songs in Spotify, like new audio features, song popularity, artist popularity...
- Data sources:
- Million Song Dataset: We will use the actual MSD dataset in its original data format (HDF5). The full dataset (280 GB) can be accessed via AWS marketplace, and for development purpose we will use their subset (1.8 GB)
- Spotify API
- Data storage:
- Amazon S3: for JSON data staging
- Amazon Redshift: for final analytics table storage. In reality, this is also the place where end-users query the final data tables for analytics purposes, so a database that can handle large query workload is necessary
- Orchestrator: Prefect. This is a new workflow orchestrator that are simpler to deploy and use than Airflow. It is also easier to use thanks to the syntax being closer to Python's syntax.
- Processing:
- Amazon EC2: For production, we need to access the MSD dataset on Amazon Workspace, and EC2 is needed to do that.
- Personal computer: for development purpose, it is sufficient to run everything in a personal machine.
- Terraform: for easy infrastructure set up.
-
At the moment, the flow is configured to run for one time only.
-
In case we want to regularly update the songs & artists list, instead of using the Million Song Dataset, we can figure out a way to get updated songs & artists list on Spotify.
-
Overview of the workflow:
Please refer to the Set Up Guide.
Please refer to the Data Dictionary file.
Currently the pipeline is built purely on Python, and use the SequentialTaskRunner of Prefect. For larger data volume, we may need to add some other elements to the pipeline, depending on the use cases. For example:
- Consider storing more data in one big file instead of separating into multiple small files.
- Consider other format to store the source files before bringing them into Redshift (for example, Parquet). May be create external tables to read directly from S3-stored Parquet files instead of loading to Redshift?
- Introduce parallelism: build some parts of the ETL in Spark (for example, the staging & analytics transformation steps), or switch to the ConcurrentTaskRunner of Prefect, and run the flow in a stronger EC2 instance.
We will need to create a Prefect deployment that is scheduled to run daily at 7am, and have to modify the tasks to run incremental updates (instead of dropping all tables and create from scratch)
In this case, we will need to pay extra attention to the query pattern of the users and create tables with correct distribution types to optimize the query performance, especially for JOIN operations. For example:
- For fact / event tables, most likely users will want to filter by time columns, so we can choose time fields as sort keys
- For dimension tables like songs or atists, people may want to query by certain dimensions like genre, available markets etc... so it may be a good idea to check which dimension has even data distribution and use them as DISTKEY
Assume that you have set up all resources via Terraform and filled in config.cfg file:
```bash
make setup-env
make download-msd-subset
make extract-msd-data
make run-etl-dev
```
If you run the terraform scripts in the terraform/prod folder, you can connect to the EC2 instance via the AWS console and access the Million Song Dataset at /mnt/snap/. When logged in, do the following:
-
Clone this repo
-
Update the
config.cfgfile. Make sure to setMSD_INPUT_DIR = /mnt/snap/data -
Run commands:
make setup-env make download-msd-subset make extract-msd-data make run-etl-prod