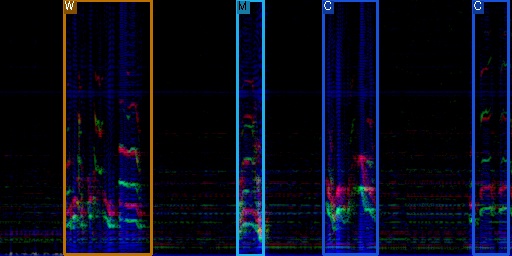
Introduction
YOLOX_AUDIO is an audio event detection model based on YOLOX, an anchor-free version of YOLO. This repo is an implemented by PyTorch.
Main goal of YOLOX_AUDIO is to detect and classify pre-defined audio events in multi-spectrogram domain using image object detection frameworks.
Updates!!
- 【2021/11/15】 We released YOLOX_AUDIO to public
Quick Start
Installation
Step1. Install YOLOX_AUDIO.
git clone https://github.com/intflow/YOLOX_AUDIO.git
cd YOLOX_AUDIO
pip3 install -U pip && pip3 install -r requirements.txt
pip3 install -v -e . # or python3 setup.py developStep2. Install pycocotools.
pip3 install cython; pip3 install 'git+https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI'Data Preparation
Step1. Prepare audio wavform files for training. AUDIO_DATAPATH/wav
Step2. Write audio annotation files for training. AUDIO_DATAPATH/label.json
{
"00000.wav": {
"speaker": [
"W",
"M",
"C",
"W"
],
"on_offset": [
[
1.34425,
2.4083125
],
[
4.0082708333333334,
4.5560625
],
[
6.2560416666666665,
7.956104166666666
],
[
9.756083333333333,
10.876624999999999
]
]
},
"00001.wav": {
"speaker": [
"W",
"M",
"C",
"M",
"W",
"C"
],
"on_offset": [
[
1.4325416666666666,
2.7918958333333332
],
[
2.1762916666666667,
4.109729166666667
],
[
7.109708333333334,
8.530916666666666
],
[
8.514125,
9.306104166666668
],
[
12.606083333333334,
14.3345625
],
[
14.148958333333333,
15.362958333333333
]
]
},
...
}Step3. Convert audio files into spectrogram images.
python tools/json_gen_audio2coco.pyPlease change the dataset path and file names for your needs
root = '/data/AIGC_3rd_2021/GIST_tr2_veryhard5000_all_tr2'
os.system('rm -rf '+root+'/img/')
os.system('mkdir '+root+'/img/')
wav_folder_path = os.path.join(root, 'wav')
img_folder_path = os.path.join(root, 'img')
train_label_path = os.path.join(root, 'tr2_devel_5000.json')
train_label_merge_out = os.path.join(root, 'label_coco_bbox.json')
Training
Step1. Change Data loading path of exps/yolox_audio/yolox_x.py
self.train_path = '/data/AIGC_3rd_2021/GIST_tr2_veryhard5000_all_tr2'
self.val_path = '/data/AIGC_3rd_2021/tr2_set_01_tune'
self.train_ann = "label_coco_bbox.json"
self.val_ann = "label_coco_bbox.json"Step2. Begin training:
python3 tools/train.py -expn yolox_audio -n yolox_audio_x \
-f exps/yolox_audio/yolox_x.py -d 4 -b 32 --fp16 \
-c /data/pretrained/yolox_x.pth
- -d: number of gpu devices
- -b: total batch size, the recommended number for -b is num-gpu * 8
- -f: path of experiement file
- --fp16: mixed precision training
- --cache: caching imgs into RAM to accelarate training, which need large system RAM.
We are encouraged to use pretrained YOLOX model for the training. https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX
Inference
Run following demo_audio.pypython3 tools/demo_audio.py --demo wav -expn yolox_audio -n yolox_audio_x \
-f exps/yolox_audio/yolox_x.py \
-c /data/pretrained/yolox_x__AGC21_tr2.pth \
--path ./assets/test.wav \
--conf 0.2 --nms 0.65 --tsize_h 256 --tsize_w 512 --save_result --device gpuFrom the demo_audio.py you can get on-offset VAD time and class of each audio chunk.
References
- YOLOX baseline implemented by PyTorch: YOLOX
@article{yolox2021,
title={YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021},
author={Ge, Zheng and Liu, Songtao and Wang, Feng and Li, Zeming and Sun, Jian},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.08430},
year={2021}
}
- Librosa for audio feature extraction: librosa
McFee, Brian, Colin Raffel, Dawen Liang, Daniel PW Ellis, Matt McVicar, Eric Battenberg, and Oriol Nieto. “librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python.” In Proceedings of the 14th python in science conference, pp. 18-25. 2015.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021-0-00014).