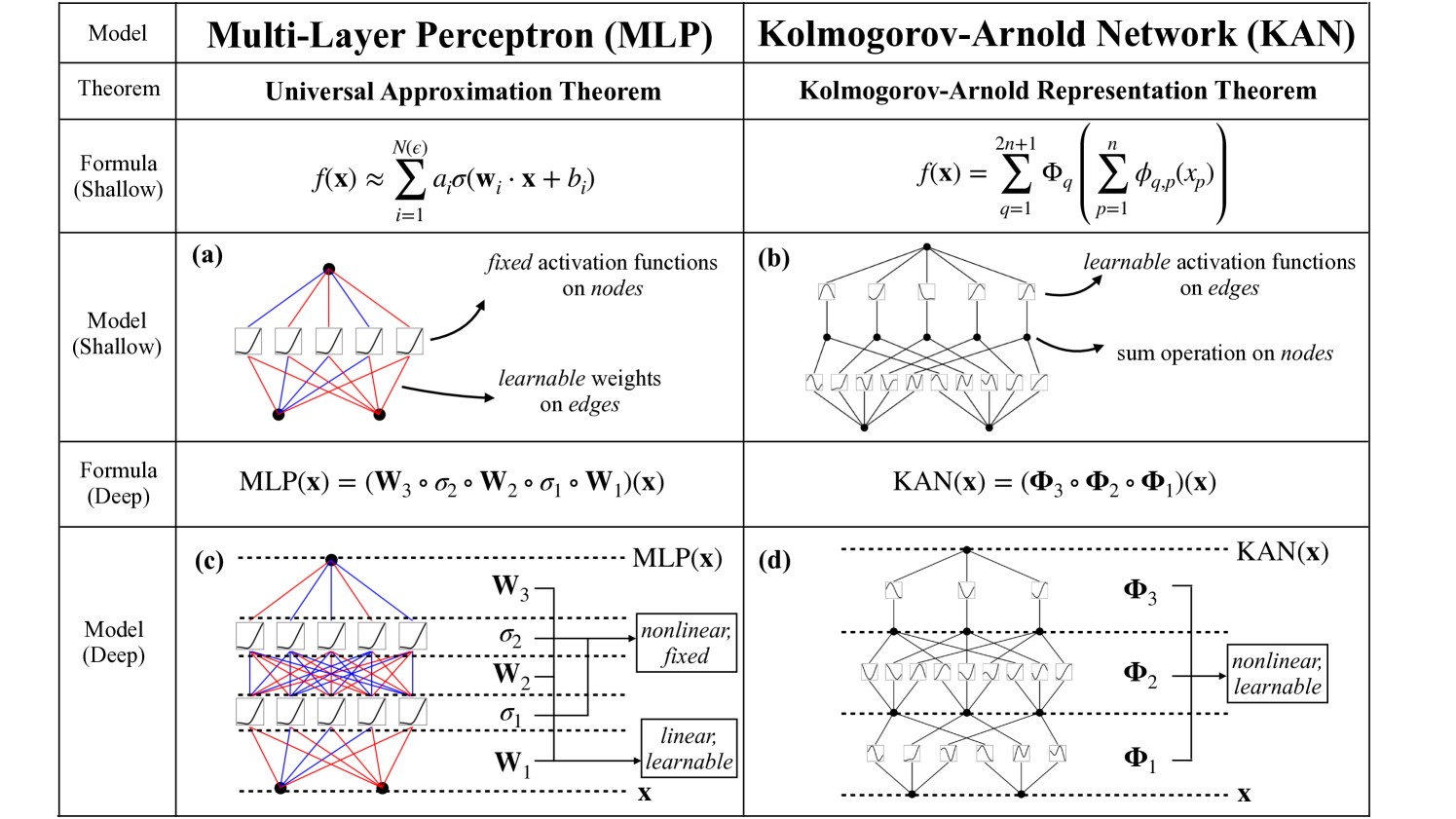
This github repo purpose is try to reimplement the KANs model and its experiments
Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks have emerged and become a phenomenon recently. Therefore, to catch up with the world, me and my team have tried to dig deep into this special network to deep down understand it. Many things have been explained quite clear in the paper1, but there were some points we need to dive to the repo of KindXiaoming2 to truely understand it. To make sure we have understand those points, we have try to reimplement it. And this is how this repo come to the world.
We have implemented some basic structure of KANs some of it can be listed here:
- Implement basic of KANs.
- Sparsification regularization.
- Pruning.
Also we have implemented basic MLP network for comparison.
First you need to clone this repo. then run the following line:
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you want to use gpu, please following the instruction at https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/ to install cuda
After that, depend on what you want to do, we would have some features:
- To train a KAN model, run this command:
python .\src\train_kan.py- The model after training is saved in ckpt folder with format. Day, month, year, hour, minute, second indicate the time it is saved.
KAN_day_month_year_hour_minute_second.pth- You can config your model parameters to fit your desire in configs\model\kan_cf.yaml:
| Parameter Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Model | G | Number of grids of an activation |
| Model | k | The degree of an activation |
| Model | width | Number of nodes |
| Model | b | Basis function |
| Model | default_grid_range | Range that activations function work |
| Model | threshold | Threshold to prune |
| Optimizer | is_lbfgs | If this is True, KAN will train with lbfgs. If this is false, KAN will train with Adam |
| Optimizer | lr | Learning rate |
| Loss | loss_func | Loss function to calculate loss |
| Loss | lamb | λ in 2.203 in the paper1 |
| Loss | lamb_l1 | μ1 in 2.203 in the paper1 |
| Loss | lamb_entropy | μ2 in 2.203 in the paper1 |
- To train a MLP model, run this command:
python .\src\train_mlp.py- The model after training is saved in ckpt folder with format. Day, month, year, hour, minute, second indicate the time it is saved.
MLP_day_month_year_hour_minute_second.pth- You can config your model parameters to fit your desire in configs\model\mlp_cf.yaml:
| Parameter Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Model | width | number of nodes each layer |
| Model | activation_class | activation function |
| Optimizer | is_lbfgs | If this is True, MLP will train with lbfgs. If this is false, MLP will train with Adam |
| Optimizer | lr | Learning rate |
-
If you want to train with another function, you can go to src\train_kan.py and change the parameter of data_module to adjust the dataset.
Parameter Description Example function Function we want to gen data As in the image. One notice that this function must be calculated in in batch, which mean the first dimension is batch size, second dimension is input dimension. In the image above, you can see i use x[:, 0] instead of x[0], which mean i take the whole batch in first dimension of input to calculate range Range of each input dimesion In the image above, i use 2 dimension of input, so i must declare range no less than 2 range (you can declare more but you know, all the others except the first two variables is useless ;] ) -
Beside it we can all also adjust the number of train, val, test data. We need to go to configs/data_module/data_cf.yaml to adjust it.

Parameter Description train_samples Amount of samples in training dataset val_samples Amount of samples in validation dataset test_samples Amount of samples in test dataset batch_size Size of a batch noise_std Standard deviation value of noise you want to add to the data -
In configs\trainer\trainer_cf.yaml:
- You can change number of epoches each training time by changing the max_epoches parameter.
- You can train using other accelerator (like gpu) by changing the accelerator to the device you want to use.
-
To create a complex model, you can train and tranfer coarser model to more complex model, iteratively. To do this, you can go to configs\config.yaml to change the grid_sizes parameter to list of girds you want to iteratively train and tranfer.
-
And also we have some test files in test folder to visualize b_splines, beizer spline, feel free to explore!
This research project have done by my team:
- Me, who own this repo.
- Hoàng Đăng Khoa.
- Hiếu Nguyễn.
Footnotes
-
KAN: Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks paper: https://arxiv.org/html/2404.19756v4 ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4