Basic Litecoin Dockerfile has been taken from this repository
Checksum verification has been already setup. Comment has been added for the checksum verification.
Security Scan using Anchore
As a tool, Anchore has been used for docker image scanning. An inline scanning with anchore has been performed.
After building the Dockerfile using:
docker build -t litecoin:0.18.1 .
Image scanning:
curl -s https://ci-tools.anchore.io/inline_scan-v0.6.0 | bash -s -- -f -d Dockerfile -b .anchore-policy.json litecoin:0.18.1
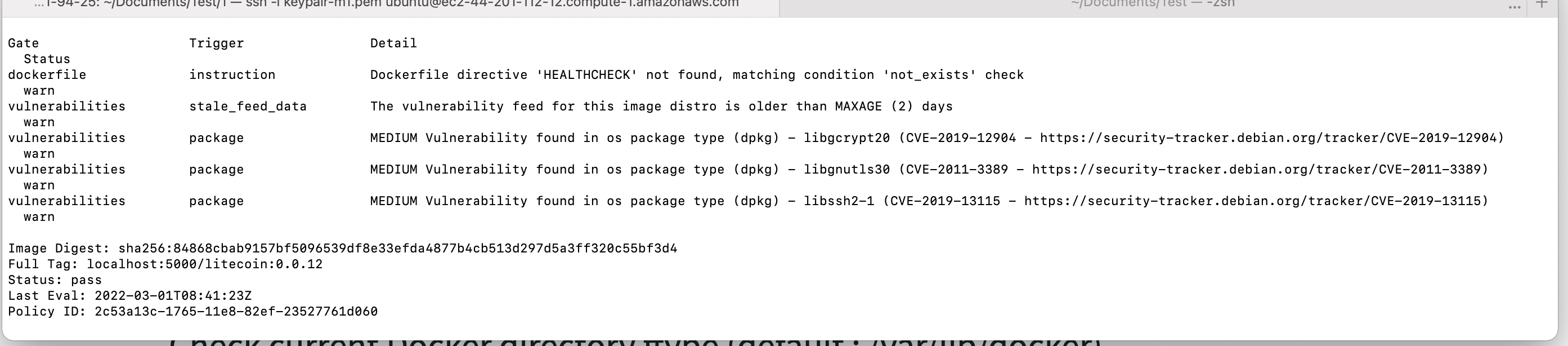
Scan result can be found below:
As seen above, there are some medium vulnerabilities which has been raised by the tool. The tool can be configured according to the security contraints in order to verify that the docker image is compliant
In order to deploy the stack as a statefulset:
first setup a quick Kubernetes environement using Minikube
minikube start
After installing Minikube, re-build the Docker image inside Minikube VM so it can be pulled from Kubernetes when deploying the statefulset.
docker build -t litecoin:0.18.1 .
The statefulset has been configured in order to deploy the pod containing the container instance of the litecoin docker image as well as mounting/creating the PVC using volumeClaimTemplate & VolumeMount.
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
containers:
- name: litecoin
image: litecoin:0.18.1
ports:
- containerPort: 9332
name: litecoin
volumeMounts:
- name: litecoin
mountPath: /home/litecoin/.litecoin
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: litecoin
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
For full configuration, please check this link.
Verify that the statefulset is correctly running & ready.

Verify that the pod deployed by the statefulset is correctly running & ready.

Verify that the PVC & PV has been correctly created and mounted.

Usually a basic CI/CD pipeline contains the following steps:
- Build code & Install external package
- Linter
- Unit testing
- Code Quality gate, Code Scanning & Dependencies scanning
- Build Docker image
- Image Scanning
- Push Docker image to the registry / Artifactory
- Deploy the docker image in K8s cluster.
As there is no code in the scope, let's implement stage 5,6,7 & 8 using Gitlab-CI. Please note that for this test I was able to demonstrate what stages and what result the pipeline will have after full configuration.
First step is to build the Docker Image.
build:
stage: build
image:
name: docker:stable
services:
- docker:stable-dind
script:
- docker build -t $REPO_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME .
Before pushing the image into the registry, first a security check must be executed in the pipeline in order to verify if the docker image is compliant. For this Anchor has been integrated to the Gitlab-Ci.
scan:
stage: scan
image:
name: anchore/anchore-engine:latest
entrypoint: [""]
services:
- name: anchore/engine-db-preload:latest
alias: anchore-db
variables:
GIT_STRATEGY: none
ANCHORE_HOST_ID: "localhost"
ANCHORE_ENDPOINT_HOSTNAME: "localhost"
ANCHORE_CLI_USER: "admin"
ANCHORE_CLI_PASS: "foobar"
ANCHORE_CLI_SSL_VERIFY: "n"
ANCHORE_FAIL_ON_POLICY: "true"
ANCHORE_TIMEOUT: 500
script:
- |
curl -o /tmp/anchore_ci_tools.py https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anchore/ci-tools/master/scripts/anchore_ci_tools.py
chmod +x /tmp/anchore_ci_tools.py
ln -s /tmp/anchore_ci_tools.py /usr/local/bin/anchore_ci_tools
- anchore_ci_tools --setup
- anchore-cli registry add "$CI_REGISTRY" gitlab-ci-token "$CI_JOB_TOKEN" --skip-validate
- anchore_ci_tools --analyze --report --image "$REPO_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME" --timeout "$ANCHORE_TIMEOUT"
- |
if ; then
anchore-cli evaluate check "$REPO_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME"
else
set +o pipefail
anchore-cli evaluate check "$REPO_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME" | tee /dev/null
fi
After security checks using Anchore, the pipeline will be allowed to push the docker image into the registry.
push:
stage: push
image:
name: docker:stable
services:
- docker:stable-dind
script:
- docker tag $$REPO_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME $REPO_REGISTRY_URL:$TAG
- docker push $REPO_REGISTRY_URL:$TAG
- docker rmi $$REPO_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME $REPO_REGISTRY_URL:$TAG
In order to deploy, first at least one single Gitlab runner into Kubernetes needs to be deployed following Helm Chart
Gitlab runner is deployed as a Pod in order to execute the Gitlab job. The Helm chart should be configured before.
A new helm chart should be created as well in order to deploy the ecosystem. In our case, only statefulset needs to be deployed, so this element can be encapsulated inside a new Helm chart. The deployment stage should be similar to this:
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: alpine/helm:latest
script:
- helm init --client-only
- helm --namespace $NAMESPACE upgrade -i $REPO_NAME --set image.tag=$TAG,env=$ENV,image.repository=$REPO_REGISTRY_URL $PATH_TO_VALUES
tags:
- k8s
- dev
The final result of the Gitlab CI/CD pipeline should be similar to this.
Another approach could be the usage of ArgoCD as it is easy to setup using Helm chart and in order to separate CI & Deployment tools. GitOps - ArgoCD & Gitlab-CI
Make script in order to delete all non-attached litecoin docker images that have age between 4 hours and 8 hours:
docker rmi $(docker images -a | grep hours | grep litecoin | awk '3<$4 && $4<8' | awk '{print $3}')
Above, docker images -a | grep hours | grep litecoin list all images that have litecoin and hours in age. awk '3<$4 && $4<8' is for filtering by age between 4 and 8. Last pipe awk '{print $3}' is to return images ids that will be given as an argument to docker rmi command in order to delete them.
The easiest way here is to run the previous shell script using Python but of course it is not the safest way. Running a shell exec is somehow risky in term of security and commands injections.
From my point of view, after a quick research a good way is to code the whole script in Python based on docker-sdk library.
I have rarely used Terraform in my past experiences. For policies I would recommend Open policy agent that handles policies through a custom admission controller. The rules are made in Rego "Policy language" and implemented inside configmaps consumed by the webhook of OPA. The communication between components must be over TLS.
The usage of cert-manager can be useful for certificate management in case we use OPA as it is useful to handle certificate authorities, certificate injection and so on..
Also I have noticed that there is some roles here.. why don't we use basic Kubernetes roles, rolebindings clusterroles, groups users etc..
I can't go further for this question as I need more clarification and answers to some questions.