Clone Coding Repository for "React WebGame" Course of ZeroCho
Lecture Link: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLcqDmjxt30RtqbStQqk-eYMK8N-1SYIFn
- Lecture Language: Korean
- To familiarize the concept of React
- Have the first experience in making web applications using React framework
- Build some simple games using React
-
nodepackages for React Dev Environment- React
react: React Corereact-dom: Connect React and DOM
- Babel
@babel/core: Babel Core@babel/preset-react: Transfiling React JSX@babel/preset-env: Transfiling ES6+ Codes
- Webpack
webpack: Webpack Corewebpack-cli: Use Webpack on command line interfacewebpack-dev-server: Build webpack in-memory and run development serverbabel-loader: Transfiling JSX and ES6+ syntaxstyle-loader: Wrap and inject compiled CSS filecss-loader: Interpret CSS file so that JavaScript can understandhtml-webpack-plugin: Inject bundled JavaScript files to HTML filemini-css-extract-plugin: Separate CSS files
- React
-
React.Component is building structure of React elements that will be appear on the screen.
- All components should extends
React.Component. - All components should override
render()function. - Components may have
state.stateis something that is modifiable inside the component.- use setState() to change state of the component.
- It is asynchronous function.
- Only used for something that needs to be changed manually
- Able to get function handler as a parameter which handles state change. The function handler may get parameter specifying the previous state. Meaning the components will re-rendered.
- All components should extends
-
ref is uesd when we need to access DOM directly.
- Similar to Vanilla JS's
querySelector()orgetElementById(). - Official Guide: https://reactjs.org/docs/refs-and-the-dom.html
- Similar to Vanilla JS's
-
React.createElement(type, [props], [... children]) generates new React Elements of given type.
typecan be tag name of HTML elements or React Component type (class or function) name.propcontains HTML properties of the element.- Should be expressed in object format.
- Can use JSX (JavaScript + XML) format (using HTML-shaped Tags) instead of
React.createElement().- HTML expression inside JavaScript causes error;
therefore, we need Babel to support JSX syntax.
- To use
Babel,typeof script should betext/babel.
- To use
- JavaScript code should be placed in curly bracket (e.g.:
<div>{... some js code ...}</div>). nullinJSXindicates no elements to return.
- HTML expression inside JavaScript causes error;
therefore, we need Babel to support JSX syntax.
- React.Fragment is used to group a list of chlidren without adding extra nodes to the DOM.
- Help removing meaningless
<div>. - Notation:
<React.Fragment> ... </React.Fragment>or<> ... </>
- Help removing meaningless
-
Recommend NOT to mix JSX and JS Codes.
- JavaScript logics can be implemented as Class Methods.
-
Element's
classandfor(onlylabel) properties cannot be used in JSX.- The HTML
classproperty is set byclassNameproperty of JSX component. - The HTML
forproperty is set byhtmlForproperty of JSX component.
- The HTML
-
ReactDOM.render() renders a React element into the existing DOM.
- This function actually draws the React Components to the web browsers.
- React need at least one element (the root div
<div id='root>) to render the React components inside.
-
Functional Components only contains
render()part of React Component (Class component), which used when we do not needstateandref. -
React Hooks is a new way (recommend way) to define a React component.
- It adds
stateandrefsupport to functional component. - React.useState() is used to define a state and its own
setState()method. - React.useRef() is used to create new reference to the DOM object.
- When access to the DOM Element, need to use
RefObject.current. refcan also be used as a 'member variable' of a functional component.- When chaning the content of ref, we ned to change
Ref.current. - When
Refchanged,render()will not be called. (The most important difference betweenrefandstate.) - It memorizes the value.
- When chaning the content of ref, we ned to change
- When access to the DOM Element, need to use
- EventHandler function should be arrow function.
-
// Example of using React Hooks const GuGuDan = () => { // State [stateName, setFunction] const [state, setState] = React.useState('Initial Value'); // ref const inputRef = React.useRef(); // EventHandler const onChangeInput = (event) => { setState(e.target.value); // Modify the state inputRef.current.focus(); } return ( <div>Hello, World!</div> <input ref={inputRef} onChange={onChangeInput} value={state}/> ) }
- Note that once state changed, all codes in the function (Hooks) re-run (but in optimized way).
- The order of Hooks matter!!
- Should not be placed in the conditional statement, loop, and function.
- It adds
-
Each child in a list needs to have a unique key, in order to identify which element to access (change, modify, delete).
- Can use index as a key, but it is an anti-pattern. It may break the application and cause to display wrong data.
-
Props are used to pass arguments to React Component.
- Developers may separate Components to increase readability and reusability.
- From callee, props are set using HTML attribute syntax. (e.g.
<Trial value={value} index={index}/>) - Inside the component, the
propsobject contains all passed argument. - A parent component passes props to the child components.
-
To comment out
JSXcodes, simply put block comments inside the curly bracket. (e.g.{/* Some Comments */}) -
React Elements are immutable.
- If you want to add an item into the array, need to create a new array.
- If not, React cannot detect what has been modified.
- If you want to add an item into the array, need to create a new array.
-
Everytime when
stateorpropschanged, Components are rendered again.- May render other not updated components, causing performance issue.
- Component.shouldComponentUpdate() can be used to hint React when it should re-render the component.
- PureComponent also can be used to solve the problem, as it will shallowly compare states and props.
- May not detect changes inside an object and an array. Need to make another object or array, rather than modifying the already existing one.
- For Functional Components (Hooks), Use React.memo().
- Rule of Thumb: If all children are memoized, the parent is recommended to be memoized.
-
React Lifecycle (Class Component)
- When creating new Element:
constructor->render()-> ref ->componentDidMount() - when updating the Element: (Initialized when
statesandpropschange) ->shouldComponentUpdate()->render()->componentDidUpdate() - When removing the Element:
componentWillUnmount() - Image illustrating the sequence can be found here
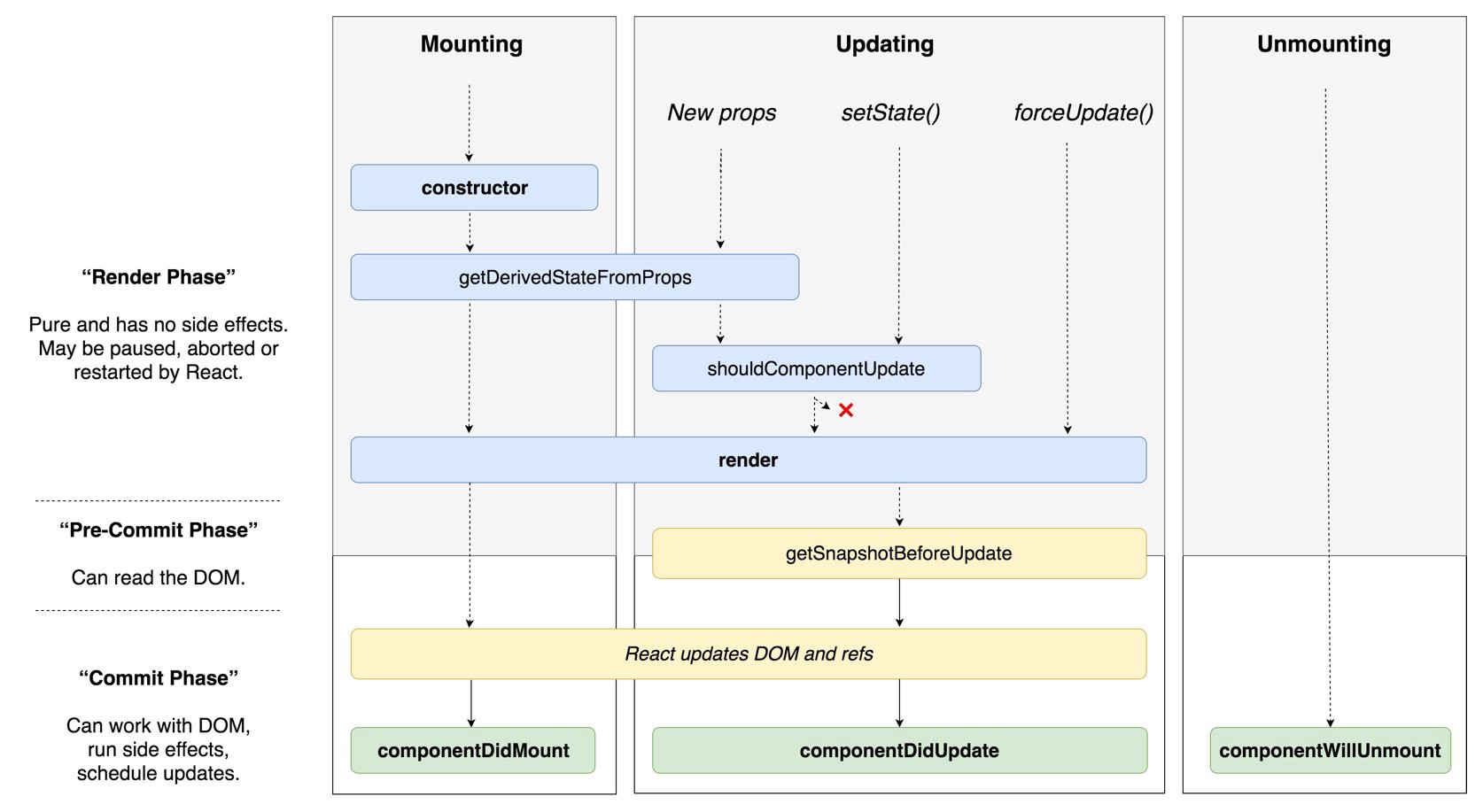
- Focuses on the Component
- Lifecycle functions should appear once in the Class Component.
- When creating new Element:
-
React Hooks Lifecycle
- Focus on data
useEffect()performs role of bothcomponentDidMount()andcomponentDidUpdate().- If we want to only run codes inside
useEffect()only when update, use following pattern.-
const mounted = useRef(false); useEffect(() => { if (!mounted.current) { // When mounted mounted.current = true; } else { // Something to do on update (e.g. Ajax) } }, [<Changing-Value>]);
-
- If we want to only run codes inside
- When function returned from
useEffect(), the returned function will run before the Element removed.- Performs role of
componentWillUnmount().
- Performs role of
useEffect()should get an array containing changing states as a second parameter.- Able to use multiple times in a Functional Component.
-
High Order Function (HOF)
- Return function as a result, or get function as parameters
- In React, it is used to call EventHandler function with parameter.
-
React.useMemo() caches calculated result and prevent unnecessary function calls.
- It is used to memorize complicated result of function.
-
React.useCallback() memorizes the function itself.
- It prevents same function to be created multiple time when Components re-render.
- It also stores all the variables that used in the function.
- When we pass function as props to the child Component, it is required to wrap the function with
React.useCalback()to prevent unnecessary re-render caused by props change.- Newly created function is different function with previous one.
-
React.useReducer() and Context API can substitute
Reduxfor simple applications. For complicated applications, to use asyncronous calls efficiently, it is better to useRedux.-
React.useReducer()is used to reduce the number of States used in the application.-
When we have tons of States, it is hard to management all pairs of States and setState functions.
-
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialArg, init);
-
dispatchget anactionobject withtypeproperty and states to update.dispatchtranslate theactionto change the state.- Like
setState(),dispatch()is an asyncronous function.
- Like
-
reduceris a function to change States.-
const reducer = (state, action) => { switch(action.type) { case 'SET_WINNER': return { ...state, // Shallow copy existing object winner: action.winner, // Change the property. }; } };
- Should not change the state directly like
state.winner = action.winner. Always need to return a new state.
- Should not change the state directly like
- Everytime when we call
dispatchthereducerfunction is called. - It is where the codes to change the state based on the
typeofactionare written.
-
-
initialArggets object of initial states. -
initfunction is used for lazy initialization.- The intiaial state will be set to the return value of
init(initialArg)function. - By using
init, developers can detach the logic to calculate the intial state outside of reducer. - Helps resetting the states later.
- The intiaial state will be set to the return value of
-
-
-
Context API let developers to pass data through the component tree without passing props.
It is designed to share data that can be considered "global" for a tree of components.- React.createContext(initialValue) is used to create new Context object.
-
export const TableContext = React.createContext({ tableData: [] });
-
- The Components that consumes the Context should be wrapped by Context.Provider.
props valuegets the data that will be passed to the children.-
<TableContext.Provider value={{ tableData: state.tableData }}> // Components that consumes the context <Form /> <Button /> </TableContext.Provider>
- Above code may cause performance issue as it continuously makes new object, which causes re-render of all child components.
- Developers need to cache the object by using
React.useMemo().
- Developers need to cache the object by using
-
- React.useContext(context) to use context in child component.
- The Context defined in the parent component should be exported.
-
const value = React.useContext(TableContext);
- When we use Context API, the the function of the Components re-runs everytime.
- Use React.useMemo() to save returning value of the functional Component.
- React.createContext(initialValue) is used to create new Context object.
-
-
React Router
- Official Tutorial: https://reactrouter.com/docs/en/v6/getting-started/tutorial
- Used to route multiple pages in the react website.
- BrowserRouter uses HTML5 history API to update UI.
- The addresses are only available on front-end, not on back-end.
- When we refresh the page or access to the link directly, it will cause 404 error.
- HashRouter uses URL's hash (#).
- The address after hash (
#) only used in the front-end, not passed to the server. - Though we refresh, the page is rendered correctly.
- Search Engine cannot retrieve the paths under hash.
- The address after hash (
- Dynamic Route Matching: Using params (
:<paramName>) to match the path.- Help reducing
Routein the code.
- Help reducing
Followed lecture contents to build simple Times Table (GuGuDan) game. Used React Class to build application.
Detailed information can be found here: https://github.com/hyecheol123/ZeroCho-React-WebGames/tree/main/9-times-table
Followed lecture contents to build Bulls and Cows game. Used React Hooks to build application.
Detailed information can be found here: https://github.com/hyecheol123/ZeroCho-React-WebGames/tree/main/bulls-and-cows
Followed lecture contents to build a simple game to measure user's response time.
Used React Hooks to build application.
Detailed information can be found here: https://github.com/hyecheol123/ZeroCho-React-WebGames/tree/main/response-time
Followed lecture contents to build a Rock Paper Scissors game.
Used React Class and React Lifecycle methods to build application.
Detailed information can be found here: https://github.com/hyecheol123/ZeroCho-React-WebGames/tree/main/rock-paper-scissors
Followed lecture contents to build a Tic Tac Toe game.
Used reducer and React Hooks (Functional Component) to build application.
Detailed information can be found here: https://github.com/hyecheol123/ZeroCho-React-WebGames/tree/main/tic-tac-toe
Followed lecture contents to build a MineSweeper game.
Used Context API and React Hooks (Functional Component) to build application.
Detailed information can be found here: https://github.com/hyecheol123/ZeroCho-React-WebGames/tree/main/minesweeper