This project is using Espressif IoT Development Framework (ESP-IDF) and has been tested on ESP-WROOM-32 module.
An overview of the full project can be found here.
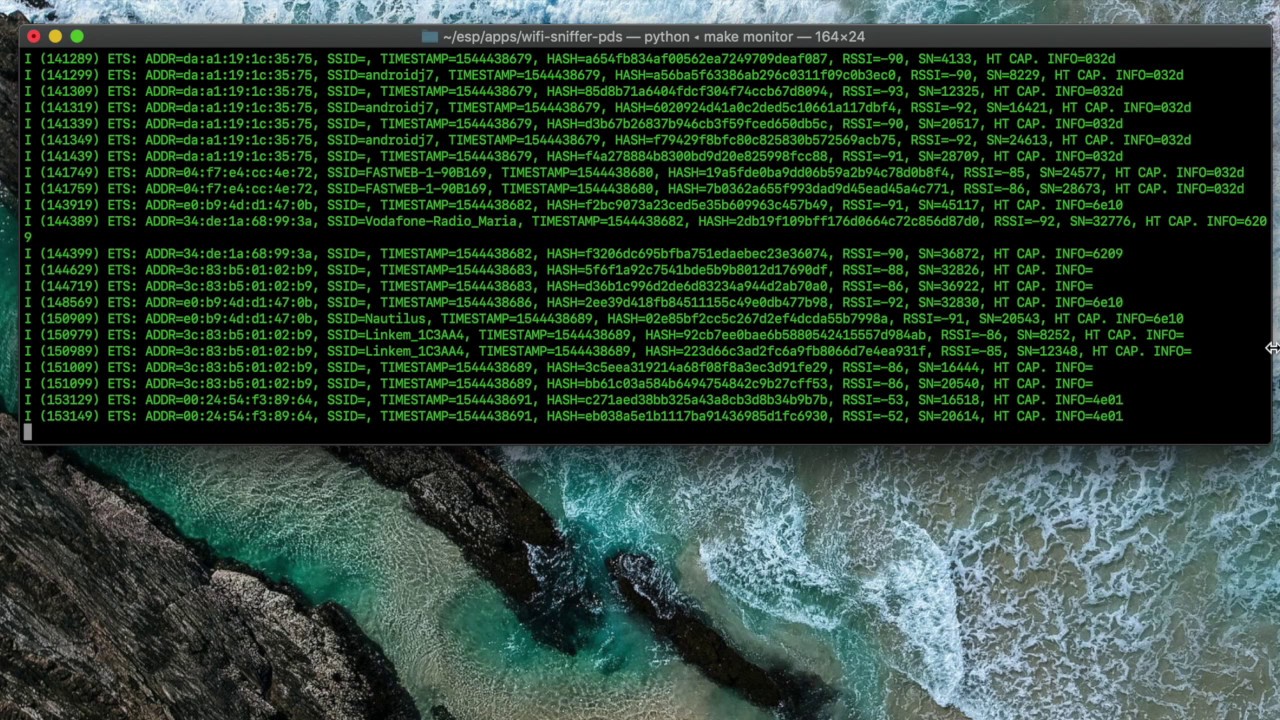
This firmware is written with the purpose to sniff probe request packets sent by smartphones that are looking for Wi-Fi connection. When the Wi-Fi connection is active on the smartphone, it will send in broadcast (in all channels frequencies) a probe request messagge asking if there is some free Wi-Fi or some known ones (i.e. the smartphone knows the password for that Wi-Fi). The ESP will sniff it and extract different types of informations.
From each sniffed packet the following informations is taken:
- MAC of the smartphone that has sent the request
- SSID of the wifi to which the request is sent
- The timestamp when the request is sent
- RSSI
- Sequence Number
- HT Capabilities Info
After each minute these informations are sent to a server and processed.
Finally, it is possible to see the processed informations (real time location of the smartphones, smartphone frequency, etc.) through a GUI.
- Firmware development
- ESP-IDF environment configuration
- Usage
- Configuration file
- Components
- Resources
The firmware consits in two main threads:
-
Sniffer task
- Sniff PROBE REQUEST packet and save the infomations described above into a file
-
Wi-Fi task
- Each minute take the informations saved by the sniffer task and send it to the server
- A lock is used in order to manage critical section for I/O operations in the file
The ESP32 is configured in WIFI_MODE_APSTA mode: it creates "soft-AP and station control block" and start "soft-AP and station". Thanks to this, the ESP32 is able to sniff and send informations to the server at the same time avoid losing packets information while sending data.
-
Setup Toolchain
-
Get ESP-IDF
Besides the toolchain (that contains programs to compile and build the application), you also need ESP32 specific API / libraries.
cd ~/esp git clone --recursive https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git -
Setup Path to ESP-IDF
The toolchain programs access ESP-IDF using IDF_PATH environment variable. This variable should be set up on your PC, otherwise projects will not build.
-
Install the Required Python Packages
python -m pip install --user -r $IDF_PATH/requirements.txt
Check the official site for more info.
-
Make sure you have exported the path
export IDF_PATH=~/esp/esp-idf export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/esp/xtensa-esp32-elf/bin -
Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/esp32-sniffer.git -
Establish serial connection between ESP32 and your PC
make menuconfigGo to
Serial flasher config, thenDefault serial portand set the port in which ESP32 is connectedNote that, if you are using a bridge, probably you need to download some driver:
This provides a guide on how establish serial connection between ESP32 and PC.
-
Build code and flash the ESP32
make all && make flash -
See logs
make monitor
File /main/Kconfig.projbuild contains two differnt menu:
-
SPIFFS (SPI Flash File System)
It contains some important information about the SPIFFS partion:
- SPIFFS Base address
- SPIFFS Size
- SPIFFS Logical block size
- SPIFFS Logical page size
SPIFFS is a file system that supports wear leveling, file system consistency checks and more.
-
Configurations
It contains different variables, e.g:
- ESP32_ID: ID of the ESP32
- WIFI_SSID: SSID of WiFi (network name)
- WIFI_PASS: WiFi password (WPA or WPA2)
- BROKER_ADDR: IP of the MQTT broker
- BROKER_PSW: password of the MQTT broker
- BROKER_PORT: port of the MQTT broker
- CHANNEL: channel in which ESP32 will sniff PROBE REQUEST
- SNIFFING_TIME: time of sniffing
- etc...
In order to configure the variables mentioned above, open terminal inside the project folder and run
make menuconfig
- Select the menu you want to modify
- Edit variables as you like
You can also add different menus with different variables:
- Open Kconfig.projbuild
- Start menu with: menu "menu name"
- Add the variables you need
- End menu with: endmenu
-
SPIFFS
You need to create a partition table
-
ESP32 MQTT
Has been used ESP32 MQTT Library
-
MD5
Hash function used on the packets in order to get a unique identifier for each packet packet
- Official esp-idf git repo to see some examples and information about the used data structure.
- Latest Documentation version for Espressif IoT Development Framework.
- ESP32 forum to ask questions and find community resources.
- ESP32-IDF Documentation for browseable modules, namespaces, data structures and files.
Check also this demonstration video to see how ESP32 works.
Longum iter est per praecepta, breve et efficax per exempla