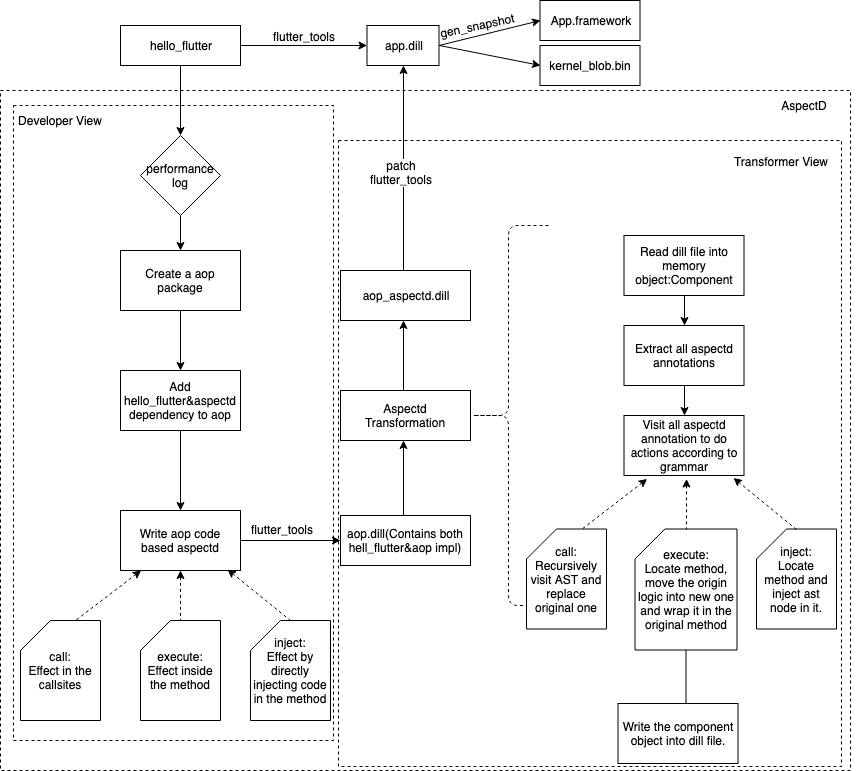
AspectD

Salute to AspectJ.
AspectD is an AOP(aspect oriented programming) framework for dart. Like other traditional aop framework, AspectD provides call&execute grammar. Besides, as we can't use dart:mirrors in flutter, AspectD also provides a way named inject enhancing the dart code manipulation.
Besides, AspectD provides a dill transformer container above which developers can implement their own transformers like hook, json, mirrors, etc.
Design
Suppose you have a flutter project named example located in hf_dir.
Installation
1. Create a dart package named aspectd_impl in hf_dir/example
flutter create --template=package aspectd_impl2. Add aspectd&example dependency to aspectd_impl package
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
aspectd:
git:
url: https://github.com/hust-MC/aspectd.git
ref: stable/v1.20.4
example:
path: ../exampleRemember to change the branch matching your flutter environment (stable supported currently). Fetch package dependency in aspectd_impl package
flutter packages get3. Modify aspectd_impl package
aspectd_impl.dart(entrypoint)
import 'package:example/main.dart' as app;
import 'aop_impl.dart';
void main()=> app.main();aop_impl.dart(aop implementation)
import 'package:aspectd/aspectd.dart';
@Aspect()
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
class ExecuteDemo {
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
ExecuteDemo();
@Execute("package:example/main.dart", "_MyHomePageState", "-_incrementCounter")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
void _incrementCounter(PointCut pointcut) {
pointcut.proceed();
print('KWLM called!');
}
}4. Patch flutter_tools to apply aspectd.dart.snapshot
cd path-for-flutter-git-repo
git apply --3way path-for-aspectd-package/0001-aspectd.patch
rm bin/cache/flutter_tools.stampAs flutter_tools doesn't support hooks now, the aspectd.patch is necessary currently. As flutter is evolving, this patch might fail sometimes. However, It would be simple to resolve the conflicts as AspectD only adds two hooks when building dill. See XianyuTech/aspectd#5 for more.
If you want to customize the aspectd_impl package, edit aspectdImplPackageRelPath(aspectd_impl package relative path to the example's pubspec.yaml) and aspectdImplPackageName(aspectd_impl package folder name and main entry file name) defined in path-for-flutter-git-repo/flutter/packages/flutter_tools/lib/src/aspectd.dart.
const String aspectdImplPackageRelPath = '.';
const String aspectdImplPackageName = 'aspectd_impl';Step 1~3 are expected to run each time you want to add aspectd_impl to a flutter(dart) package. 4 is expected to run only once unless the dart-sdk changes. For example, If you upgrade flutter, you need to check if to re-run 4.
If you're using example with an aspectd_impl package not generated locally, remember to run flutter packages get in aspectd_impl package to get aspectd and check 4.
5. Implement your own transform if needed
As said above, Aspectd is not only an AOP framework , it also provides a dill transformer container. You can implement your own transformer (say pluginDemo) over Aspectd following steps below:
a. Declare pluginDemo in the plugins section of config.yaml.
b. Run dart bin/generate_plugins_entry.dart to generate a unified folder structure located in lib/src/plugins/pluginDemo.
c. Write your annotations to export in pluginDemo.dart if needed.
d. Write your transformer implementation in PluginDemoWrapperTransformer.transform located in pluginDemo_transformer_wrapper.dart.
There are two points you need to pay attention to:
a. If you want to implement your own transformers, you'd better import Aspectd by path ref instead of git dependency. Otherwise, your modifications might be overwritten mistakenly.
b. Each time you change the dill transformer implementation, you should delete snapshot/aspectd.dart.snapshot to make your changes take effect.
Tutorial
Now AspectD provides three ways to do AOP programming.
call
Every callsites for a specific function would be manipulated.
import 'package:aspectd/aspectd.dart';
@Aspect()
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
class CallDemo{
@Call("package:app/calculator.dart","Calculator","-getCurTime")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
Future<String> getCurTime(PointCut pointcut) async{
print('Aspectd:KWLM02');
print('${pointcut.sourceInfos.toString()}');
Future<String> result = pointcut.proceed();
String test = await result;
print('Aspectd:KWLM03');
print('${test}');
return result;
}
@Call("package:app/calculator.dart","Calculator","+getCurTemporature")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
String getCurTemporature(PointCut pointcut) {
print('Aspectd:KWLM04');
print('${pointcut.sourceInfos.toString()}');
try{
String res = pointcut.proceed();
} catch (error, trace){
print('Aspectd:KWLM05');
}
return null;
}
@Call("package:flutter/src/widgets/binding.dart","","+runApp")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
static void runAppKWLM(PointCut pointcut){
print('Aspectd:KWLM07');
print('${pointcut.sourceInfos.toString()}');
pointcut.proceed();
}
}In this case, notice that @Aspect() is needed to mark a class so that the aspectd will know that this class contains AspectD annotation informations. @pragma("vm:entry-point") is needed so that the class/function will not be removed by tree-shaking. For @Call("package:app/calculator.dart","Calculator","-getCurTime"), there are several things to know. Now call/execute/inject accept three positional parameters, package name, class name(If the procedure is a library method, this part is empty string), and function name. The function name may have a prefix('-' or '+'), '-' refers to instance method while '+' refers to library static method(like main) and class method. There is also a named parameter lineNum for inject so that AspectD know which line to inject a code snippet. The lineNum parameter is 1 based and code snippet would be injected before that line.
Besides, when you want to manipulate a static method(including library method and class method), your aop method(runAppKWLM here) should also be declared static. This requirement also applies when using execute command.
execute
Every implementation for a specific function would be manipulated.
import 'package:aspectd/aspectd.dart';
@Aspect()
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
class ExecuteDemo{
@Execute("package:app/calculator.dart","Calculator","-getCurTime")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
Future<String> getCurTime(PointCut pointcut) async{
print('Aspectd:KWLM12');
print('${pointcut.sourceInfos.toString()}');
Future<String> result = pointcut.proceed();
String test = await result;
print('Aspectd:KWLM13');
print('${test}');
return result;
}
@Execute("package:app/calculator.dart","Calculator","+getCurTemporature")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
String getCurTemporature(PointCut pointcut) {
print('Aspectd:KWLM14');
print('${pointcut.sourceInfos.toString()}');
try{
String res = pointcut.proceed();
} catch (error, trace){
print('Aspectd:KWLM15');
}
return null;
}
@Execute("package:flutter/src/widgets/binding.dart","","+runApp")
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
static void runAppKWLM(PointCut pointcut){
print('Aspectd:KWLM17');
print('${pointcut.sourceInfos.toString()}');
pointcut.proceed();
}
}inject
For a original function like below:(package:flutter/src/widgets/gesture_detector.dart)
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final Map<Type, GestureRecognizerFactory> gestures = <Type, GestureRecognizerFactory>{};
if (onTapDown != null || onTapUp != null || onTap != null || onTapCancel != null) {
gestures[TapGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<TapGestureRecognizer>(
() => TapGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(TapGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onTapDown = onTapDown
..onTapUp = onTapUp
..onTap = onTap
..onTapCancel = onTapCancel;
},
);
}
...
}import 'package:aspectd/aspectd.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
@Aspect()
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
class InjectDemo{
@Inject("package:flutter/src/widgets/gesture_detector.dart","GestureDetector","-build", lineNum:452)
@pragma("vm:entry-point")
static void onTapBuild() {
Object instance; //Aspectd Ignore
Object context; //Aspectd Ignore
print(instance);
print(context);
print('Aspectd:KWLM25');
}
}After that, the original build function will look like below:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final Map<Type, GestureRecognizerFactory> gestures = <Type, GestureRecognizerFactory>{};
if (onTapDown != null || onTapUp != null || onTap != null || onTapCancel != null) {
gestures[TapGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<TapGestureRecognizer>(
() => TapGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(TapGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onTapDown = onTapDown
..onTapUp = onTapUp
..onTap = onTap
..onTapCancel = onTapCancel;
},
print(instance);
print(context);
print('Aspectd:KWLM25');
);
}
...
}Notice that //Aspectd Ignore part when using injection, we need to compile the aop package successfully so we need to declare the instance/context variable. However, when injecting to origin function (build in this case), variable declaration
Object instance; //Aspectd Ignore
Object context; //Aspectd Ignorewould be discarded to avoid overring the original one.
Compatibility
Flutter 1.0 and above.
Notice
Because of the dart compilation implementation, there are several points to pay attention to:
- package:aspectd_impl/aspectd_impl.dart should contains the main entry for aspectd_impl package and contains a app.main call.
- Every aop implementation file should be imported by aspectd_impl.dart so that it will work in debug mode.
- @pragma("vm:entry-point") is needed to mark class/function to avoid been trimmed by tree-shaking.
- inject might fail in some cases while call&execute are expected to be more stable.
- If you want to disable AspectD, remove the aspectd.dart.snapshot located in aspectd or change the name of aspectd_impl package, or remove the @Aspect() annotation. Anyone will be fine.
- If you want to hook an instance method, the hook class should declare a default constructor and mark it with @pragma("vm:entry-point").
Contact
If you meet any problem when using AspectD, file a issue or contact me directly.