- Added Euler's method to schedulers (contributed by @israfelsr)
- Added DINOv2 for high-performance visual features (contributed by @Laurent2916)
- Added FreeU for improved quality at no cost (contributed by @isamu-isozaki)
- Added Restart Sampling for improved image generation (example)
- Added Self-Attention Guidance to avoid e.g. too smooth images (example)
- Added T2I-Adapter for extra guidance (example)
- Added MultiDiffusion for e.g. panorama images
- Added IP-Adapter, aka image prompt (example)
- Added Segment Anything to foundational models
- Added SDXL 1.0 to foundational models
- Made possible to add new concepts to the CLIP text encoder, e.g. via Textual Inversion
Refiners is still an early stage project, and we do not release minor versions yet. We recommend installing the latest version via a git install:
pip install git+https://github.com/finegrain-ai/refiners.gitTo include the training utils, use:
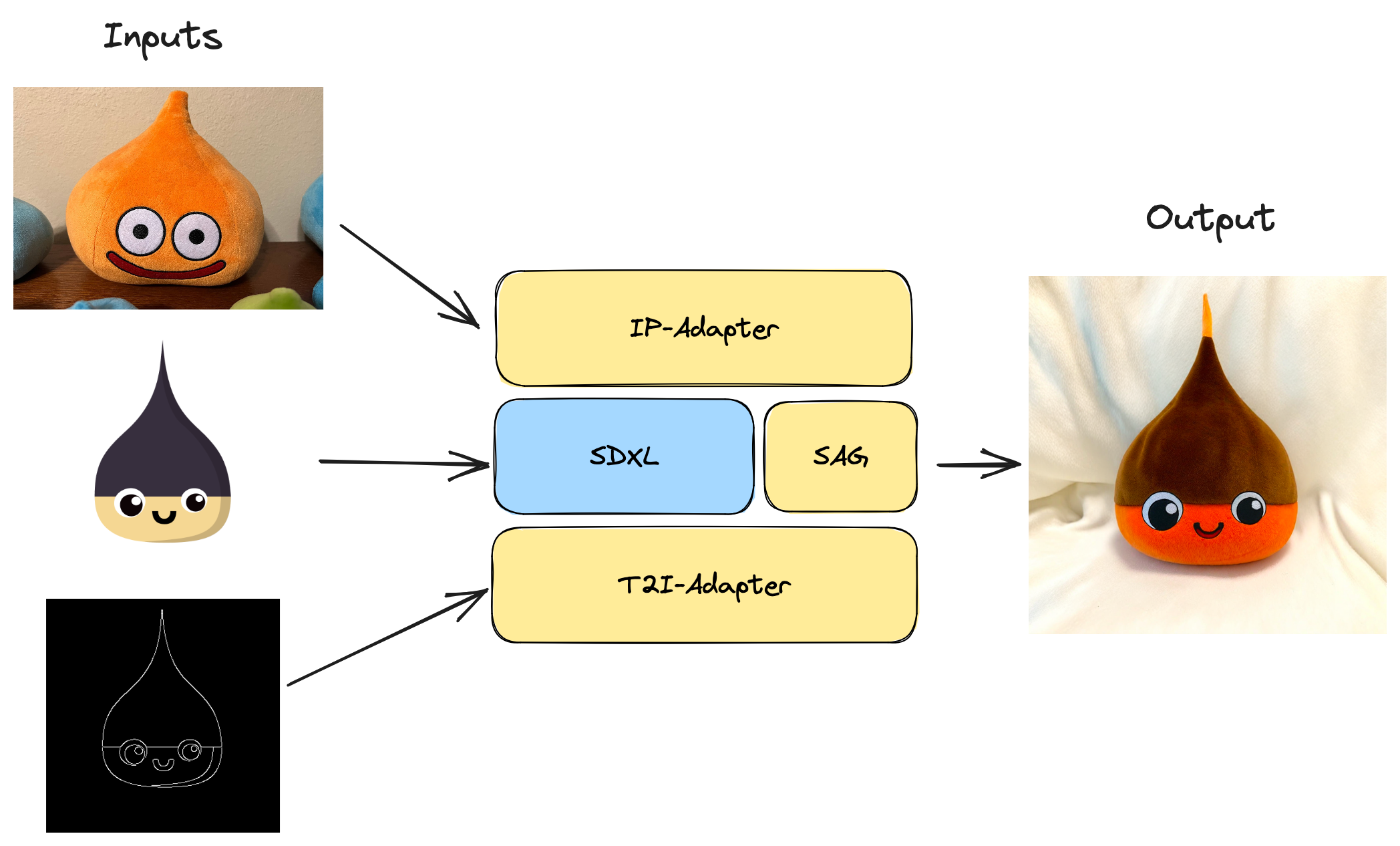
pip install 'refiners[training] @ git+https://github.com/finegrain-ai/refiners.git'Goal: turn Refiners' mascot into a Dragon Quest Slime plush in a one-shot manner thanks to a powerful combo of adapters:
- IP-Adapter: to capture the Slime plush visual appearance into an image prompt (no prompt engineering needed)
- T2I-Adapter: to guide the generation with the mascot's geometry
- Self-Attention-Guidance (SAG): to increase the sharpness
Step 1: convert SDXL weights to the Refiners' format:
python scripts/conversion/convert_transformers_clip_text_model.py --from "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0" --subfolder2 text_encoder_2 --to clip_text_xl.safetensors --half
python scripts/conversion/convert_diffusers_unet.py --from "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0" --to unet_xl.safetensors --half
python scripts/conversion/convert_diffusers_autoencoder_kl.py --from "madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix" --subfolder "" --to lda_xl.safetensors --halfNote: this will download the original weights from https://huggingface.co/ which takes some time. If you already have this repo cloned locally, use the
--from /path/to/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0option instead.
And then convert IP-Adapter and T2I-Adapter weights (note: SAG is parameter-free):
python scripts/conversion/convert_diffusers_t2i_adapter.py --from "TencentARC/t2i-adapter-canny-sdxl-1.0" --to t2i_canny_xl.safetensors --half
python scripts/conversion/convert_transformers_clip_image_model.py --from "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip" --to clip_image.safetensors --half
curl -LO https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter/resolve/main/sdxl_models/ip-adapter_sdxl_vit-h.bin
python scripts/conversion/convert_diffusers_ip_adapter.py --from ip-adapter_sdxl_vit-h.bin --halfStep 2: download input images:
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/finegrain-ai/refiners/main/assets/dropy_logo.png
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/finegrain-ai/refiners/main/assets/dropy_canny.png
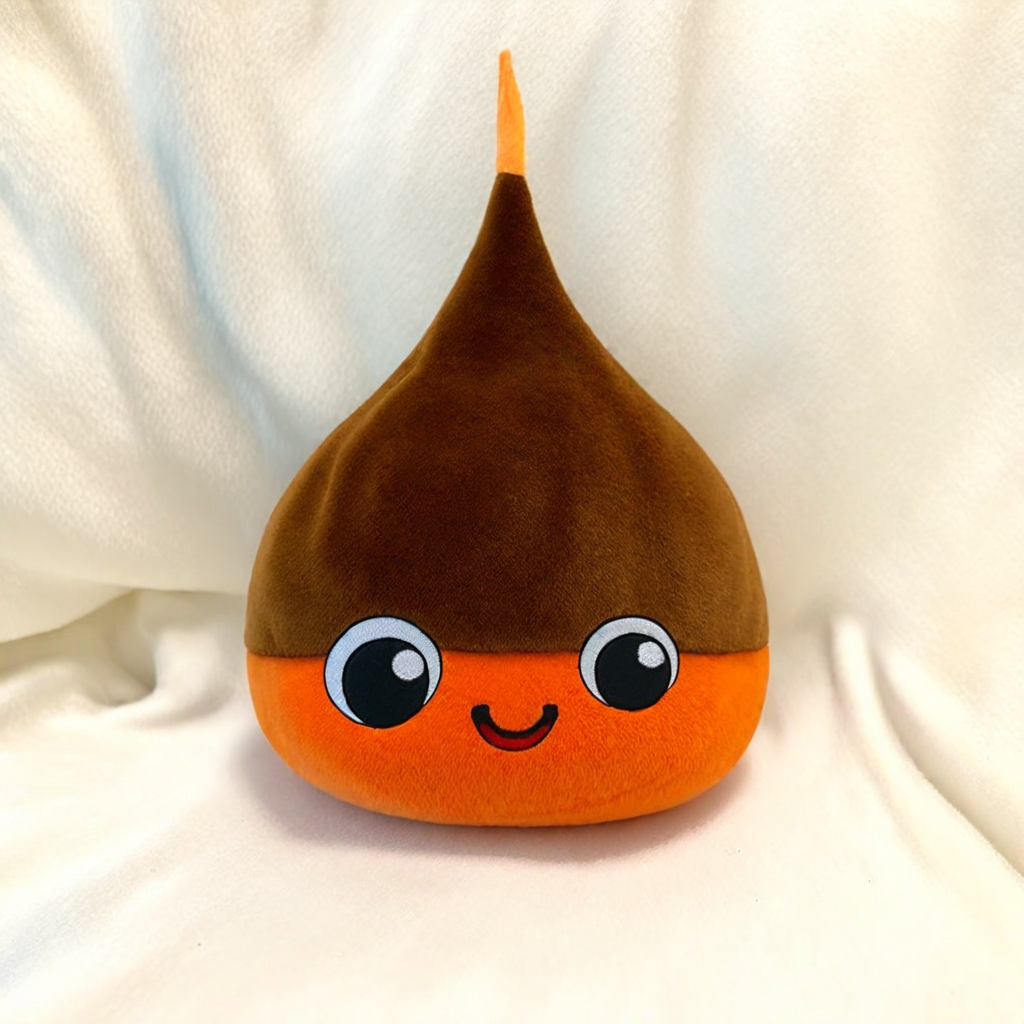
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/finegrain-ai/refiners/main/assets/dragon_quest_slime.jpgStep 3: generate an image using the GPU:
import torch
from PIL import Image
from refiners.foundationals.latent_diffusion.stable_diffusion_xl import StableDiffusion_XL
from refiners.foundationals.latent_diffusion import SDXLIPAdapter, SDXLT2IAdapter
from refiners.fluxion.utils import manual_seed, no_grad, image_to_tensor, load_from_safetensors
# Load inputs
init_image = Image.open("dropy_logo.png")
image_prompt = Image.open("dragon_quest_slime.jpg")
condition_image = Image.open("dropy_canny.png")
# Load SDXL
sdxl = StableDiffusion_XL(device="cuda", dtype=torch.float16)
sdxl.clip_text_encoder.load_from_safetensors("clip_text_xl.safetensors")
sdxl.lda.load_from_safetensors("lda_xl.safetensors")
sdxl.unet.load_from_safetensors("unet_xl.safetensors")
# Load and inject adapters
ip_adapter = SDXLIPAdapter(target=sdxl.unet, weights=load_from_safetensors("ip-adapter_sdxl_vit-h.safetensors"))
ip_adapter.clip_image_encoder.load_from_safetensors("clip_image.safetensors")
ip_adapter.inject()
t2i_adapter = SDXLT2IAdapter(
target=sdxl.unet, name="canny", weights=load_from_safetensors("t2i_canny_xl.safetensors")
).inject()
# Tune parameters
seed = 9752
first_step = 1
ip_adapter.set_scale(0.85)
t2i_adapter.set_scale(0.8)
sdxl.set_num_inference_steps(50)
sdxl.set_self_attention_guidance(enable=True, scale=0.75)
with no_grad():
# Note: default text prompts for IP-Adapter
clip_text_embedding, pooled_text_embedding = sdxl.compute_clip_text_embedding(
text="best quality, high quality", negative_text="monochrome, lowres, bad anatomy, worst quality, low quality"
)
clip_image_embedding = ip_adapter.compute_clip_image_embedding(ip_adapter.preprocess_image(image_prompt))
ip_adapter.set_clip_image_embedding(clip_image_embedding)
time_ids = sdxl.default_time_ids
condition = image_to_tensor(condition_image.convert("RGB"), device=sdxl.device, dtype=sdxl.dtype)
t2i_adapter.set_condition_features(features=t2i_adapter.compute_condition_features(condition))
manual_seed(seed=seed)
x = sdxl.init_latents(size=(1024, 1024), init_image=init_image, first_step=first_step).to(
device=sdxl.device, dtype=sdxl.dtype
)
for step in sdxl.steps[first_step:]:
x = sdxl(
x,
step=step,
clip_text_embedding=clip_text_embedding,
pooled_text_embedding=pooled_text_embedding,
time_ids=time_ids,
)
predicted_image = sdxl.lda.decode_latents(x=x)
predicted_image.save("output.png")
print("done: see output.png")You should get:
Refiners has a built-in training utils library and provides scripts that can be used as a starting point.
E.g. to train a LoRA on top of Stable Diffusion, copy and edit configs/finetune-lora.toml to suit your needs and launch the training as follows:
python scripts/training/finetune-ldm-lora.py configs/finetune-lora.tomlFor now, given finegrain's mission, we are focusing on image edition tasks. We support:
| Adapter | Foundation Model |
|---|---|
| LoRA | SD15 SDXL |
| ControlNets | SD15 |
| Ref Only Control | SD15 |
| IP-Adapter | SD15 SDXL |
| T2I-Adapter | SD15 SDXL |
At Finegrain, we're on a mission to automate product photography. Given our "no human in the loop approach", nailing the quality of the outputs we generate is paramount to our success.
That's why we're building Refiners.
It's a framework to easily bridge the last mile quality gap of foundational models like Stable Diffusion or Segment Anything Model (SAM), by adapting them to specific tasks with lightweight trainable and composable patches.
We decided to build Refiners in the open.
It's because model adaptation is a new paradigm that goes beyond our specific use cases. Our hope is to help people looking at creating their own adapters save time, whatever the foundation model they're using.
We are huge fans of PyTorch (we actually were core committers to Torch in another life), but we felt it's too low level for the specific model adaptation task: PyTorch models are generally hard to understand, and their adaptation requires intricate ad hoc code.
Instead, we needed:
- A model structure that's human readable so that you know what models do and how they work right here, right now
- A mechanism to easily inject parameters in some target layers, or between them
- A way to easily pass data (like a conditioning input) between layers even when deeply nested
- Native support for iconic adapter types like LoRAs and their community trained incarnations (hosted on Civitai and the likes)
Refiners is designed to tackle all these challenges while remaining just one abstraction away from our beloved PyTorch.
The Chain class is at the core of Refiners. It basically lets you express models as a composition of basic layers (linear, convolution, attention, etc) in a declarative way.
E.g.: this is how a Vision Transformer (ViT) looks like with Refiners:
import torch
import refiners.fluxion.layers as fl
class ViT(fl.Chain):
# The Vision Transformer model structure is entirely defined in the constructor. It is
# ready-to-use right after i.e. no need to implement any forward function or add extra logic
def __init__(
self,
embedding_dim: int = 512,
patch_size: int = 16,
image_size: int = 384,
num_layers: int = 12,
num_heads: int = 8,
):
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size)
super().__init__(
fl.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=embedding_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size),
fl.Reshape(num_patches**2, embedding_dim),
# The Residual layer implements the so-called skip-connection, i.e. x + F(x).
# Here the patch embeddings (x) are summed with the position embeddings (F(x)) whose
# weights are stored in the Parameter layer (note: there is no extra classification
# token in this toy example)
fl.Residual(fl.Parameter(num_patches**2, embedding_dim)),
# These are the transformer encoders:
*(
fl.Chain(
fl.LayerNorm(embedding_dim),
fl.Residual(
# The Parallel layer is used to pass multiple inputs to a downstream
# layer, here multiheaded self-attention
fl.Parallel(
fl.Identity(),
fl.Identity(),
fl.Identity()
),
fl.Attention(
embedding_dim=embedding_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
key_embedding_dim=embedding_dim,
value_embedding_dim=embedding_dim,
),
),
fl.LayerNorm(embedding_dim),
fl.Residual(
fl.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim * 4),
fl.GeLU(),
fl.Linear(embedding_dim * 4, embedding_dim),
),
fl.Chain(
fl.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim * 4),
fl.GeLU(),
fl.Linear(embedding_dim * 4, embedding_dim),
),
)
for _ in range(num_layers)
),
fl.Reshape(embedding_dim, num_patches, num_patches),
)
vit = ViT(embedding_dim=768, image_size=224, num_heads=12) # ~ViT-B/16 like
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224)
y = vit(x)The Chain class has a context provider that allows you to pass data to layers even when deeply nested.
E.g. to implement cross-attention you would just need to modify the ViT model like in the toy example below:
@@ -21,8 +21,8 @@
fl.Residual(
fl.Parallel(
fl.Identity(),
- fl.Identity(),
- fl.Identity()
+ fl.UseContext(context="cross_attention", key="my_embed"),
+ fl.UseContext(context="cross_attention", key="my_embed"),
), # used to pass multiple inputs to a layer
fl.Attention(
embedding_dim=embedding_dim,
@@ -49,5 +49,6 @@
)
vit = ViT(embedding_dim=768, image_size=224, num_heads=12) # ~ViT-B/16 like
+vit.set_context("cross_attention", {"my_embed": torch.randn(2, 196, 768)})
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224)
y = vit(x)The Adapter API lets you easily patch models by injecting parameters in targeted layers. It comes with built-in support for canonical adapter types like LoRA, but you can also implement your custom adapters with it.
E.g. to inject LoRA layers in all attention's linear layers:
from refiners.fluxion.adapters.lora import SingleLoraAdapter
for layer in vit.layers(fl.Attention):
for linear, parent in layer.walk(fl.Linear):
SingleLoraAdapter(target=linear, rank=64).inject(parent)
# ... and load existing weights if the LoRAs are pretrained ...If you're interested in understanding the diversity of use cases for foundation model adaptation (potentially beyond the specific adapters supported by Refiners), we suggest you take a look at these outstanding papers:
We took inspiration from these great projects:
- tinygrad - For something between PyTorch and karpathy/micrograd
- Composer - A PyTorch Library for Efficient Neural Network Training
- Keras - Deep Learning for humans
@misc{the-finegrain-team-2023-refiners,
author = {Benjamin Trom and Pierre Chapuis and Cédric Deltheil},
title = {Refiners: The simplest way to train and run adapters on top of foundational models},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/finegrain-ai/refiners}}
}