Welcome to the CS52 workshop session on Bootstrap. During this workshop, you will learn the basics of using the Bootstrap framework by creating a clean, responsive, and mobile friendly web page.
For this workshop, you will be asked to incorporate many of the components of Bootstrap into a simple website. Your challenge, should you choose to accept it, is:
Take the poorly formatted and un-styled HTML that we have provided for you in this workshop and use Bootstrap to turn it into a masterpiece, without using any CSS.
In order to complete the challenge, follow these steps:
- Fork the repository
- Set up Bootstrap
- Create the Navigation Bar
- Add a Jumbotron
- Encapsulate Content in a Grid Layout
- Style the footer
To start our workshop, please clone this repository to your computer. It contains a bare-bones HTML file with content that we will be starting with. Open it up – notice how ugly it looks right now?
Setting up Bootstrap is simple – all you have to do is link it into the html from a CDN. For example, you can link in Bootstrap by including the following line in the <head> of your HTML:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
Also, add these scripts to the very end of the <body> (only necessary for certain mobile responsive features):
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.2.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
Lastly, to ensure proper rendering and touch zooming, add the following <meta> tag inside the <head>:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
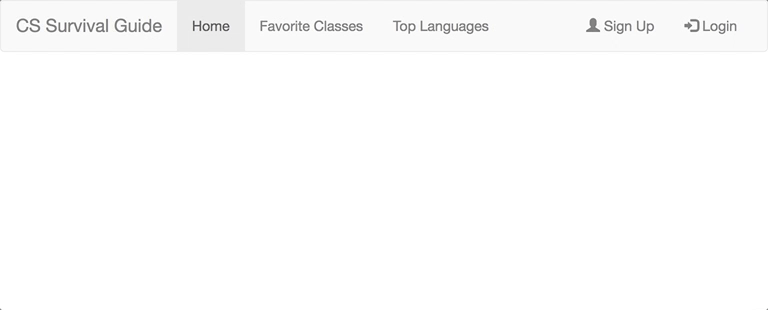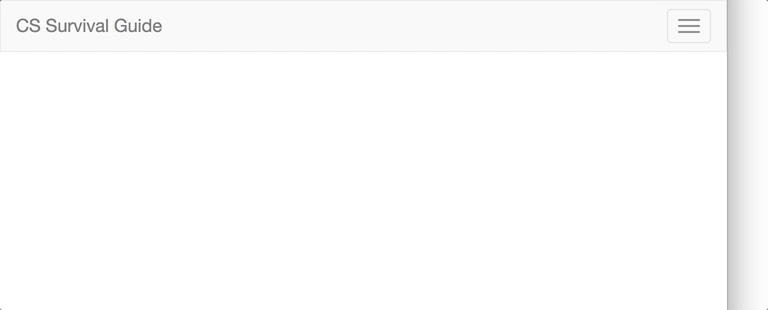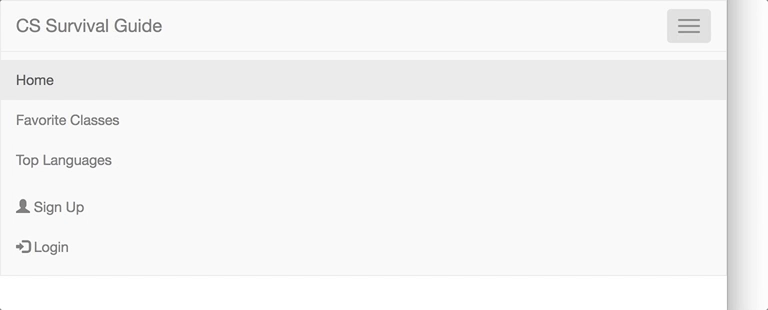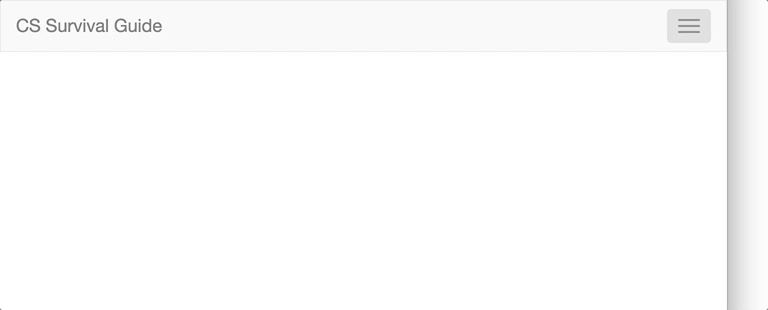
First, we will begin by setting up a simple navbar for the site. Bootstrap provides many different classes that can be used to customize a navbar.
To customize the navbar using Bootstrap, we will incorporate Bootstrap classes into the <nav> section of the HTML.
To add a standard navbar, use <nav class="navbar navbar-default">.
Next, within the nav element, add the container-fluid class to the div – this class creates a full width container spanning the entire width of your viewport.
To make the title of the website a header, add the navbar-header class to the "Dartmouth CS Survival Guide" div and navbar-brand to the anchor tag. This will give the text a slightly larger size.
To add links to the navbar, simply add to both unordered list tags the classes nav navbar-nav.
At this point, it should look miles better already!
All just by adding a few simple classes to your HTML. But let's make it a little better.
Often times, you want to align specific parts of the navbar to the left or right. Let's do that here. Add the navbar-right class to the unordered list tag containing the "Sign Up" and "Login" items.
To indicate that the Home page is the page we are currently on, add the active class to Home's list item element.
Now, let's make this navbar responsive. We will make the navigation bar hidden on small screens and replaced by a button in the top right corner.
The first step to adding this is to add the button itself. Add a button tag inside the navbar-header div, with the following attributes:
- type: button
- class: navbar-toggle
- data-toggle: collapse
For the actual display button, create a "hamburger" button using the .icon-bar class. Inside the button tag, add a few copies of <span class = "icon-bar"></span>, however many you like.
Now, the content that you want to actually be collapsed when the screen is narrow needs to be wrapped in a <div> with classes collapse and navbar-collapse. For example, if you want to remove everything except for the header, wrap the two unordered lists in a div with those classes.
Lastly, to connect the hamburger button to the collapsing content, add and match the data-target attribute of your button to the id of your collapsing div. For those of you who completed the CSS Checkbox Hack for Lab 1, this step is similar to linking the input and label elements. Just like that, you have a responsive menu navigation bar!
As a final touch, add icons to the two right items. Inside these two list item tags and within the anchor tags, add <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> and <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> (note the space codes separating the icon and the following text), respectively.
And that's it! Note that many variations of this exist, such as navbar-inverse instead of navbar-default to invert the colors, or navbar-fixed-top to pin to the top even when scrolling (try it out). If you're interested in more complex Bootstrap navigation bar examples, there are many links online demonstrating additional features.
A jumbotron indicates a big box for calling extra attention to some special content or information. To create a jumbotron in Bootstrap, replace the page_header class in the corresponding div with jumbotron. See the instant difference!
To ensure that the jumbotron doesn't extend to the edge of the screen, you can place the jumbotron inside of a div with the container class.
Now that you have formatted the navbar and the jumbotron to look nicely, it's time to format the content of the web page. In the class labeled grid_layout, we have provided you with some content to be formatted using the grid layout. Feel free to edit the content as you wish, but the main focus here should be formatting it.
To begin, change the class to be titled container_fluid. As mentioned in the navbar section, this class creates a full width container spanning the entire width of the viewport - this is used to encapsulate the content.
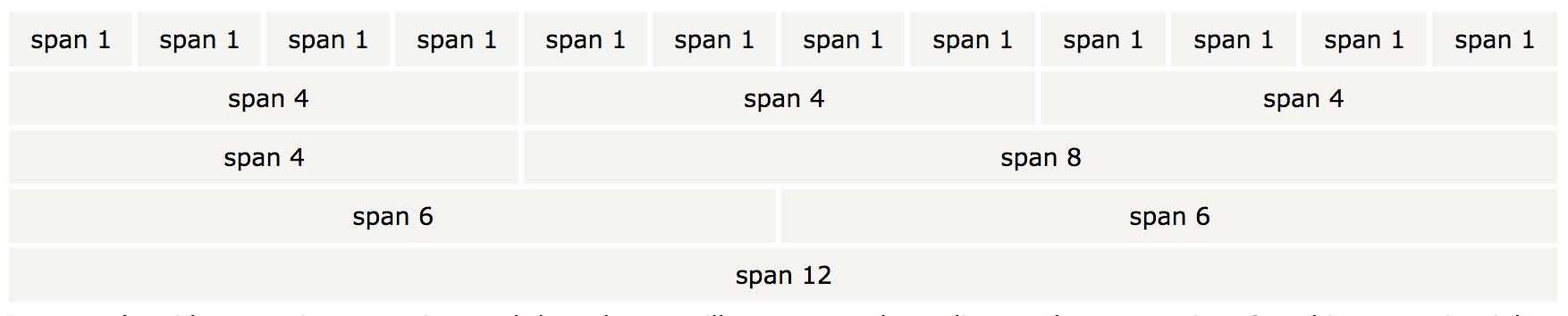
Now that you have the content encapsulated in a container, you can begin using the grid layout to format the content. The basic structure of the grid layout is a series of rows that are separated into columns. Each row can be divided into at the most twelve columns or at the least two columns. Inside of the columns will be your desired content. This is obviously vague, so here is an example of how this works:
The HTML to create a row and divide it into three equal length columns would look as follows:
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">YOUR CONTENT HERE</div>
<div class="col-md-4">YOUR CONTENT HERE</div>
<div class="col-md-4">YOUR CONTENT HERE</div>
</div>
Notice the class that we used for the column is titled "col-md-4". Bootstrap provides four different widths of columns, "xs" for mobile phones, "sm" for tablets, "md" for desktops, and "lg" for extended desktops. For the purposes of this tutorial, it is probably best to use "col-md-*".
It is up to you to decide on how you would like to format the content we have provided into a grid layout. For instance, you could put each <h3> and <p> in a row in equal width columns, like such:
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<h3>Header Content</h3>
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<p>Paragraph Content</p>
</div>
</div>
Or, you could put two header and content pairs per row, and so on - again, it is up to you to decide which layout looks the best.
There aren't many things for footers specifically in Bootstrap, but the tools you have used in the first three parts should be enough to have a decent style. Try to make your footer look like the image below, using the various classes we have previously used.
(Need a hint? Try using the various container/nav-related classes from above)
Four sections, each of which should be nicely formatted and responsive
- Navigation bar
- Jumbotron
- Grid layout
- Footer
Now, to complete the Bootstrap workshop, add TWO extra features on your own. We have a few suggestions below, but feel free to pick something not listed if you wish:
- Tabs/Pills
- Modals
- Buttons
- Dropdown menu in the navbar
- Incorporate some of Bootstrap's unique typography
- Carousels (advanced – counts as two)
- Scrollspy (advanced – counts as two)
Be creative! One of the best parts about Bootstrap is that there are an endless amount of features and classes already built-in, and extra ones are being added with every new version.
We hope this workshop has demonstrated to you the power of Bootstrap. Without any CSS you quickly applied a basic format and style to plain HTML; keep in mind that although there is a still a lot of work left to be done on this page, having Bootstrap handle so much of the initial styling makes adding in your own customized CSS on top even less painful!