use https://github.com/husarion/rosbot-stm32-firmware instead
The ROSbot mobile platform's microcontroller firmware. Written in C++ using arm's Mbed OS framework ( mbed-os-5.14.1).
______ _____ _____ _ _ __
| ___ \| _ |/ ___|| | | | / _|
| |_/ /| | | |\ `--. | |__ ___ | |_ | |_ __ __
| / | | | | `--. \| '_ \ / _ \ | __| | _|\ \ /\ / /
| |\ \ \ \_/ //\__/ /| |_) || (_) || |_ | | \ V V /
\_| \_| \___/ \____/ |_.__/ \___/ \__| |_| \_/\_/
Firmware version: 0.13.1
You need to install following tools:
- Visual Studio Code IDE
- GNU Arm Embedded version 6 toolchain
- STM32 ST-LINK Utility (Windows)
- stlink flasher (Mac/Linux)
- Mbed CLI
- Microsoft C/C++ extension (
ms-vscode.cpptools) - Cortex-Debug (
marus25.cortex-debug)
To install the tool follow the official documentation:
After installation set the path to the binary directory of your GCC Arm Embedded Compiler installation:
Example for Windows:
$ mbed config -G GCC_ARM_PATH "C:\Program Files (x86)\GNU Tools ARM Embedded\6 2017-q2-update\bin"
Example for Linux:
$ mbed config -G GCC_ARM_PATH ~\opt\gcc-arm-none-eabi-6-2017-q2-update\bin
Make sure you have the GNU Arm Embedded version 6 toolchain installed on your system. Check the Prerequisites section.
To check current configuration run:
$ mbed config --list
Create a new folder core2-mbed-workspace. It will serve as workspace for your mbed projects. Run:
$ mkdir core2-mbed-workspace && cd core2-mbed-workspaceNext step is to import mbed-os library. It will be used by all your projects. In your workspace folder run:
$ mbed import mbed-osSet Mbed OS version to supported by this template:
$ cd mbed-os
$ mbed update mbed-os-5.14.1During Mbed OS installation you can be asked to install additional python libraries. Switch to mbed-os dir and run:
$ pip install -r requirements.txt --userSet path to mbed-os directory in Mbed CLI. These way all your projects can use one instance of the library (default configuration is to have separate instance of library for each project). Run:
$ mbed config -G MBED_OS_DIR <path to mbed-os>Example:
$ mbed config -G MBED_OS_DIR "E:\mbed_projects\core2-mbed-workspace\mbed-os"In mbed-os directory create .mbedignore (filename starts with dot) file with following content:
features/cellular/*
features/cryptocell/*
features/deprecated_warnings/*
features/lorawan/*
features/lwipstack/*
features/nanostack/*
features/netsocket/*
features/nfc/*
features/unsupported/*
components/wifi/*
components/cellular/*
components/802.15.4_RF/*
components/TARGET_PSA/*
targets/TARGET_STM/TARGET_STM32F4/TARGET_STM32F407xG/device/TOOLCHAIN_GCC_ARM/STM32F407XG.ld
targets/TARGET_STM/TARGET_STM32F4/TARGET_STM32F407xG/device/TOOLCHAIN_GCC_ARM/startup_stm32f407xx.S
Open Visual Studio Code, press CTRL + SHIFT + P and type Git: Clone in Command Pallet. Copy and paste https://github.com/husarion/rosbot-firmware-new.git URL.
You will be prompted to select your r\epo location. Choose core2-mbed-workspace directory.
Open rosbot-firmware-new in Visual Studio Code IDE. In .vscode directory find settings.json file and change the value of C_cpp.default.compilerPath with path to arm-none-eabi-g++ location on your system:
Example (Windows):
{
"C_Cpp.default.compilerPath": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\GNU Tools ARM Embedded\\6 2017-q2-update\\bin\\arm-none-eabi-g++"
}After that update all repository dependencies. In rosbot-firmware-new/lib directory run:
$ mbed update masterTo build and flash your firmware press CTRL + SHIFT + P and type Tasks: Run Task in Command Pallete. Here is the list of available tasks:
BUILD (RELEASE)BUILD (DEBUG)FLASH FIRMWARE (RELEASE)*FLASH FIRMWARE (DEBUG)*CREATE STATIC MBED-OS LIB (RELEASE)CREATE STATIC MBED-OS LIB (DEBUG)BUILD FROM STATIC LIB (RELEASE)BUILD FROM STATIC LIB (DEBUG)CLEAN DEBUGCLEAN RELEASE
* require ST-LINK programmer
You can add new tasks and customize existing ones by editing task.json file.
To build firmware use BUILD (RELEASE) or BUILD (DEBUG) tasks.
The debug version is intended to be used with ST-LINK probe. You can launch debugger in VSC by pressing CTRL + SHIFT + D. We use Cortex-Debug extension and ST-Util GDB.
Before proceeding with the following steps make sure you conducted mass erase of the memory and made all flash memory sectors write unprotected.
To flash firmware connect ST-LINK to debug connector of CORE2 and use FLASH FIRMWARE (RELEASE) or FLASH FIRMWARE (DEBUG) task.
$ arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O ihex firmware.elf firmware.hex
$ ./core2-flasher firmware.hexYou will find firmware.elf in ./BUILD/RELEASE or ./BUILD/DEBUG.
Here you can learn where to find core2-flasher for your system:
https://husarion.com/manuals/core2/#updating-core2-bootloader
https://github.com/husarion/stm32loader
This tool allows you to upload firmware using RPi connector.
If you have the bootloader the first two sectors are write protected. Before uploading new firmware you must unlock them (this will erase the bootloader):
$ sudo stm32loader -c <your_sbc> -u -WTo upload new firmware run:
$ sudo stm32loader -c <your_sbc> -e -v -w firmware.binwhere <your_sbc> :
tinkerfor Asus Tinker Boardupboardfor Upboardrpifor Raspberry Pi
You will find firmware.bin in ./BUILD/RELEASE or ./BUILD/DEBUG.
To debug:
- make sure you have stlink from texane installed on your system: https://github.com/texane/stlink/blob/master/README.md
- install extension: https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=marus25.cortex-debug
- compile and flash DEBUG firmware
CTRL + SHIFT + Dand click onstart debugbutton
To use this firmware you have to disable communication with Husarion Cloud. On your SBC run:
$ sudo systemctl disable husarnet-configurator
$ sudo rebootTo start rosserial communication run:
$ rosrun rosserial_node serial_node.py.py _port:=<SBC_port_name> _baud:=<port_baudrate><SBC_port_name>:
/dev/ttyS1for Asus Tinker Board,/dev/serial0for Raspberry Pi/dev/ttyS4for UpBoard
<port_baudrate>:
460800for UpBoard500000for Asus Tinker Board230400for Raspberry Pi
The baudrate should be adjusted for SBC you use. The default value for this firmware is 500000 (ROSbot 2.0).
You can build firmware for the another baudrate changing only one line in mbed_app.json:
"rosserial-mbed.baudrate": 460800,The following rosserial.launch file can be used to start roscore and rosserial_python communication:
<launch>
<arg name="serial_port" default="/dev/ttyUSB0"/>
<arg name="serial_baudrate" default="500000"/>
<node pkg="rosserial_python" type="serial_node.py" name="serial_node" output="screen">
<param name="port" value="$(arg serial_port)"/>
<param name="baud" value="$(arg serial_baudrate)"/>
</node>
</launch>Usage for Asus Tinker Board:
$ roslaunch rosserial.launch serial_port:=/dev/ttyS1 serial_baudrate:=500000ROSbot subscribes to:
-
/cmd_velwith message typegeometry_msgs/Twist -
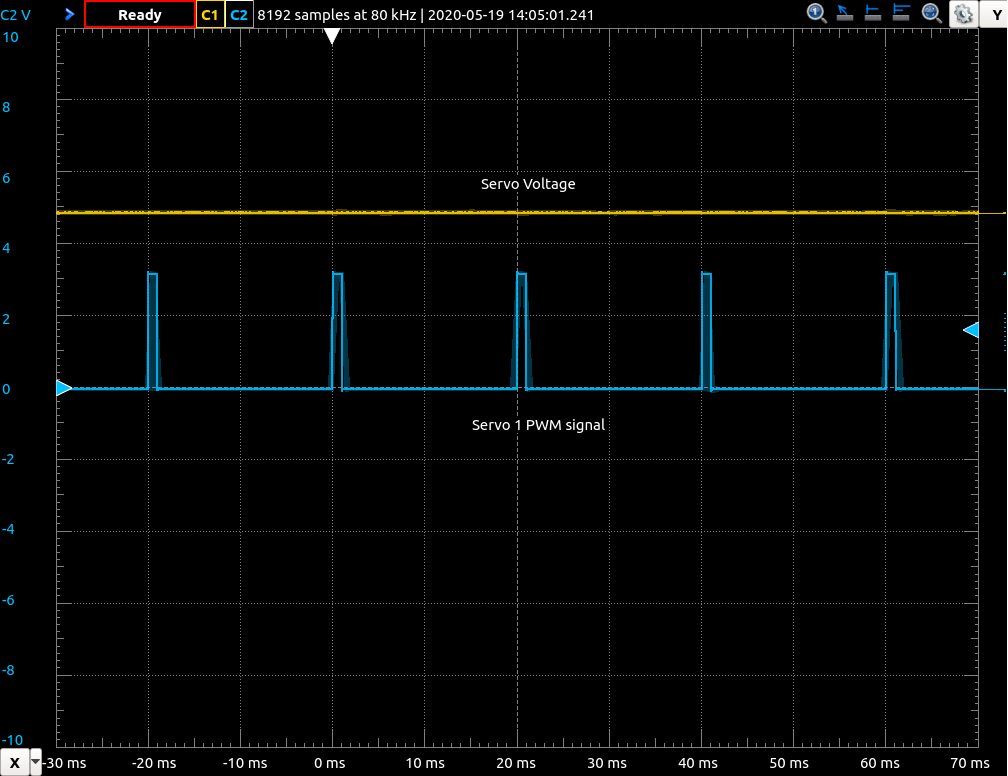
/cmd_serwith message typestd_msgs/UInt32- control configured servo output. SeeCSERservice command to learn how to configure servo outputs. Message format:MSB [ duty_cycle_us | output_id] LSB 28bits 4bitsServos are numbered from 1 to 6, where 1 means hServo 1 output etc. To set SERVO 1 duty cycle to 1000us (0x3E8) run:
$ rostopic pub /cmd_ser std_msgs/UInt32 "data: 0x3E81" --once
ROSbot publishes to:
/velocitywith message typegeometry_msgs/Twist/batterywith message typesensor_msgs/BatteryState/posewith message typegeometry_msgs/Pose/range/flwith message typesensor_msgs/Range/range/frwith message typesensor_msgs/Range/range/rlwith message typesensor_msgs/Range/range/rrwith message typesensor_msgs/Range/joint_stateswith message typesensor_msgs/JointState/mpu9250with custom message typerosbot_ekf/Imu/buttonswith message typestd_msgs/UInt8
ROSbot provides service server:
/configwith custom message typerosbot_ekf/Configuration
$ rossrv show rosbot_ekf/Configuration
string command
string data
---
uint8 SUCCESS=0
uint8 FAILURE=1
uint8 COMMAND_NOT_FOUND=2
string data
uint8 resultAt the moment following commands are available:
-
CSER- CONFIGURE SERVOChange a configuration of servo outputs. Can be repeated as many times as required to change several configuration parameter at once. The parameter name should be separated from the value with a full column
:character. Available parameters:S- select servo output, required withPandWoptions [1:6]V- select voltage mode:0- about 5V1- about 6V2- about 7.4V3- about 8.6V
E- enable servo output [1,0]P- set period in usW- set duty cycle in us
To set servo voltages to 5V and enable
SERVO 1output with period 20ms and width 1ms run:$ rosservice call /config "command: 'CSER' >data: 'V:0 S:1 E:1 P:20000 W:1000 '"
-
CPID- CONFIGURE PIDChange the motor's pid configuration. This command is similar to CSER command. You can change multiple parameters at the same time. Available parameters:
kp- proportional gain (default: 0.8)ki- integral gain (default: 0.2)kd- derivative gain (default: 0.015)out_max- upper limit of the pid output, represents pwm duty cycle (default: 0.80, max: 0.80)out_min- lower limit of the pid output, represents pwm duty cycle when motor spins in opposite direction (default: -0.80, min: -0.80)a_max- acceleration limit (default: 1.5e-4 m/s2)speed_max- max motor speed (default: 1.0 m/s, max: 1.25 m/s)
To limit pid outputs to 75% run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: 'CPID' >data: 'out_max:0.75 out_min:-0.75'"
-
GPID- GET PID CONFIGURATIONTo get current PID configuration run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: 'GPID' data: ''"
Response:
data: "kp:0.800 ki:0.200 kd:0.015 out_max:1.000 out_min:-1.000 a_max:1. 500e-04 speed_max:\ \ 1.500" result: 0
-
SLED- SET LED:To set LED2 on run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: 'SLED' >data: '2 1'"
-
EIMU- ENABLE/DISABLE IMU:To enable IMU MPU9250 run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: 'EIMU' >data: '1'"
data: '1'- enabledata: '0'- disable
-
RIMU- RESET IMU (for Kalman related odometry)To reset IMU MPU9250 run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: 'RIMU' >data: ''"
-
EJSM- ENABLE/DISABLE JOINT STATES MESSAGESTo enable JointStates messages run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: `EJSM` >data: '1'"
data: '1'- enabledata: '0'- disable
-
RODOM- RESET ODOMETRYTo reset odometry run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: `RODOM` >data: ''"
-
CALI- ODOMETRY CALIBRATION (update coefficients)To update
diameter_modificatorandtyre_deflationrun:$ rosservice call /config "command: `CALI` >data: 'X Y'"
X-diameter_modificatorvalueY-tyre_deflationvalue
-
EMOT- ENABLE/DISABLE MOTORSTo disable motors run:
$ rosservice call /config "command 'EMOT' >data '0'
0- disconnect motors1- connect motors
-
SANI- SET WS2812B LEDS ANIMATIONTo enable the ws2812b interface open the
mbed_app.jsonfile and change the line:"enable-ws2812b-signalization": 0
to
"enable-ws2812b-signalization": 1
To set fading blue animation run:
$ rosservice call /config "command: `SANI` >data: 'F #0000aa'"
Available commands:
O- OFFS <hex color code>- SOLID COLORF <hex color code>- FADE IN FADE OUT ANIMATIONB <hex color code>- BLINK FRONT/REAR ANIMATIONR- RAINBOW ANIMATION
In order to use the service you have to download the package rosbot_ekf that can be found HERE. For installation details check the README.
The package incorporate a ready to use Extended Kalman Filter that combines both the imu and encoders measurements to better approximate the ROSbot position and orientation. The package also contains custom messages that are required by the new firmware.
To launch the rosserial communication and Kalman filter run:
$ roslaunch rosbot_ekf all.launchFor PRO version add parameter:
$ roslaunch rosbot_ekf all.launch rosbot_pro:=trueThe project uses SemVer for versioning. For the versions available, see the tags on this repository.
See CHANGELOG.md.
Documentation: