ExoPlayer Example
ExoPlayer is an alternative to Android's MediaPlayer API for playing Video and Audio locally as well as over the internet. In this repository I will be adding most of the ExoPlayer features and will compare with MediaPlayer API. Built with Android Architecture Components. ExoPlayer support DASH and SmoothStreaming adaptive playbacks over Android’s MediaPlayer API.
Advantages of ExoPlayer
- Player Customization
- Playlist Creation
- Video Clipping
- Video Looping
- Video Subtitle
- Support DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)
- SmoothStreaming with FMP4 container (Adaptive Bitrate Streaming)
- Advance HLS (HTTP Live Streaming)
- Widevine common encryption
- Interactive Media Ads SDK
Supported Device
- FireOS (version 4 and earlier)
- Nexus Player (only when using an HDMI to DVI cable)
- Emulators (system image has an API level of at least 23)
Player Components
Types of Media Source
- ProgressiveMediaSource - progressive media files
- DashMediaSource - DASH
- SsMediaSource - SmoothStreaming
- HlsMediaSource - HLS
- SingleSampleMediaSource - loading single media sample, side-loaded subtitle files
- MergingMediaSource - merge multiple media source, playlist
- LoopingMediaSource - loop
- ClippingMediaSource - clip
- ConcatenatingMediaSource - concat
Types of Renderers
- MediaCodecVideoRenderer
- MediaCodecAudioRenderer
- TextRenderer
- MetadataRenderer
Type of TrackSelector
- DefaultTrackSelector
Type of LoadControl
- DefaultLoadControl
Threading Model
Application thread for ExoPlayer instance must be use. Needed for ExoPlayer's UI components or the IMA extension. Looper can be accessed using Player.getApplicationLooper(). Listener also work on same thread. Internal thread for playback.
Player States
- ExoPlayer.STATE_IDLE
- ExoPlayer.STATE_BUFFERING
- ExoPlayer.STATE_READY
- ExoPlayer.STATE_ENDED
EventLogger
EventLogger:state[eventTime=0.10, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, true, IDLE]EventLogger:seekStarted[eventTime=0.10, mediaPos=0.00, window=0]EventLogger:positionDiscontinuity[eventTime=0.10, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, SEEK]EventLogger:timeline[eventTime=0.16, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, periodCount=1, windowCount=1, reason=PREPARED period [?] window [?, false, false] ]EventLogger:seekProcessed[eventTime=0.16, mediaPos=0.00, window=0]EventLogger:surfaceSize[eventTime=0.25, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, 1080, 792]EventLogger:loading[eventTime=0.26, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, period=0, true]EventLogger:tracks[eventTime=2.22, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, period=0, []]EventLogger:isPlaying[eventTime=2.37, mediaPos=0.00, window=0, period=0, true]
Advanced Media Source
ConcatenatingMediaSource
Helps to create heterogeneous playlist
ConcatenatingMediaSource(mediaSource1, mediaSource2, mediaSource1, mediaSource2)
Tags when item changes in playlist
Player.DISCONTINUITY_REASON_PERIOD_TRANSITION- when automatically change from one item to nextPlayer.DISCONTINUITY_REASON_SEEK- when call player.nextPlayer.TIMELINE_CHANGE_REASON_DYNAMIC- when item added, removed or moved
getCurrentTag() - To check which items in playling on the player.
MergingMediaSource
MergingMediaSource(mediaSource, subtitleSource)
The Timeline of the sources being merged must have the same number of periods. Mostly use to merge video with their subtitles.
LoopingMediaSource
LoopingMediaSource(mediaSource, 2)
Pass the loop count and this will loop the given media source that number of times.
ClippingMediaSource
ClippingMediaSource(mediaSource, 120000000, 150000000)
Pass the media source and start and end position in microseconds from where you have to clip the video.
What is DASH
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) so what is Adaptive Streaming first? Also known as Adaptive Bitrate Streaming, (bitrate - speed of the internet connection) it is a technique to stream multimedia. What it does differently is it detect's the user bandwidth and machine capacity and adjust the media quality based on it.

Let's understand the problem Earlier days we have something called progressive streaming. Let's understand this with an example. Suppose we have a video file 1280*720px on our server. People with different screen resolution, sizes will now stream this video.
- Screen with 1920*1080px, video is too small
- Screen with 1280*720px, video will play ok
- Screen with 854*480px, video is too large
Second problem is Buffering Video provider creates file according to the screen size. This solves the first problem. For Slow and Fast internet, adaptive video stream switch to lower file type which will give user no buffering situation in slow internet. Encoder broke the video in multiple segments of 2-4secs long, and at the end of a segment based on user bandwidth, segment can be switch to lower or upper quality.
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP also known as MPEG-DASH, the media file broken into the multiple segments and are provided over HTTP. This uses bit rate adaptation (ABR) algorithm.
There are .mpd files, MPEG-DASH Media Presentation Description, which consist of Period which has information of different view angles or with different codecs, audio components for different languages or with different types of information, subtitle or caption components and much more in deep.
What is SmoothStreaming
Smooth Streaming seems like streaming but it is HTTP progressive download. This is developed by Microsoft.
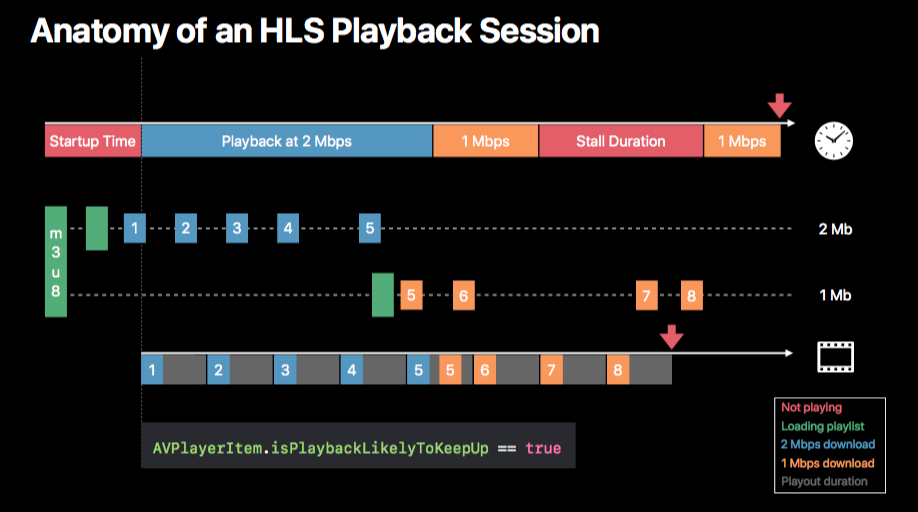
What is HLS
HTTP Live Streaming by Apple, is a media streaming protocol to deliver content across internet. M3U (or M3U8) is a plain text file format developed to organize mp3 files. Two type of M3U8 file,
- Master playlist - URLs to media playlists
- Media playlist - URLs of the files (chunks) needed for streaming
Implementation
ExoPlayer with Notification
BasicAudioPlayerWithNotification here, I had started a Service to play audio, also when app is not visible to the user, that is in background. It shows the media controls in notification panel. Screen has player view to control the playlist and also views to show the title, description and image of the current playing song. Used LiveData. Need to update.
Screenshot 📱
Service in Android
One of the Android Component. Other android component can start service and also bind with it to interact with it (IPC). Service runs in the main thread. It does not create its own thread. Recommended to create different and leaving main for user interaction.
Three typs of service
- Foreground - must have notification, user interaction
- Background - no user interaction
- Bound - calling
bindService(), allows components to interact with the service. If unbind, serivce will destroy
Important methods
startService()- When any component wants to start a servicebindService()- When any component wants to bind to a service for IPC, use of interface and return IBinder to component.onCreate()- system calls this to when service initiatedonDestroy()- system calls when service destroy, must clean everything herestopSelf()- if any component started a service usingstartService(), it must stop with this method
android:exported=fasle - start your service by yourself and stop other to access it.
How system restart when service kills?
START_NOT_STICKY- If there are pending intents left, do no recreateSTART_STICKY- recreate the service, last result will be lost, suitable for media playersSTART_REDELIVER_INTENT- recreate the service and deliver the last result
Service can use the broadcast to deliver a result to component it started. LocalBroadcastManager
Bound Service
ServiceConnection - onServiceConnected() get called by system as soon as the connection gets done in client and service, after we bind the service bindService() and get the IBinder as an argument to communicate with service.