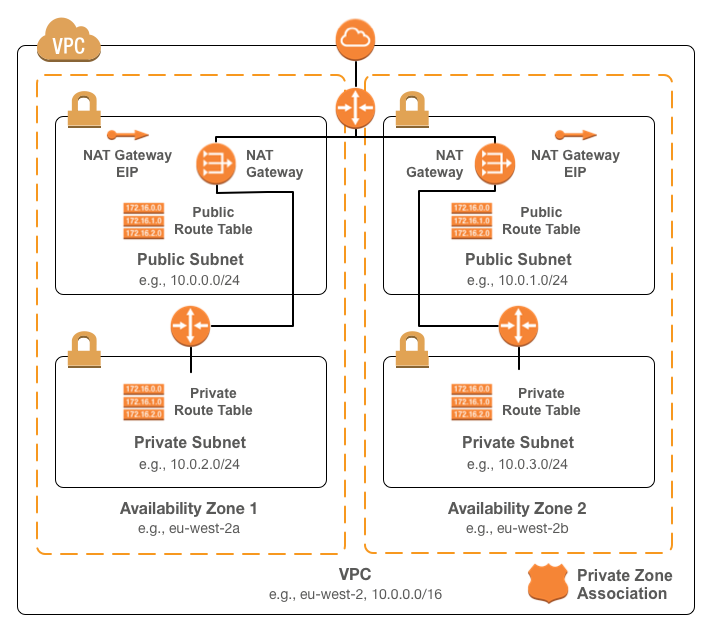
A Terraform module for building a base network in AWS.
The network consists of:
- Public and private subnets for each supplied availability zone
- A NAT gateway for each supplied availability zone for outbound Internet connectivity
- Routes from the public subnets to the Internet gateway
- Routes from the private subnets to the NAT
- Standard tags for all resources
To use the module, include something like the following in your Terraform configuration:
module "base-network" {
source = "infrablocks/base-networking/aws"
version = "4.0.0"
vpc_cidr = "10.0.0.0/16"
region = "eu-west-2"
availability_zones = ["eu-west-2a", "eu-west-2b"]
component = "important-component"
deployment_identifier = "production"
private_zone_id = "Z3CVA9QD5NHSW3"
}See the Terraform registry entry for more details.
| Name | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
vpc_cidr |
The CIDR to use for the VPC. | - | Yes |
region |
The region into which to deploy the VPC. | - | Yes |
availability_zones |
The availability zones for which to add subnets. | - | Yes |
public_subnets_offset |
The number of /24s to offset the public subnets in the VPC CIDR. | 0 |
No |
private_subnets_offset |
The number of /24s to offset the private subnets in the VPC CIDR. | 0 |
No |
component |
The component this network will contain. | - | Yes |
deployment_identifier |
An identifier for this instantiation. | - | Yes |
dependencies |
A comma separated list of components depended on my this component. | [] |
No |
include_route53_zone_association |
Whether or not to associate VPC with the private Route 53 zone ("yes" or "no"). |
"yes" |
No |
private_zone_id |
The ID of the private Route 53 zone` | - | If include_route53_zone_association is "yes" |
include_nat_gateways |
Whether or not to deploy NAT gateways for outbound Internet connectivity ("yes" or "no"). |
"yes" |
No |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
vpc_id |
The ID of the created VPC. |
vpc_cidr |
The CIDR of the created VPC. |
availability_zones |
The availability zones in which subnets were created. |
number_of_availability_zones |
The number of populated availability zones available. |
public_subnet_ids |
The IDs of the public subnets. |
public_subnet_cidrs |
The CIDRs of the public subnets. |
public_route_table_ids |
The IDs of the public route tables. |
private_subnet_ids |
The IDs of the private subnets. |
private_subnet_cidrs |
The CIDRs of the private subnets. |
private_route_table_ids |
The IDs of the private route tables. |
nat_public_ips |
The EIPs attached to the NAT gateways. |
internet_gateway_id |
The ID of the created IGW. |
This module is compatible with Terraform versions greater than or equal to Terraform 1.0 and Terraform AWS provider versions greater than or equal to 3.27.
- ec2:DescribeVpcs
- ec2:DescribeAddresses
- ec2:DescribeVpcAttribute
- ec2:DescribeVpcClassicLink
- ec2:DescribeVpcClassicLinkDnsSupport
- ec2:DescribeRouteTables
- ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups
- ec2:DescribeNetworkAcls
- ec2:DescribeSubnets
- ec2:DescribeInternetGateways
- ec2:DescribeNatGateways
- ec2:ModifyVpcAttribute
- ec2:AllocateAddress
- ec2:ReleaseAddress
- ec2:AssociateRouteTable
- ec2:DisassociateRouteTable
- ec2:AttachInternetGateway
- ec2:DetachInternetGateway
- ec2:DeleteInternetGateway
- ec2:CreateRoute
- ec2:CreateNatGateway
- ec2:CreateVpc
- ec2:CreateTags
- ec2:CreateSubnet
- ec2:CreateRouteTable
- ec2:CreateInternetGateway
- ec2:DeleteRoute
- ec2:DeleteRouteTable
- ec2:DeleteSubnet
- ec2:DeleteNatGateway
- ec2:DeleteVpc
- s3:ListBucket
- s3:GetObject
- s3:GetObjectTagging
- s3:DeleteObject
- route53:AssociateVPCWithHostedZone
- route53:DisassociateVPCFromHostedZone
- route53:GetChange
- route53:GetHostedZone
In order for the build to run correctly, a few tools will need to be installed on your development machine:
- Ruby (3.1)
- Bundler
- git
- git-crypt
- gnupg
- direnv
- aws-vault
Installing the required tools is best managed by homebrew.
To install homebrew:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"Then, to install the required tools:
# ruby
brew install rbenv
brew install ruby-build
echo 'eval "$(rbenv init - bash)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'eval "$(rbenv init - zsh)"' >> ~/.zshrc
eval "$(rbenv init -)"
rbenv install 3.1.1
rbenv rehash
rbenv local 3.1.1
gem install bundler
# git, git-crypt, gnupg
brew install git
brew install git-crypt
brew install gnupg
# aws-vault
brew cask install
# direnv
brew install direnv
echo "$(direnv hook bash)" >> ~/.bash_profile
echo "$(direnv hook zsh)" >> ~/.zshrc
eval "$(direnv hook $SHELL)"
direnv allow <repository-directory>Running the build requires an AWS account and AWS credentials. You are free to configure credentials however you like as long as an access key ID and secret access key are available. These instructions utilise aws-vault which makes credential management easy and secure.
To run the full build, including unit and integration tests, execute:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./goTo run the unit tests, execute:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go test:unitTo run the integration tests, execute:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go test:integrationTo provision the module prerequisites:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:prerequisites:provision[<deployment_identifier>]To provision the module contents:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:root:provision[<deployment_identifier>]To destroy the module contents:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:root:destroy[<deployment_identifier>]To destroy the module prerequisites:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:prerequisites:destroy[<deployment_identifier>]Configuration parameters can be overridden via environment variables. For
example, to run the unit tests with a seed of "testing", execute:
SEED=testing aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go test:unitWhen a seed is provided via an environment variable, infrastructure will not be destroyed at the end of test execution. This can be useful during development to avoid lengthy provision and destroy cycles.
To subsequently destroy unit test infrastructure for a given seed:
FORCE_DESTROY=yes SEED=testing aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go test:unitTo generate an SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 4096 -C integration-test@example.com -N '' -f config/secrets/keys/bastion/sshTo generate a self signed certificate:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365To decrypt the resulting key:
openssl rsa -in key.pem -out ssl.keyTo encrypt a GPG key for use by CircleCI:
openssl aes-256-cbc \
-e \
-md sha1 \
-in ./config/secrets/ci/gpg.private \
-out ./.circleci/gpg.private.enc \
-k "<passphrase>"To check decryption is working correctly:
openssl aes-256-cbc \
-d \
-md sha1 \
-in ./.circleci/gpg.private.enc \
-k "<passphrase>"Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/infrablocks/terraform-aws-base-networking. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space for collaboration, and contributors are expected to adhere to the Contributor Covenant code of conduct.
The library is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.