From the Greek Καθαρά. Implementation of the notorious Netkit using Python and Docker. 10 times faster than Netkit and more than 100 times lighter, allows easy configuration and deploy of arbitrary virtual networks with for SDN, NFV and traditional routing protocols.
Kathará comes with P4, OpenVSwitch, Quagga, Bind, and more, but can also be extended with your own container images.
Thanks to Docker, the framework has the performances to run in production and our images can emulate most network equipments.
Check the Wiki for the installation guide.
You can download both Kathará and the GUI by cloning recursively using
git clone --recursive https://github.com/KatharaFramework/Kathara.git
Or by downloading the pre-compiled version from the releases page.
Being based on Netkit, all previous tools still work.
In particular we suggest Netkit Lab Generator, a GUI that allows the easy creation of a lab configuration and the visualization of its network topology.
A list of the Docker images we provided can be found at this page in the Docker Hub.
The interface of Kathará is basically the same we used for Netkit, and it's available here: Man page of NETKIT.
The main difference is the way we specify the interfaces in the vstart command (now requiring --eth 0:A --eth 1:B ...) but why would you ever use vstart when you have lstart? However an example for the syntax of vstart now may be: vstart --eth 0:A --eth 1:B pc1 where "pc1" is the name of the network node to be started.
In addition there is another command, lwipe, that erases every container and network created by Kathará, including its cache.
Also the subnet 172.0.0.0/8 (basically any IP starting with 172) is reserved and should not be used when configuring links.
For ltestthere are 2 minor adjustments:
--verifyneeds to be followed by=before the option (e.g.ltest --verify=user).--script-modehas been replaced by simply sending stdout to/dev/null(e.g.ltest --verify=user &> /dev/null).
- Installa Kathará by following the installation steps above
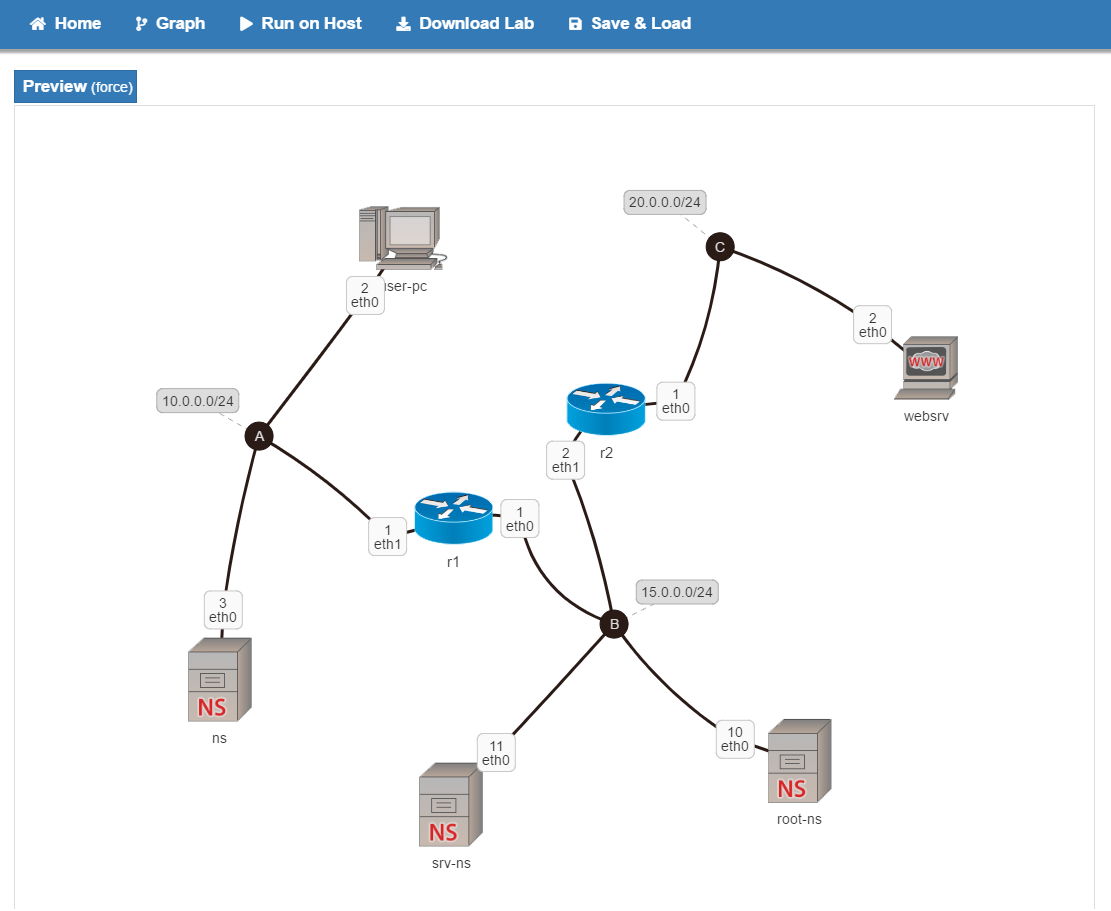
- Download and unpack MARACAS_lab from here.
- The topology of this lab can be found here.
cdinside MARACAS_lab and runlstart:- Linux:
$NETKIT_HOME/lstart - Windows:
%NETKIT_HOME%\lstart
- Linux:
- Kathará will read the configuration of the lab from
lab.conf,lab.depand the various*.startupfiles and start the containers, opening terminal windows to interact with the virtual network nodes. - After you're done experimenting, simply run
lclean:- Linux:
$NETKIT_HOME/lclean - Windows:
%NETKIT_HOME%\lclean
- Linux:
- This will kill and remove any container.
Extending Kathará is actually very simple. Any local or remote Docker image tagged as kathara/IMAGENAME can be used with vstart --image=IMAGENAME --eth=0:A node_name or with lstart having something like that in lab.conf: node_name[image]=IMAGENAME.
To alter (locally) an existing Kathará image refer to the following steps (remember that, by default, Docker needs root or sudo on Linux).
docker pull kathara/netkit_base(orkathara/p4)docker run -tid --name YOUR_NEW_NAME kathara/netkit_basedocker exec -ti YOUR_NEW_NAME bash- Do your thing, then exit.
docker commit YOUR_NEW_NAME kathara/YOUR_NEW_NAMEdocker rm -f YOUR_NEW_NAME
- Components and configuration checker.

