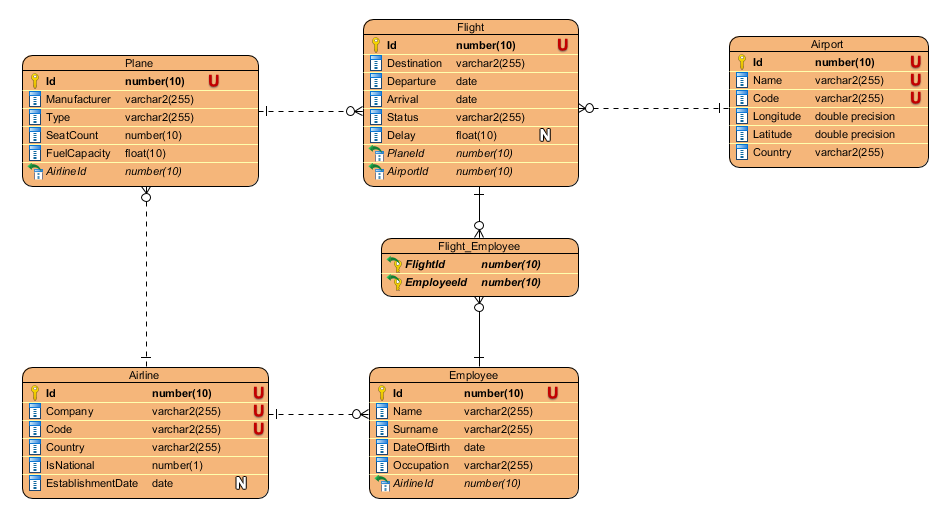
With sample database schema (and fake data) we explore Oracle 19c capabilities.
In 6 tables we have about 2.25 MB of data (35k rows total).
With 3 query sets (5 queries each) the longest one takes 3.32s (in Oracle SQL Developer VM image with 2GB RAM and 4 cores).
Event (i) - Condition (i, ii) - Action (ii)
5 rules have been proposed along with:
- rule description
- initiating events
- conditions
- action
- action complexity estimation
- with active rules the query sets took longer time
- experiment 1: the maximum number of calls in the Oracle database is 50
- experiment 2: the Oracle database does not ensure the order in which the rules are executed
The initial schema is extended by 3 XML modifications. 3 query sets were changed accordingly to fit the new schema.
Times for XML were significantly lower.
4 exentions on initial schema were made by changing some columns to geometrical shapes like a point, a line or a multiline. 3 query sets were changed accordingly.
Tests were made for spatial data indexed and with no index. In almost each case the times are much lower than operations on non-indexed data.
3 extension (changing a whole table to in-memory storage) were made on initial schema.
Unfortunately the results are not reliable due to incorrect memory cofiguration on VM.
-
all average times were significantly higher for column store
-
experiment 1: for non-modifying (select) operations, query execution times have slightly improved for column store
-
experiment 2: regardless of the type of compression selected (query low/high, capacity low/high), the size of the table was identical