This repository contains a script that can be used to easily debug ZooKeeper code. The script can be used to run a ZK cluster locally, while remotely debugging one of the servers using IntelliJ IDEA.
After having docker running, you simply execute:
./debug_zk.sh
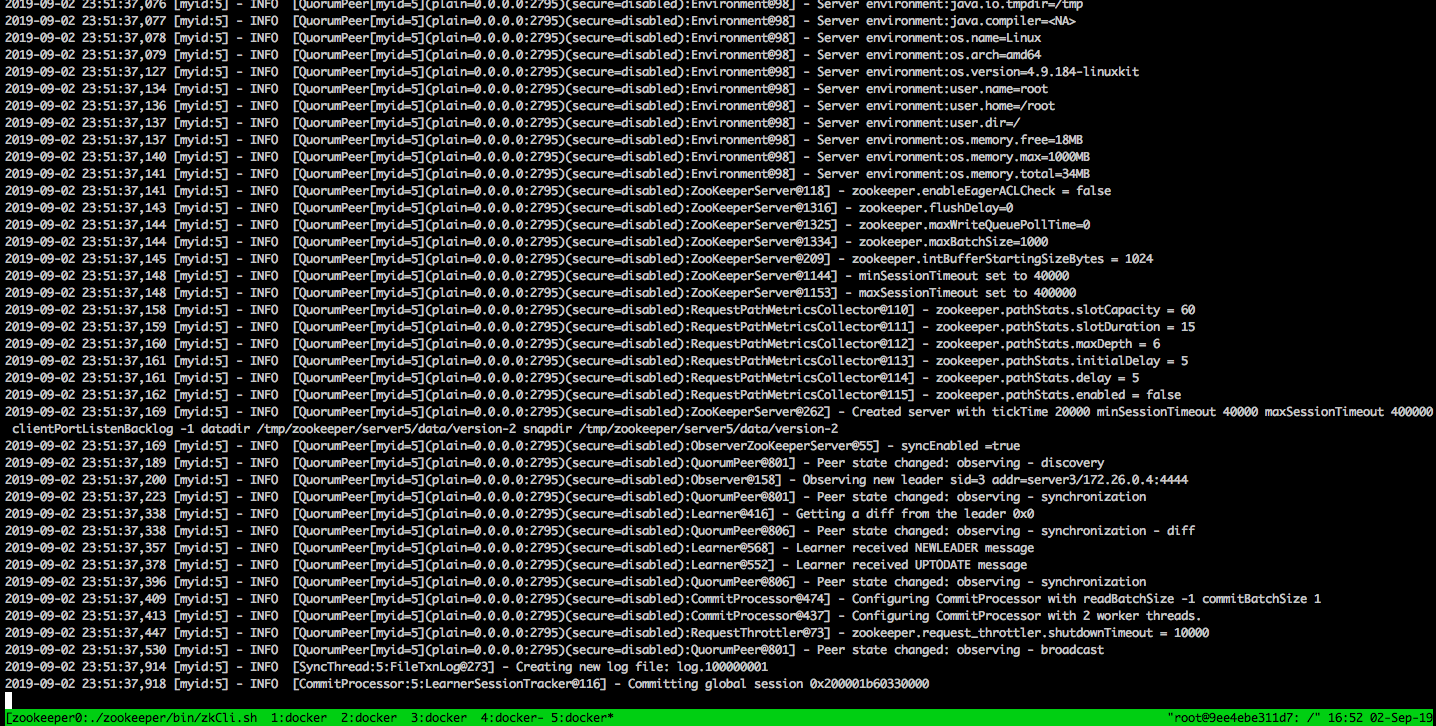
The first time the script is executed, it clones the latest version of ZooKeeper. The script then build ZooKeeper and creates a tmux sessions that includes a window for each of the ZooKeeper servers (running in foreground) as seen below.
The first tmux window contains a client connected to the cluster and can be used to issue commands against the cluster.
If you want to run the script in debug mode, simply execute:
./debug_zk.sh true
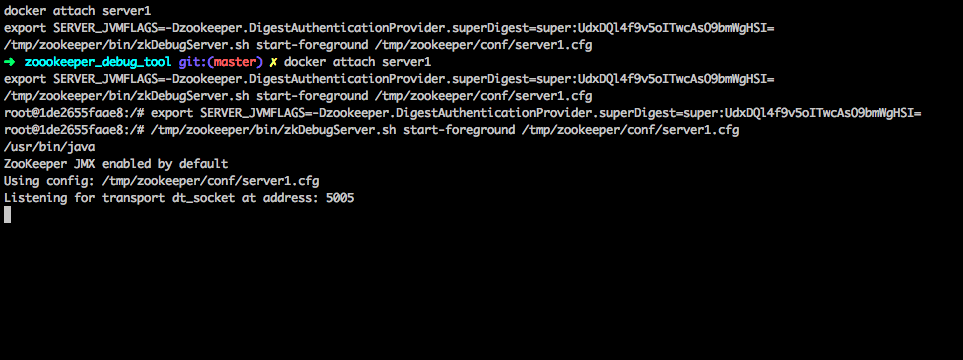
Notice that in this case, the ZooKeeper server in the second tmux window is not running:
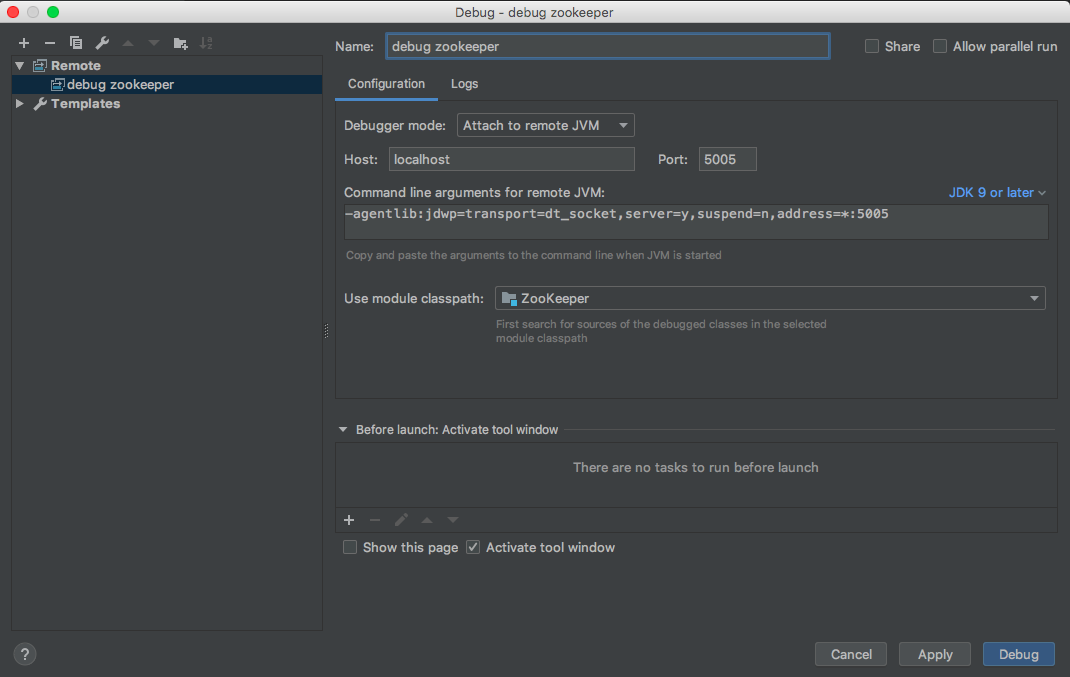
This is because it waits to be connected to IntelliJ for remote debugging. For this, first import (see below) the ZooKeeper codebase in IntelliJ.
When you start remote debugging from IntelliJ, the first server starts.
Just kill the tmux session by executing:
tmux kill-session -t zookeeper_session
If you would like to see how ZooKeeper behaves after some code changes, then:
- stop your debugging session
- perform the code changes
- execute
./debug_zk.shand you can start debugging the modified codebase.
The current script creates 3 participant and 2 observer servers. If you want to change this, you have to change the configuration file.
You can easily connect to any ZooKeeper server from local machine by doing:
./zookeeper/bin/zkCli.sh -server 127.0.0.1:2791 (for connecting to the first server)
or even
telnet localhost 2792
and then issuing some 4wl command.
If you would like to see how ZooKeeper performs under a network partition, you can simply use iptables and perform similar commands as the ones shown in create_np.sh or heal_np.sh to heal a network partition.