简体中文 | English
dayu (pronounced /ta˥˨ y˨˩˨/, loosely daa-jyu /dɑːjuː/) is a parser and (very rudimentary) decompiler for the .abc files (Ark Bytecode files) used on Open/HarmonyOS.
Dayu, or Yu the Great, was an ancient Chinese king credited with successfully coping with the Great Flood and thus saving people from suffering. On a similar note, Noah's Ark helped lives survive the Deluge. In a broad sense, dayu represented/represents Ark in another form.
Disclaimer: dayu is a toy project developed in my free time. My availability and expertise are limited, so decompilation correctness and future maintenance are NOT guaranteed. Use at your own risk. This is a free and open-source project; don't expect too much from it.
See "Examples" section below for an example use.
usage: main.py [-h] [-pc] [-pmc CLASS] [-dmo] [-dc DECOMPILE_CLASS] [-dme DECOMPILE_METHOD] [-cfg] [-abc ABC] [-pa PA]
[-O OUTPUT_LEVEL]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-pc, --print-classes print names of all classes
-pmc CLASS, --print-methods-in-class CLASS
print names of all methods (including their class names) in the specified CLASS
-dmo, --decompile-module
decompile the whole file
-dc DECOMPILE_CLASS, --decompile-class DECOMPILE_CLASS
decompile all methods in the specified class
-dme DECOMPILE_METHOD, --decompile-method DECOMPILE_METHOD
decompile the specified method; must be specified in the format "<class name>.<method name>"
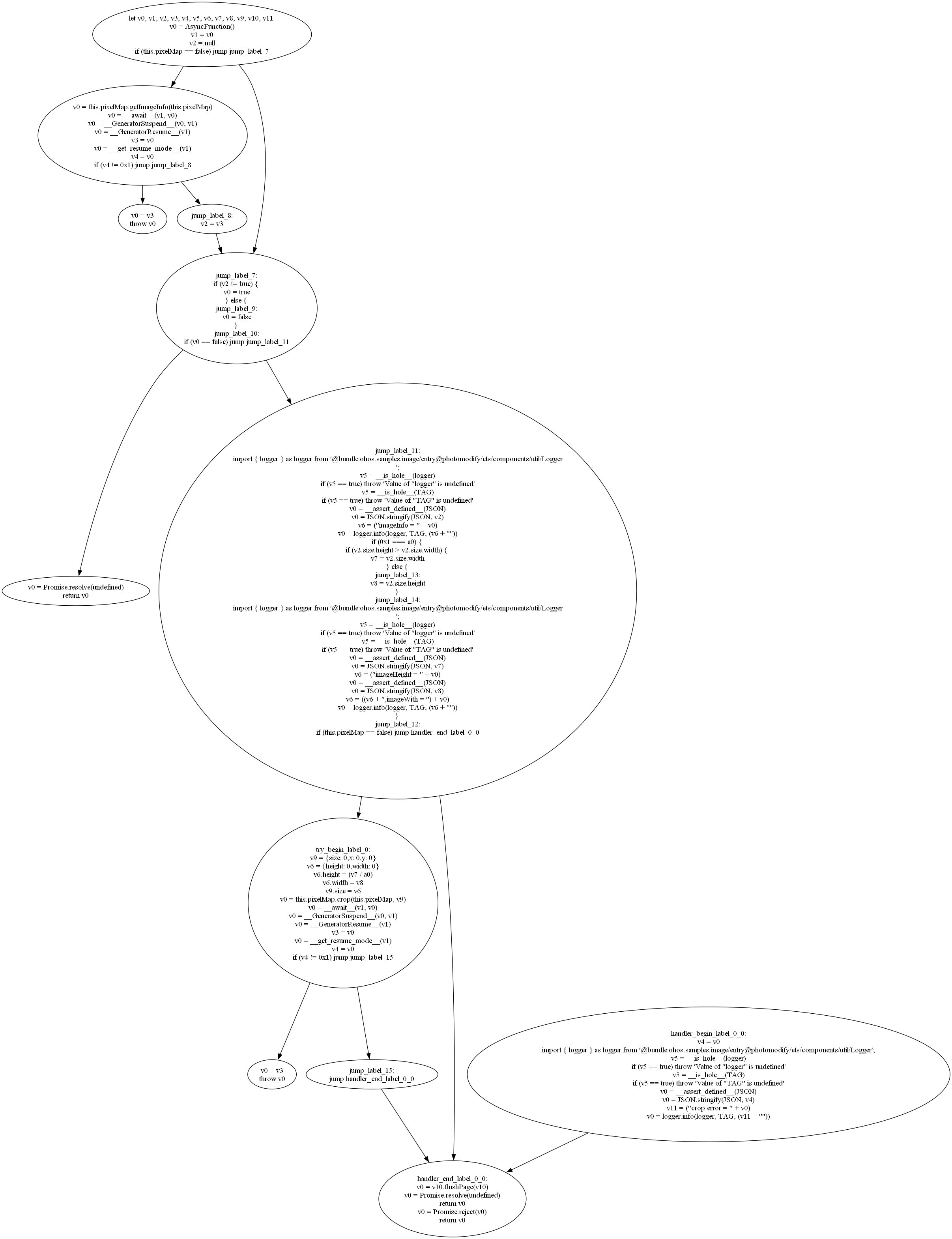
-cfg, --view-cfg display the Control Flow Graph (CFG) of the specified method (graphviz required); must specify
method with -dme
-abc ABC specify the input abc file
-pa PA specify the input text-form Panda Assembly file
-O OUTPUT_LEVEL, --output-level OUTPUT_LEVEL
output decompiled code at the specified level (possible values: llir, mlir, hlir, pcode,
default: pcode)
Example:
from ark.abcreader import AbcReader
from decompile.config import DecompilerConfig, DecompileGranularity, DecompileOutputLevel
from decompile.decompiler import Decompiler
from pandasm.reader import PandasmReader
# specify input files, Panda Assembly file (obtained by using ark_disasm tool from the SDK) is required for decompilation
abcfile = AbcReader.from_file('<path to abc file>')
pafile = PandasmReader.from_file('<path to Panda Assembly file>')
# configure the decompiler
config = DecompilerConfig({
'abc': abcfile,
'pandasm': pafile,
'output_level': DecompileOutputLevel.PSEUDOCODE,
'class': '<name of class containing the method to decompile>',
'method': '<name of method to decompile>',
'granularity': DecompileGranularity.METHOD
})
# ready, steady, go!
decompiler = Decompiler(config)
method = decompiler.decompile()
# print the decompiled code
decompiler.print_code(method)
# view the CFG
decompiler.write_cfg_to_file(method, f'cfg/cfg_{method.name}', True)Suppose we have this simple snippet of code and we've compiled it into modules.12.abc:
function foo() {
let i = 0
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
hilog.info(0x0, 'hello', `world${i}`)
}
return i
}Use ark_disasm from HarmonyOS SDK to obtain Panda Assembly modules.12.abc.txt:
ark_disasm modules.12.abc modules.12.abc.txtPrint names of all classes in Panda Assembly:
python main.py -pa modules.12.abc.txt -pcAssuming our method to decompile is in the class com.example.myapplication.entry.ets.pages.Index, print names of all methods in this class with:
python main.py -pa modules.12.abc.txt -pmc com.example.myapplication.entry.ets.pages.IndexWe see that the full name of our foo method is com.example.myapplication.entry.ets.pages.Index.foo. Decompile with:
python main.py -abc modules.12.abc -pa modules.12.abc.txt -dme com.example.myapplication.entry.ets.pages.Index.fooAfter decompiling using the default configuration, this is what we get:
let v0, v1, v2
v0 = 0x0
jump_label_1:
while (v0 < 0x5) {
import { default } as hilog from '@ohos:hilog';
v1 = __is_hole__(hilog)
if (v1 == true) throw 'Value of "hilog" is undefined'
v2 = hilog.info(hilog, 0x0, "hello", (("world" + v0) + ""))
v2 = __ToNumeric__(v0)
v0 = (v2 + 0x1)
}
jump_label_0:
v2 = v0
return v2Now, let's try it on a method in one of Huawei's sample ArkTS projects. This is the source code:
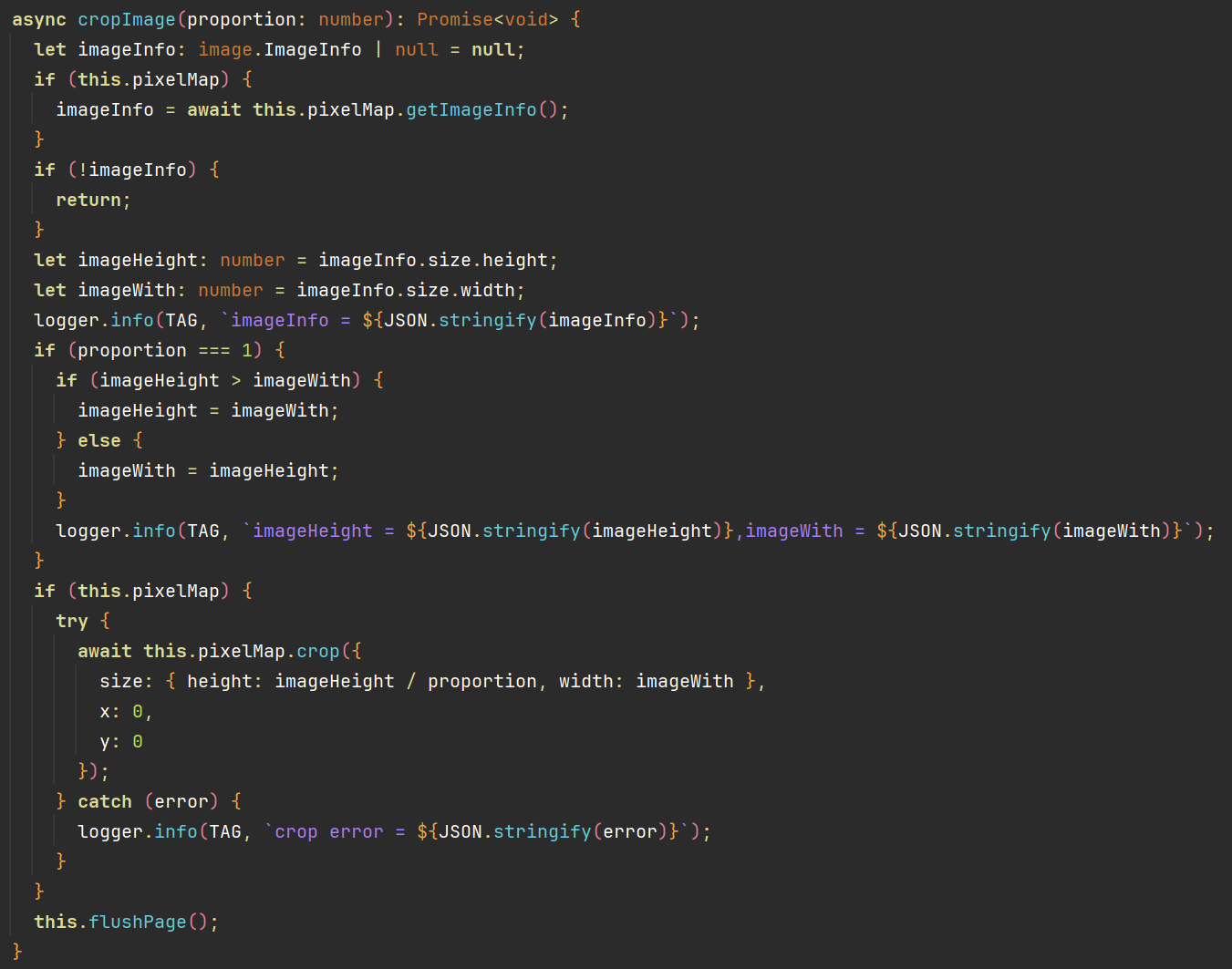
Decompiled:
There's an unsupported try-catch structure, and the result is more tedious and harder to read now, but it's basically correct.
As much as dayu tries to output code that conforms to the syntax of ArkTS/TypeScript, this isn't always possible or easy to achieve (for me). Some points to note:
First, since dayu is still limited in its control flow structure recovery, the final pseudocode may be littered with gotos (in the form of jump statements). ArkTS (as well as TypeScript) doesn't support goto, so the user will have to sort some of the control flow out for themselves.
Second, in the final pseudocode, there may be some "pseudo-functions". They stand for operations that can't be easily translated. For example, retrieving lexical environment is represented as __get_lexenv__.
Some pseudo-functions can be manually implemented. For example, __assert_defined__ may be implemented as:
function __assert_defined__(obj) {
if (typeof obj == "undefined") {
throw "undefined"
}
} Under the Hood - how dayu works
- Slow. Very slow. Largely caused by two things: Panda Assembly parsing and copy propagation, both of which are badly written.
- Limited coverage of the instruction set
- Loop structures and conditional structures are not recovered in some cases
- No support for
try-catchstructures - Lack of type analysis (both ArkTS and TypeScript are typed)
dayu wasn't built in a day. It's the product of strenuous endeavor (plus many cups of bubble tea), and it can't go without help from others. We thank them for what they've done and continue to do:
- Static Program Analysis, Nanjing University, taught by Professors Yue Li and Tian Tan
- Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools, Second Edition by Alfred V. Aho, Monica S. Lam, Ravi Sethi and Jeffrey D. Ullman
- CS447 Compiler Theory, University of Western Ontario, taught by Professor Marc Moreno Maza
- Lecture Notes on Decompilation from 15-411 Compiler Design, Carnegie Mellon University, course by Professor Frank Pfenning, notes by Max Serrano
- Advanced Compiler Design and Implementation by Steven S. Muchnick
GNU AGPL v3.0