Pew pew! Sane defaults for mocking behavior! Patch objects, variables, attributes, etc by passing in the thing in question, rather than passing in dot-delimited path strings! Create tests faster than ever!
Supported Python Versions: 3.10+
Pip installation:
pip install megamock
poetry (as a development dependency):
poetry add megamock --group=dev
MegaMock is a library that provides a better interface for mocking and patching in Python. Its version
of patch doesn't have any gotchas based on how you import something, and it also automatically
creates mocks using best practices. Additionally, the generated mock types are unions of the mocked object
and MegaMock, allowing you to better leverage your IDE's autocomplete.
Mock:
class_mock = mock.create_autospec(ClassICareAbout, instance=True)
# cmd / alt clicking on "method_call" doesn't direct you to the definition
class_mock.method_call.return_value = "some value"
# can't simply cmd / alt click and go to ClassICareAbout
with mock.patch("some.hard.to.remember.and.long.dot.path.ClassICareAbout", class_mock) as mock_instance:
do_something()MegaMock:
# cmd / alt clicking on ClassICareAbout takes you to the definition
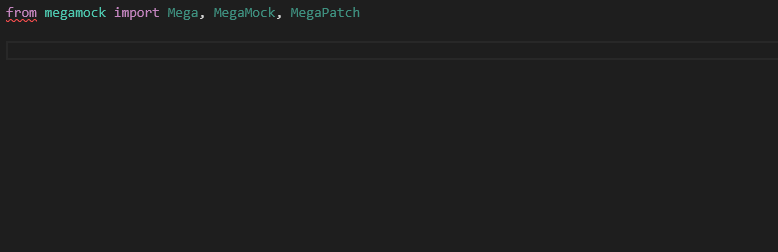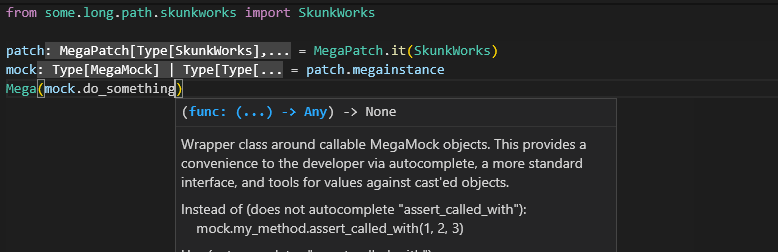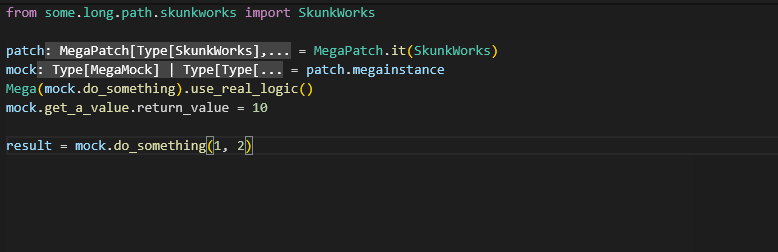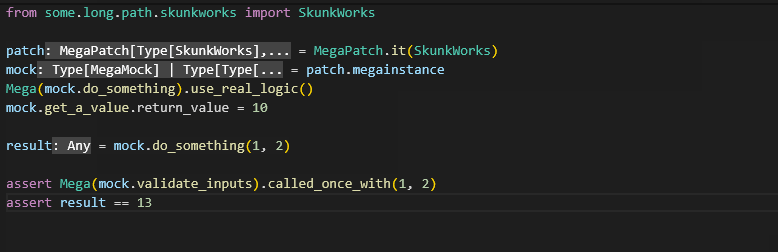
patch = MegaPatch.it(ClassICareAbout)
mock_instance = patch.megainstance
# cmd / alt clicking on "method_call" directs you to the definition
mock_instance.method_call.return_value = "some value"
do_something()MegaMock was created to address some shortcomings in the built-in Python library:
- Legacy code holds back "best practice" defaults, so many developers write sub-optimal mocks that allow things that should not be allowed. Likewise, writing better mocks are more work, so there's a tendency to write simpler code because, at that point in time, the developer felt that is all that was needed. MegaMock's simple interface provides sane defaults.
mock.patchis very commonly used, and can work well whenautospec=True, but has the drawback that you need to pass in a string to the thing that is being patched. Most (all?) IDEs do not properly recognize these strings as references to the objects that are being patched, and thus automated refactoring and reference finding skips them. Likewise, automatically getting a dot referenced path to an object is also commonly missing functionality. This all adds additional burden to the developer. WithMegaPatch, you can import an object as you normally would into the test, then pass in thing itself you want to patch. This even works for methods, attributes, and nested classes! Additionally, your IDE's autocomplete for attributes will work in many situations as well!mock.patchhas a gotcha where the string you provide must match where the reference lives. So, for example, if you have inmy_module.py:from other_module import Thing, then doingmock.patch("other_module.Thing")won't actually work, because the reference inmy_modulestill points to the original. You can work around this by doingimport other_moduleand referencingThingbyother_module.Thing. MegaMock does not have this problem, and it doesn't matter how you import.
See the full features list.
from module.submodule import MyClassToMock
def my_method(...):
...
a_thing = MyClassToMock(...)
do_something_with_a_thing(a_thing)
...
def do_something_with_a_thing(a_thing: MyClassToMock) -> None:
result = a_thing.some_method(...)
if result == "a value":
...from megamock import MegaPatch
from module.submodule import MyClassToMock
def test_something(...):
patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClassToMock.some_method)
patch.return_value = "a value"
my_method(...)With pytest, MegaMock is easily leveraged by using the included pytest plugin. You can use it by adding -p megamock.plugins.pytest
to the command line.
Command line example:
pytest -p megamock.plugins.pytest
pyproject.toml example:
[tool.pytest.ini_options]
addopts = "-p megamock.plugins.pytest"The pytest plugin also automatically stops MegaPatches after each test. To disable this behavior, pass in the --do_not_autostop_megapatches
command line argument. If pytest-mock is installed, the default mocker will be switched to the pytest-mock mocker.
If you're not using the pytest plugin, import and execution order is important for MegaMock. When running tests, you will need to execute the start_import_mod
function prior to importing any production or test code. You will also want it so the loader is not used in production.
Core Classes
MegaMock - the primary class for a mocked object. This is similar to MagicMock. Use MegaMock.it(MyObject) to make MyObject the spec.
MegaPatch - the class for patching. This is similar to patch. Use MegaPath.it(MyObject) to replace new instances of the MyObject class.
Mega - helper class for accessing mock attributes without having to memorize the due to lost type inference. Use Mega(some_megamock).
Note that the assert_ methods, such as assert_called_once, is now called_once and returns a boolean. The assertion error
is stored in Mega.last_assertion_error.
Dependency injection example:
from megamock import MegaMock
def test_something(...):
manager = MegaMock.it(MyManagerClass)
service = SomeService(manager)
...MegaPatch example:
from elsewhere import Service
from megamock import MegaPatch
def test_something(...):
patched = MegaPatch.it(Service.make_external_call)
patched.return_value = SomeValue(...)
service = SomeService(...)
code_under_test(service)
...MegaMock objects have the same attributes as regular MagicMocks plus megamock and megainstance
For example, my_mega_mock.megamock.spy is the object being spied, if set. my_class_mock.megainstance is the instance returned when the class is instantiated.
The guidance document is available to provide in-depth information on using mocking and MegaMock. Continuing reading to quickly jump in to examples.
All examples below have the following imports:
from my_module import MyClass
from megamock import Mega, MegaMock, MegaPatchCreating a mock instance of a class:
mock_instance = MegaMock.it(MyClass)Creating a mock class itself:
mock_class = MegaMock.it(MyClass, instance=False)Spying an object:
my_thing = MyClass()
spied_class = MegaMock(spy=my_thing)
# ... do stuff with spied_class...
Mega(spied_class.some_method).call_args_list # same as wraps
# check whether a value was accessed
# if things aren't as expected, you can pull up the debugger and see the stack traces
assert len(spied_class.megamock.spied_access["some_attribute"]) == 1
spy_access_list = spied_class.megamock.spied_access["some_attribute"]
spy_access: SpyAccess = spy_access_list[0]
spy_access.attr_value # shallow copy of what was returned
spy_access.stacktrace # where the access happened
spy_access.time # when it happened (from time.time())
spy_access.top_of_stacktrace # a shorthand property intended to be used when debugging in the IDE
spy_access.format_stacktrace() # return a list of strings for the stacktrace
spy_access.print_stacktrace() # display the stacktrace to the consolePatching a class:
mock_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass)
# the class itself
mock_patch.new_value
# the class instance
mock_patch.megainstance
# the return value of the __call__ method on the class
mock_patch.megainstance.return_valuePatching a class attribute:
# temporarily update the max retries to 0
mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass.max_retries, new=0)Patching a class method:
mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass.my_method, return_value=...)Alternatively:
mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass.my_method)
mega_patch.mock.return_value = ...mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass.my_method)
mega_patch.new_value.return_value = ...You can also alter the return value of your mock without creating a separate mock object first.
mega_patch.return_value.user = SomeUser()Working with MegaPatch and classes:
mega_patch.new_value is the class type itself
mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass)
mega_patch.new_value.x is MyClass.xmega_patch.return_value is the class instance returned. However, there is the property
megainstance which is preferred because it has better type hinting.
mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(MyClass)
# instead of this, for which the static type is Any:
mega_patch.return_value is MyClass()
# use this, which has a static type of MegaMock | MyClass:
mega_patch.megainstance is MyClass()Patching a module attribute:
import my_module
MegaPatch.it(my_module.some_attribute, new=...)Patching a method of a nested class:
import my_module
MegaPatch.it(
my_module.MyClass.MyNestedClass.some_method,
return_value=...
)Setting the return value:
my_mock.my_method.return_value = "foo"Turning on real logic:
import my_module
from mega_mock import UseRealLogic
mega_patch = MegaPatch.it(my_module.SomeClass)
Mega(mega_patch.megainstance.some_pure_logic_method).use_real_logic()
do_something_that_invokes_that_function(...)Nobody said it was a big art gallery. Feel free to submit a PR that helps fix that. No artistic skill required.