Covert the Postman collection to the K6 java script code.
The feature will convert the JSON files of the Postman collection into k6 script. Then we will launch the K6 scripting files to get the result of the performance test.
Install the k6 load testing tool on macOS using Homebrew.
# brew install k6By running brew install k6, Homebrew will connect to its package repository, download the necessary files, and install k6 on your macOS system. It will handle the installation process and set up the required dependencies and configurations.
After creating the collection in the postman export the collection as a json file.
# postman-to-k6 collection.json -o k6-script.jspostman-to-k6: This is a command-line tool that converts Postman collections into k6 script files.
collection.json: This is the input file, which should be a Postman collection exported in JSON format. Replace collection.json with the actual filename and path of your Postman collection file.
-o k6-script.js: This flag specifies the output file name and format. In this case, it's set to -o k6-script.js, indicating that the converted k6 script should be saved to a file named k6-script.js.
By running this command, the postman-to-k6 tool will parse the Postman collection specified in collection.json and generate a k6 script that replicates the requests, assertions, and flow defined in the collection. The generated k6 script (k6-script.js) can then be used with the k6 load testing tool to execute the same requests and scenarios defined in Postman but within the k6 environment.
Note: If you use the environment/global variable with your Postman collection, also export the environment/global file, since we should include it to generate the k6 script file.
# postman-to-k6 collection.json --environment environment.json -o k6-script.js--environment environment.json: This flag specifies the environment file to be used during the conversion process. An environment file contains variables and values that can be used within the requests and scripts in the Postman collection. Replace environment.json with the actual filename and path of your environment file.
# postman-to-k6 collection.json --global globals.json -o k6-script.js--global globals.json: This flag specifies the globals file to be used during the conversion process. A globals file contains global variables and values that can be used within the requests and scripts in the Postman collection. Replace globals.json with the actual filename and path of your globals file.
After generating the execute the above comments you can see the k6-script.js file is exported on your local system.
To run the generated script file execute the below comments
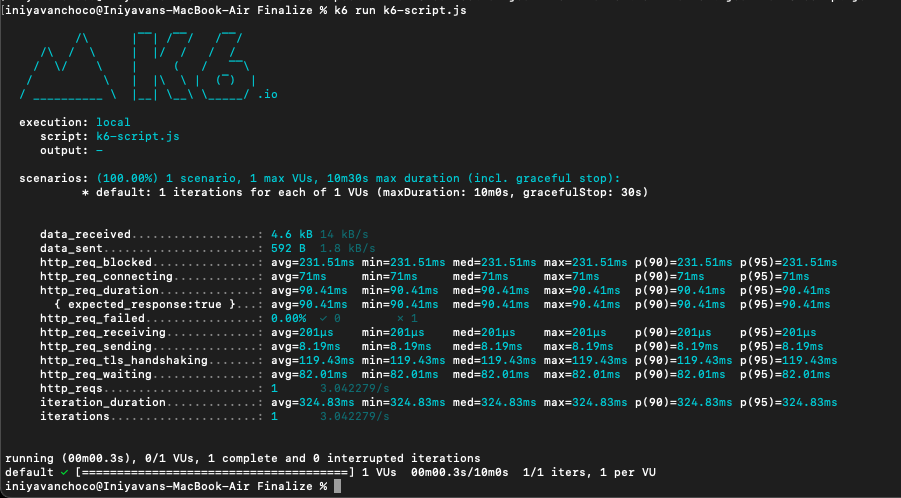
# k6 run k6-script.jsk6 run: This is the command to run the k6 load testing tool.
k6-script.js: This is the filename of the k6 script that contains the load testing scenarios and logic. Replace k6-script.js with the actual filename of your k6 script.
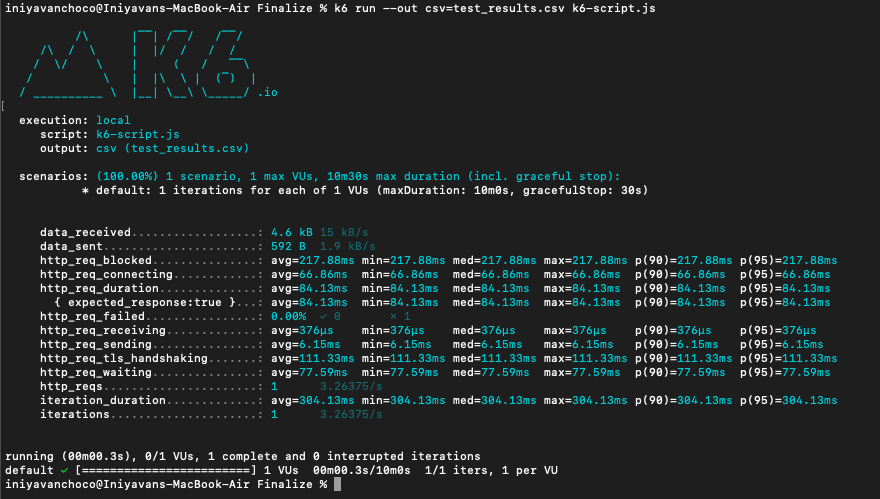
We can generate the reports multiple way. But mostly community use csv file to export the test report. Refer the Grafana K6.io offical documentation to get more informantion. Follow the below comment to get the CSV output.
# k6 run --out csv=test_results.csv k6-script.js--out csv=test_results.csv: This flag specifies the output format and the file to which the results will be exported. In this case, it's set to CSV format, and the results will be saved to a file named test_results.csv. The csv= prefix indicates the desired output format and the filename to save the results.
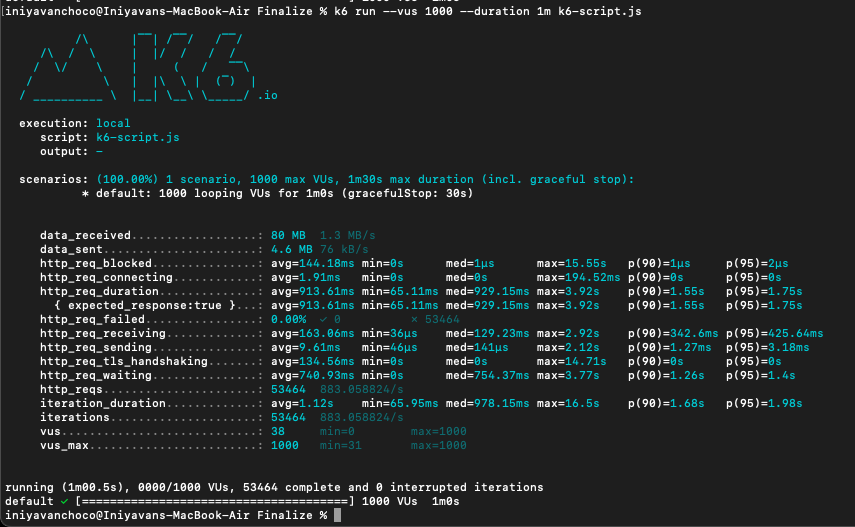
We can run the script file with a customized scenarios
# k6 run --vus 1000 --duration 1m k6-script.js--vus 1000: This flag specifies the number of virtual users (VUs) to simulate during the load test. In this case, it's set to 1000, indicating that 1000 virtual users will be created to generate concurrent load on the system under test.
--duration 1m: This flag specifies the duration of the load test. In this case, it's set to 5 minutes (5m), indicating that the load test will run for 5 minutes.
Here's an explanation of some common columns you may find in a k6 CSV output file:
time: The timestamp indicating when the measurement was recorded. It is typically in Unix timestamp format or a human-readable date and time format.
iteration: The iteration number or index of the virtual user (VU) executing the test at that specific point in time. group: If you've organized your test scenarios into groups, this column indicates the group name to which the measurement belongs.
name: The name of the specific test or request being measured.
http_req_duration: The duration of the HTTP request/response cycle in milliseconds (ms).
http_reqs: The number of HTTP requests sent.
http_req_failed: The number of failed or unsuccessful HTTP requests.
http_req_connecting: The number of requests currently in the connecting state.
http_req_tls_handshaking: The number of requests currently in the TLS handshaking state.
http_req_sending: The number of requests currently in the sending state.
http_req_waiting: The number of requests currently in the waiting state.
http_req_receiving: The number of requests currently in the receiving state.
http_req_duration: The duration of the HTTP request/response cycle in milliseconds (ms).
http_reqs: The number of HTTP requests sent.
http_req_failed: The number of failed or unsuccessful HTTP requests.