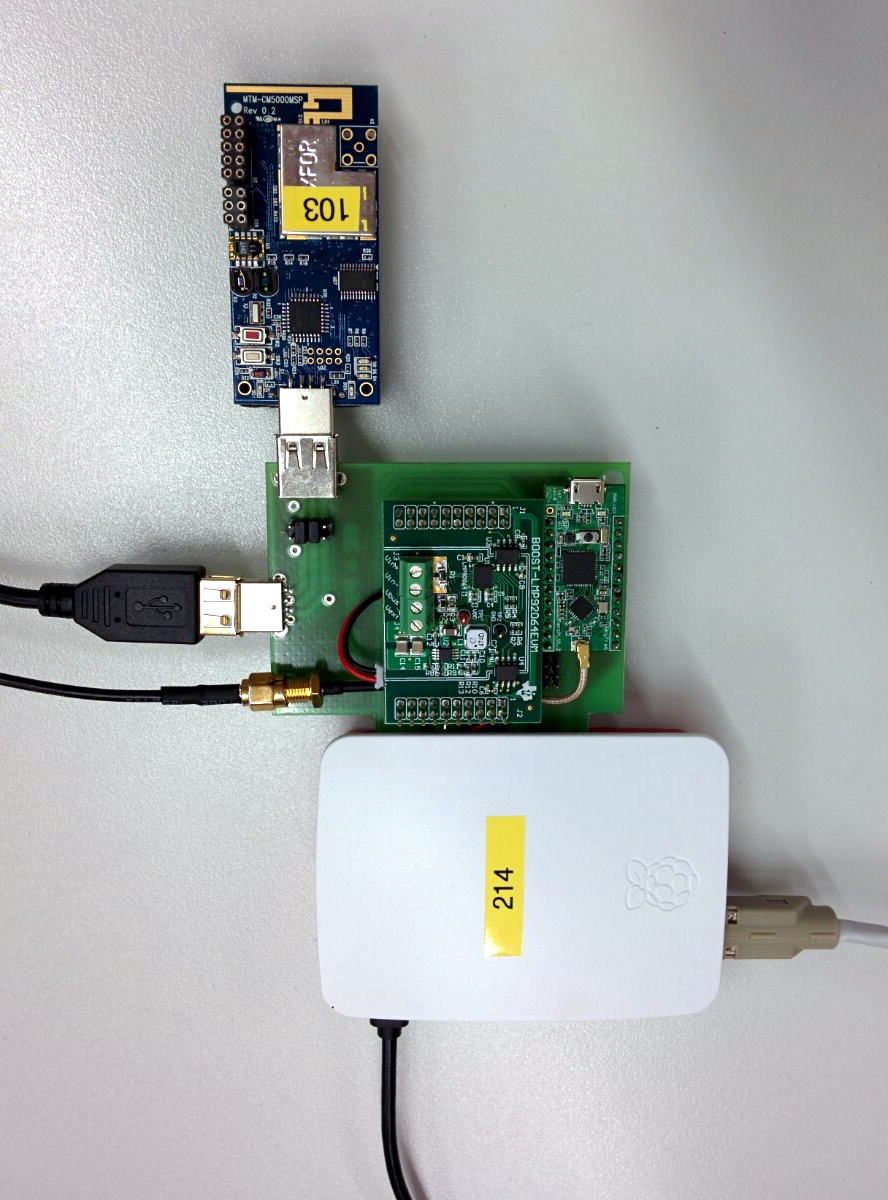
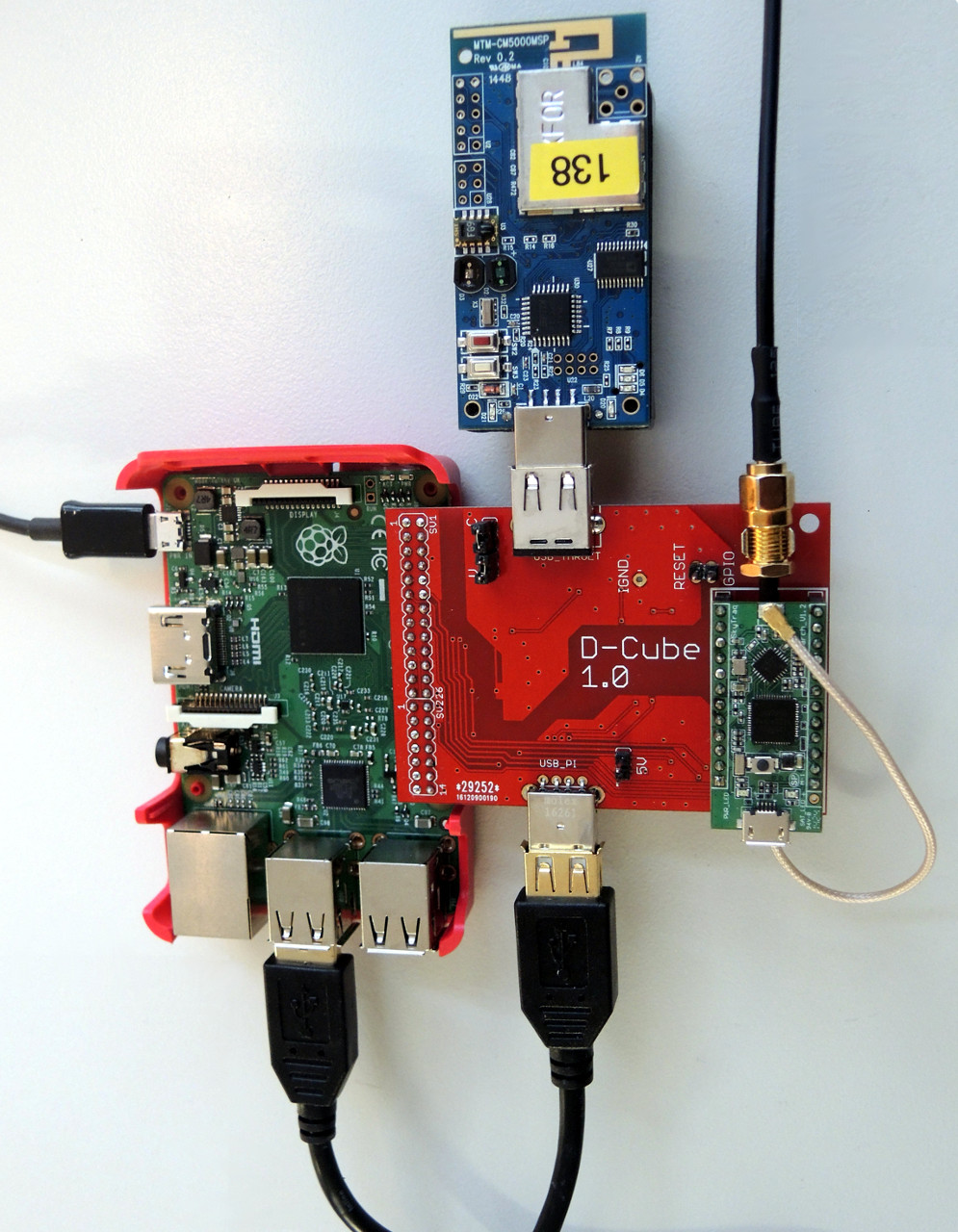
D-Cube is published as open source hardware under CC-BY-SA (online). D-Cube is a low-cost tool that allows to accurately profile the end-to-end delay, reliability, and power consumption, of low-power wireless sensor nodes, as well as to graphically visualize their evolution in real-time. This tool has been used to set-up the EWSN 2016, 2017 and 2018 dependability competitions.
- EWSN 2016 Dependability Competition (Graz, Austria)
- EWSN 2017 Dependability Competition (Uppsala, Sweden)
- EWSN 2018 Dependability Competition (Madrid, Spain)
A scientific paper about D-Cube was published at the 14th International Conference on Embedded Wireless Systems and Networks (EWSN), and is available here.
The design files in this repository where used to fabricate the current iteration of D-Cube. The GPS module used is a Navspark-GL. For the complementary MOSFET a NTJD4105CT2G was chosen in the final design.
The Software consists of two parts
- A task reading the ADC into a FIFO (on top of a real-time Linux kernel)
- A task reading the FIFO and writing it to the database (InfluxDB)
D-Cube contains a power switch circuit which controls the power before the DCDC isolator. A high signal on GPIO23 is required for the ADC and the target to be supplied with power. The gpio.sh file contains an example for this.
We used https://github.com/emlid/linux-rt-rpi but others should work fine
InfluxDB has many frontends available, we used grafana (http://grafana.org/)