This project contains the source code of cuda_sort and a benchmark program that sorts arrays of integers and floating point numbers of various sizes with cuda_sort, thrust::sort (Nvidia's own GPU-accelerated sort implementation) and std::sort and prints the results.
The project is purely educational by nature; the code is not meant for general use.
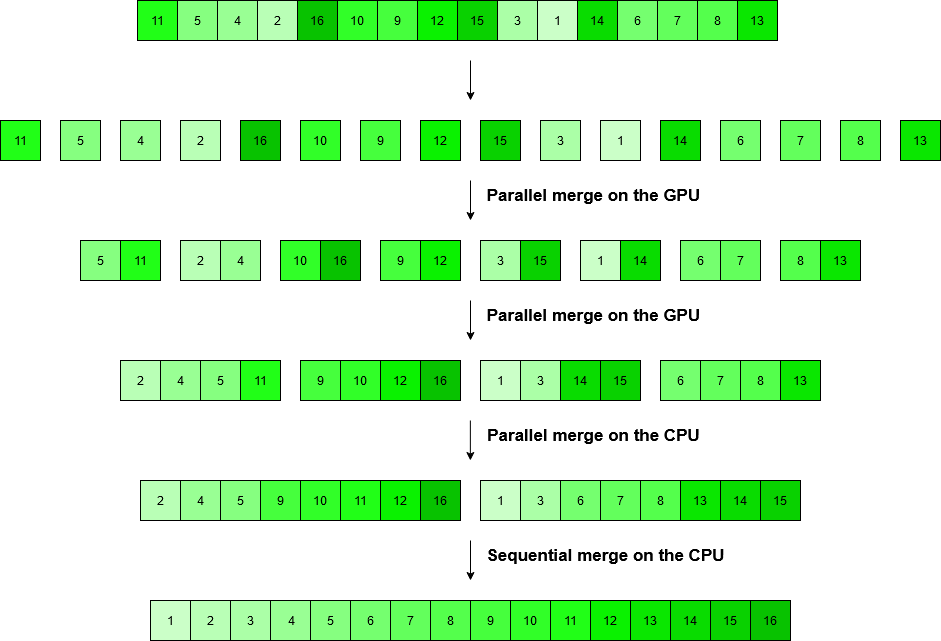
Cuda_sort works exactly like an ordinary merge sort would, except that the merging is done in parallel rather than sequentially in a recursive manner, and both the GPU and CPU are involved. The distribution of work between the two processing units is visualized below.
In summary:
- The input data is copied from RAM to VRAM.
- The GPU performs parallel merging as long as it is more efficient than merging on the CPU.
- The input data is copied from VRAM to RAM.
- The CPU performs parallel merging on multiple threads.
- The final merge is done sequentially on a single CPU thread.
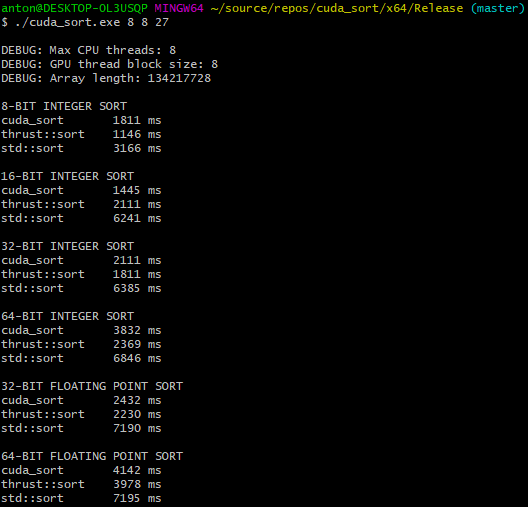
Below is a screenshot of the results of the benchmark.
Obviously, the highly optimized thrust::sort is faster than cuda_sort. However, to my satisfaction, the performance of cuda_sort is in the same ballpark.
Interestingly, it appears that both GPU sorts are slow in the 64-bit category, whereas the performance of std::sort seems rather constant.
The interface of cuda_sort is simple enough:
template<typename T> T* cuda_sort(T* h_src, size_t array_length, size_t cpu_threads = 8, size_t gpu_thread_block_size = 8)
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
T |
The element type contained by the array. Has to be a variation of int or float |
h_src |
The array to be sorted |
array_length |
The number of elements in the array. Must be a power of 2 |
cpu_threads |
The maximum number of CPU threads running concurrently. Must be a power of 2 (default: 8) |
gpu_thread_block_size |
The number of threads per GPU thread block. Must be a power of 2 (default: 8) |
return value |
h_src |
The user is responsible for checking that the conditions set above are met.
The benchmark program has a very simple command line interface:
cuda_sort.exe <number of CPU threads> <GPU thread block size> <array size as power of two>
The constraints set for the parameters of cuda_sort apply. Passing d as a command line argument will make the benchmark use the default value.
On Windows:
- Install Microsoft Visual Studio + Microsoft Visual C++ Compiler
- Install CUDA Toolkit (with Visual Studio extension)
- Open
cuda_sort.slnin Visual Studio and compile the solution
Cuda_sort has only been tested with an Nvidia GTX 1070 graphics card and an Intel i7-4790K processor.
The If-you-are-crazy-enough-to-use-this-go-ahead License 1.0. The author will not be responsible for the frying of any piece of silicon or any other form of harm that could ensue.