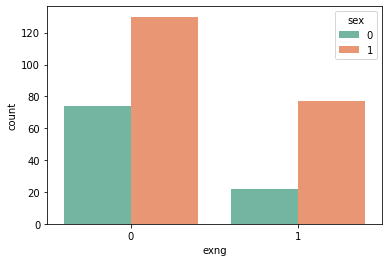age : Age of the patient
sex : Sex of the patient
1 = male
0 = female
exng: exercise induced angina (1 = yes; 0 = no)
cp : Chest Pain type chest pain type
Value 1: typical angina
Value 2: atypical angina
Value 3: non-anginal pain
Value 4: asymptomatic
trtbps : resting blood pressure (in mm Hg)
chol : cholestoral in mg/dl fetched via BMI sensor
fbs : (fasting blood sugar > 120 mg/dl) (1 = true; 0 = false)
rest_ecg : resting electrocardiographic results
Value 0: normal
Value 1: having ST-T wave abnormality (T wave inversions and/or ST elevation or depression
of > 0.05 mV)
Value 2: showing probable or definite left ventricular hypertrophy by Estes' criteria
thalach : maximum heart rate achieved
exang: exercise induced angina
1 = yes
0 = no
oldpeak = ST depression induced by exercise relative to rest
slope: the slope of the peak exercise ST segment
Value 0: upsloping
Value 1: flat
Value 2: downsloping
ca: number of major vessels (0-3)
thal:
0 = error (in the original dataset 0 maps to NaN's)
1 = fixed defect
2 = normal
3 = reversable defect
target :
0= less chance of heart attack
1= more chance of heart attack
For Report : click
male = 1
exercise induced angina have a high possibility in Male then female.
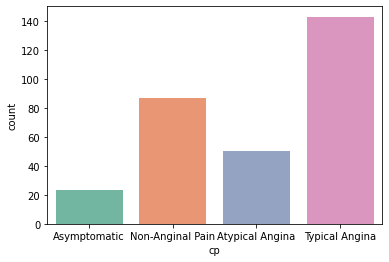
Typical-Angina have the highest possibility of occurrence
,also NON-Anginal pain have high possibility.
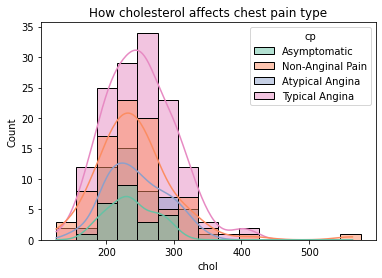
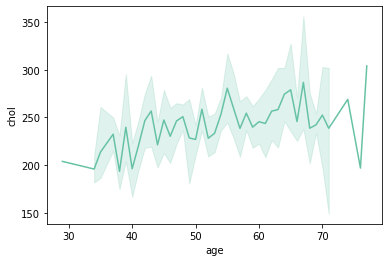
individuals having chol around 200-275 have the most possibility of having chest pain.
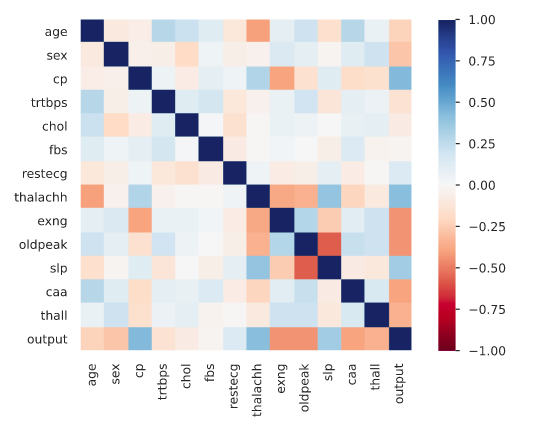
since age and chol have a +ve co-relation as the age inc. chol tends to inc.
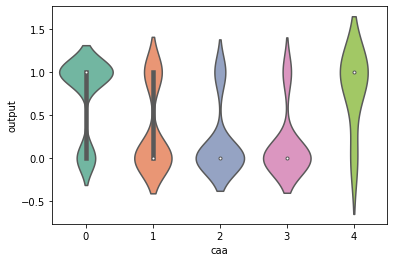
(0,4) have a significant high chance of heart attack.
(1,2,3) have a significant low chance of heart attack.
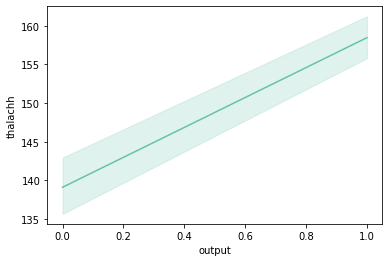
There's positive correlation co-efficient of 0.421741 ("pearson") between them,
so we can assume that having a higher heart rate is a factor contributing to heart attack.
train_data = data.drop(['output'], axis=1)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
train_data, data['output'], random_state=0)
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=4)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
prediction = knn.predict(X_test)
print(np.mean(prediction == y_test))accuracy of model => 0.6842105263157895 or 68.42%
increase accuracy to 86% using auto-sklearn