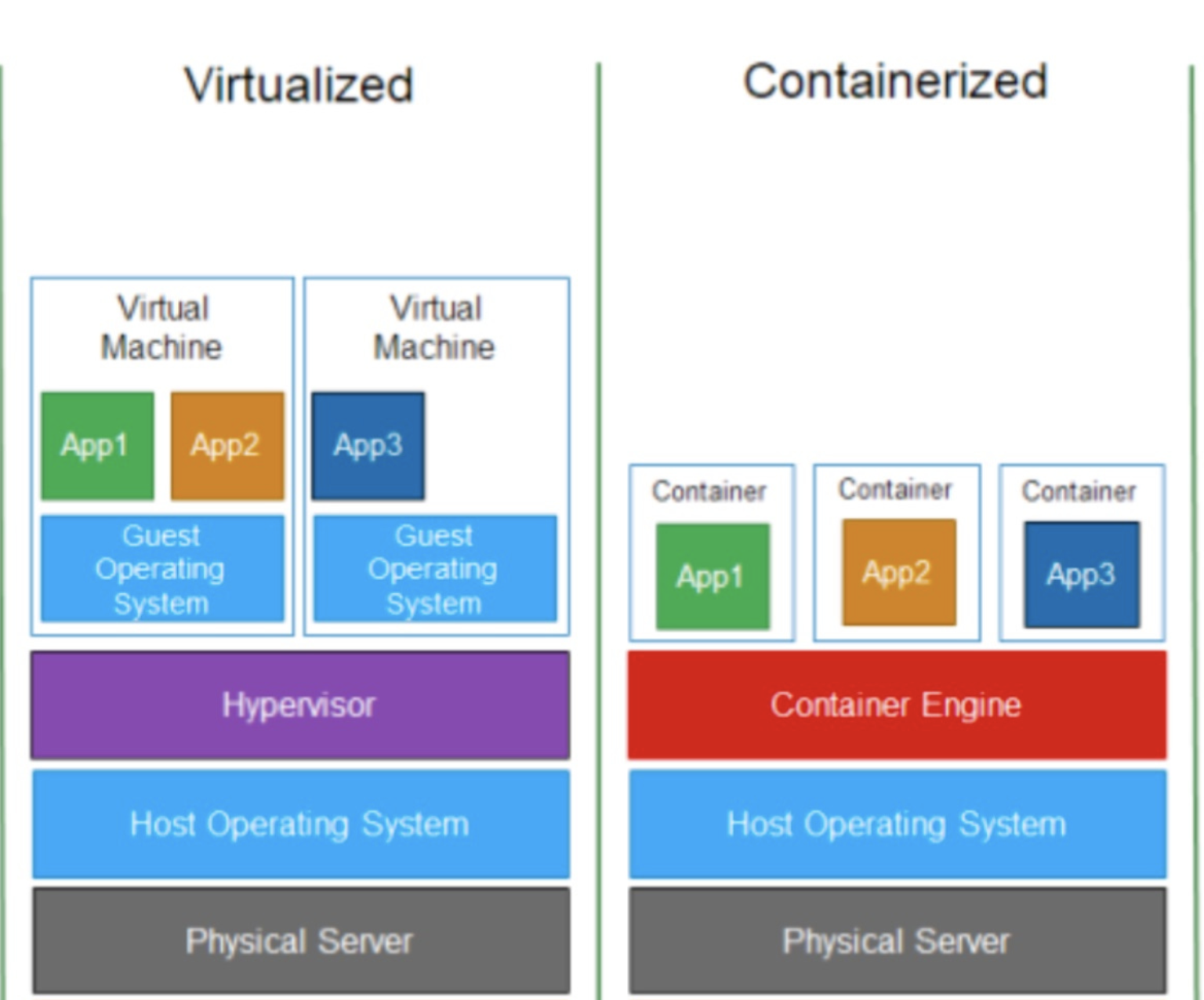
- Containers are a form of operating system virtualization.
- To containerize the application with its libraries/dependencies to run application anywhere and anytime.
- Containerization is considered to be a lightweight version of virtualization as compared to VMs.
Namespaces are a feature of the linux kernel that partitions kernel resources such that one set of processes sees one set of resources while another set of processes sees a different set of resources.
In simple words, namespaces isolate processes from each other or you can also say namespaces restrict what a process can see.
-
Different types of namespaces:
- PID namespace:
Assigns a set of PIDs to processes that are independent from the set of PIDs in other namespaces. eg: first process created in a new namespace hasPID 1and child processes are assigned subsequent PIDs. If a child process is created with its own PID namespace, it hasPID 1in that namespace as well as its PID in the parent process namespace. - Network namespace:
To run programs on any port without conflicting it with what’s already running. - Mount namespace:
To mount and unmount filesystems without affecting the host filesystem. - IPC namespace:
To have its own IPC resources, for example POSIX message queues.
- PID namespace:
-
you can use unshare linux command to create namespaces.
A control group (cgroup) is a linux kernel feature that limits and isolates the resource usage (CPU, memory, disk I/O, network etc) of a collection of processes.
In simple words, we use cgroups to control how much of a given key resources (CPU, memory, network, and disk I/O) can be accessed or used by a process.
- ContainersFromScratch
- building basic container from scratch in Go
- involves linux concepts like namespaces, cgroups, chroot etc.