Emacs Refactor (EMR) is a framework for providing language-specific refactoring in Emacs. It includes refactoring commands for a variety of languages, including elisp itself!
To use EMR when editing, simply move point to an expression and
M-x emr-show-refactor-menu.
EMR ships with many refactoring commands, and pull requests for extensions are welcome. See Extension for details on extending EMR to other language modes. It's easy (honest!).
Install emr from MELPA, then configure your
init.el:
(define-key prog-mode-map (kbd "M-RET") 'emr-show-refactor-menu)Most EMR commands are context-sensitive and are available through the refactor menu. Some actions affect the whole buffer and are available in the menu bar.
These commands are available for all programming languages.
The following context-sensitive refactoring commands are available:
- comment region
- uncomment region
The following context-sensitive refactoring commands are available:
- tidy includes
The following buffer-wide actions are available:
- insert include
Refactoring support for C is a work in progress. Contributions are welcome.
These commands are available to all Lisp dialects, including Clojure, Elisp and Common Lisp.
The following context-sensitive refactoring commands are available:
- comment form
- uncomment block
The following context-sensitive refactoring commands are available:
- delete unused definition
- delete unused let binding form
- eval and replace
- extract autoload
- extract constant
- extract function
- extract to let
- extract variable
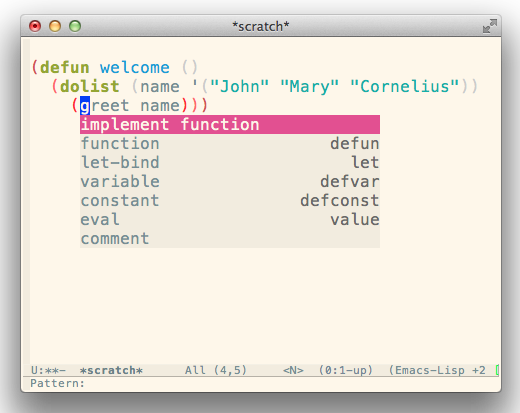
- implement function
- inline function
- inline let variable
- inline variable
- insert autoload directive
- tidy autoloads
The following buffer-wide actions are available:
- find unused definitions
JavaScript refactoring support requires js2 refactor.
The following refactoring commands are available:
- extract function
- extract method
- extract variable
- add parameter
- local variable to instance variable
- log region
Ruby refactoring support requires ruby refactor.
The following refactoring commands are available:
- extract function
- extract variable
- extract constant
- add parameter
- extract to let
The following refactoring commands are available:
- extract function
- extract variable
Use the emr-declare-command function to declare a refactoring action. The
action will automatically become available in the refactoring popup menu.
This function supports predicate expressions, allowing the options displayed to be context-sensitive.
As an example, here is the declaration for a refactoring command that ships with EMR:
(emr-declare-command 'emr-el-extract-constant
:title "constant"
:description "defconst"
:modes 'emacs-lisp-mode
:predicate (lambda ()
(not (or (emr-el:looking-at-definition?)
(emr-el:looking-at-let-binding-symbol?)))))This wires the emr-el-extract-constant function to be displayed in
emacs-lisp-mode, provided point is not looking at an Elisp definition or
let-binding form.
If your favourite language mode already offers refactoring commands, it is simple to wire them up with EMR using this interface.